SPH Affector
Simulates fluid dynamics on Particles with an SPH simulation.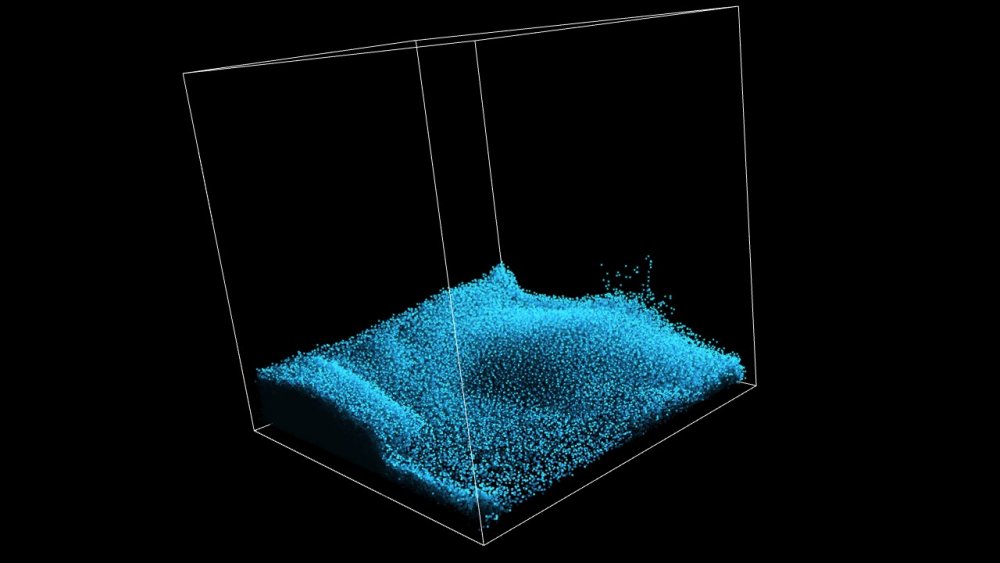
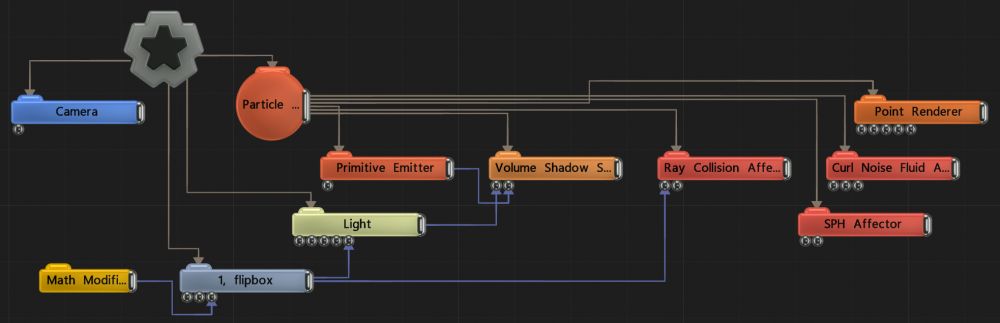


This node simulates fluid dynamics on a particle system using the SPH (Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics) simulation method. This is typically used to simulate liquid effects. It solves a fluid simulation by locally solving pressure forces between a particle and others nearby. This allows particles to affect each other and to move in a locally coherent manner. SPH works well for liquid effects like water.
The solver takes into account both the position and velocity of particles and their neighbours. The Viscosity attribute is used to make the simulation behave as a thicker liquid. Surface Tension is used to keep particles together like droplets of water. The radius around each particle in which they interact with their neighbours is controlled using the Cell Size attribute. Larger cell sizes may result in a smoother simulation that increases performance demands. The simulation may be switched from 3D to 2D, in which case one axis is dropped from the simulation.
The grid resolution and size used for the pressure solver is key to the detail and performance of the resultant simulation. A higher resolution grid over a smaller area will give a more detailed simulation, but higher resolution grids are slower to process.
These properties control the 3D transforms of the node. Transforms will generally be inherited by child nodes, although they can be ignored through the Inherit Transform Channels attributes.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | Move along the local x-axis. |
| Position Y | Move along the local y-axis. |
| Position Z | Move along the local z-axis. |
| Rotation Heading | Rotate around the local y-axis. |
| Rotation Pitch | Rotate around the local x-axis. |
| Rotation Bank | Rotate around the local z-axis. |
| Scale X | Scale along the local x-axis. |
| Scale Y | Scale along the local y-axis. |
| Scale Z | Scale along the local z-axis. |
Toggle which transform channels should be inherited from the parent node. By default, all transforms will be inherited.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | Toggle inheritance of the X Position from the parent. |
| Position Y | Toggle inheritance of the Y Position from the parent. |
| Position Z | Toggle inheritance of the Z Position from the parent. |
| Rotation Heading | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation Heading from the parent. |
| Rotation Pitch | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation Pitch from the parent. |
| Rotation Bank | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation Bank from the parent. |
| Scale X | Toggle inheritance of the X Scale from the parent. |
| Scale Y | Toggle inheritance of the Y Scale from the parent. |
| Scale Z | Toggle inheritance of the Z Scale from the parent. |
| World Position Only | Inherit the world position from the parent only, rotation and scale will be ignored. Overrides above properties. |
| Inherit Time | Toggle inheritance of time from the parent. |
These properties control the core behaviours of the node.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Weight | How strong an effect has on the particles. |
| Cell Size | The area around each particle that resists other particles from getting within a certain distance. |
| Viscosity | The viscosity of the fluid, where smaller values make it more gas-like and larger values make it thicker - more like treacle. |
| Gravity | How strong gravity is on the particles. |
| Pressure Scale | Scales the amount by which particles push apart from each other. |
| Rest Density | Controls the base density of the fluid. |
| Surface Tension | How much the particles want to stay together at their surface. |
| Max Force | The limit on the force applied to the particles as a result of the simulation. |
| Dampening | The amount particle forces are damped - so they decay over time, rather than moving constantly. |
| Area Scale | Scales the area of space the simulation is processing. |
| Mode | Choose how the fluid simulation is calculated.
|
| Dimension | Choose whether the effect is 2d or 3d. |
| Life Effect Coeffs | How much the particles are affected by the affector at different stages of the particles life cycle. Values 1 and 2 are control points used to control a bezier curve between values 0 and 3. |
| Grid Resolution | The resolution of the underlying grid used in neighbourhood searches. |
| Name | Description | Typical Input |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Transform Nodes | ERROR: Variable not found: {input-node-particles-grid-transform-node-description} | ERROR: Variable not found: {input-node-particles-grid-transform-node-typical-input} |
| Affected Emitters | Choose which particle emitters can be affected by the affector. | Primitive Emitter |
| Procedural Falloff | Use the distance field from a procedural system to vary how strong the affector is. | Procedural Root |
| Transform Modifiers | Apply the transforms of another node to this node. | Null |
| Target Node | Modifiy the rotations of the node to always direct the z axis towards the input. | Null |
| Local Transform Override | Apply the transforms of another node to this node, relative to its parent. | Null |