Procedural Meshing
Renders a procedural system as geometry.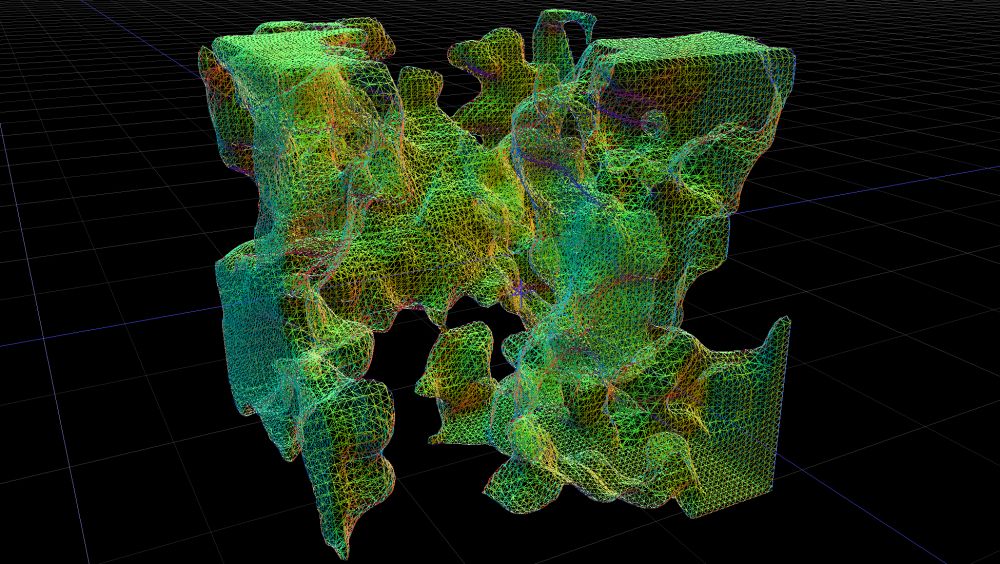


Genrates a surface from a procedural by first voxelising it, and then constructing a smoothed surface over the voxels. The surface produced is a triangle mesh which can be textured, deformed, can cast shadows, and can be used as a particle emitter among other things.
This node outputs the normal transformation and translation values, but it also outputs geometry which can be modified with Deformer nodes, or used as a mesh sources for nodes which accept mesh connections, such as the Field 3D Object Emitter or the Procedural 3D Object.
These properties control the 3D transforms of the node. Transforms will generally be inherited by child nodes, although they can be ignored through the Inherit Transform Channels attributes.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | Move along the local x-axis. |
| Position Y | Move along the local y-axis. |
| Position Z | Move along the local z-axis. |
| Rotation Heading | Rotate around the local y-axis. |
| Rotation Pitch | Rotate around the local x-axis. |
| Rotation Bank | Rotate around the local z-axis. |
| Scale X | Scale along the local x-axis. |
| Scale Y | Scale along the local y-axis. |
| Scale Z | Scale along the local z-axis. |
Toggle which transform channels should be inherited from the parent node. By default, all transforms will be inherited.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | Toggle inheritance of the X Position from the parent. |
| Position Y | Toggle inheritance of the Y Position from the parent. |
| Position Z | Toggle inheritance of the Z Position from the parent. |
| Rotation Heading | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation Heading from the parent. |
| Rotation Pitch | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation Pitch from the parent. |
| Rotation Bank | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation Bank from the parent. |
| Scale X | Toggle inheritance of the X Scale from the parent. |
| Scale Y | Toggle inheritance of the Y Scale from the parent. |
| Scale Z | Toggle inheritance of the Z Scale from the parent. |
| World Position Only | Inherit the world position from the parent only, rotation and scale will be ignored. Overrides above properties. |
| Inherit Time | Toggle inheritance of time from the parent. |
These properties control the core behaviours of the node.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Grid Width | Width of the adaptive voxel grid. |
| Grid Height | Height of the adaptive voxel grid. |
| Grid Depth | Depth of the adaptive voxel grid. |
| Error Tolerance | If the procedural distance field has too much distortion then it may be necessary to raise the error tolerance. a higher error tolerance may reduce performance, so this is a trade-off. |
| Smoothing Iterations | Iteratively smoothes the meshes vertices by the number of levels specified, averaging out all the vertices in the mesh and producing a smoother result. Smoothing is done before rendering. High values can impact performance greatly, and may not be temporally stable if the underlying mesh changes. |
| HQ Smoothing | When enabled, vertex positions will be projected back on to the procedural surface. this preserves sharp edges without increasing the voxel grid size. |
| Distance Field Normals | Vertex normals will be extracted from the procedural distance field. this can be more accurate, but slower. |
| Seal Boundaries | When a procedural intersects the bounding box, usually a hole is created. enabling this option will fill in the hole. |
| Generate Colours | Uses colours set in procedural nodes (such as 3d primitive) to colourise the generated vertices. this can reduce performance slightly. |
| Generate UVs | Generate texture coordinates at the generated vertices, for use with a material. this can reduce performance slightly. |
| Visible | Control whether the node is visible or not to the scene. |
| Dynamic | When set above 1.0, the mesh will be re-generated on every frame. when set to 0.0, the last-generated mesh will be cached and re-used as a static output. |
| Vertex Buffer Size (100,000s) | Limits the generated vertex buffer size. |
| Triangle Buffer Size (100,000s) | Limits the generated triangle buffer size. |
| Show Metrics | Displays information about the amount of mesh geometry being generated. |
| Tessellation Enabled | Enables gpu-side tessellation. note that post-tessellated geometry is processed last. |
| Max Tessellation Factor | The maximum level of gpu tessellation. |
See Materials.
| Name | Description | Typical Input |
|---|---|---|
| Procedural Root | Use a Procedural Root as an input, so the renderer is treated seperately from the roots transforms. In this case, the renderer itself would be connected to the scene Root node. | Procedural Root |
| Bounding Box | The region in which the surface will be voxelised and generated | Bounding Box |
| Render Transform | Takes the transformation of another node and applies it to the rendered mesh. | |
| Material | A material to apply to the rendered mesh | Materials |
| Transform Modifiers | Apply the transforms of another node to this node. | Null |
| Target Node | Modifiy the rotations of the node to always direct the z axis towards the input. | Null |
| Local Transform Override | Apply the transforms of another node to this node, relative to its parent. | Null |