Shape 3D
Generate a 3D primitive mesh.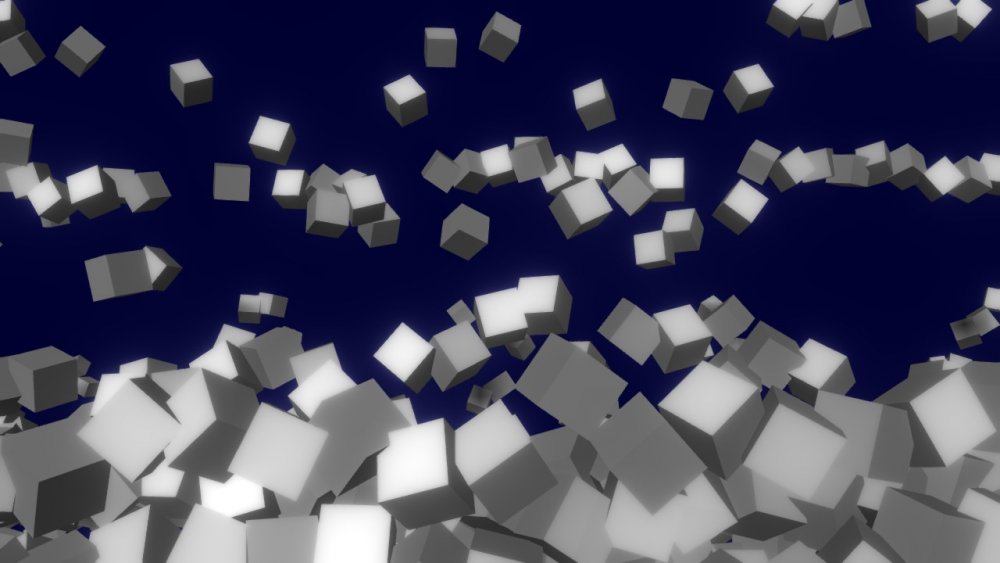
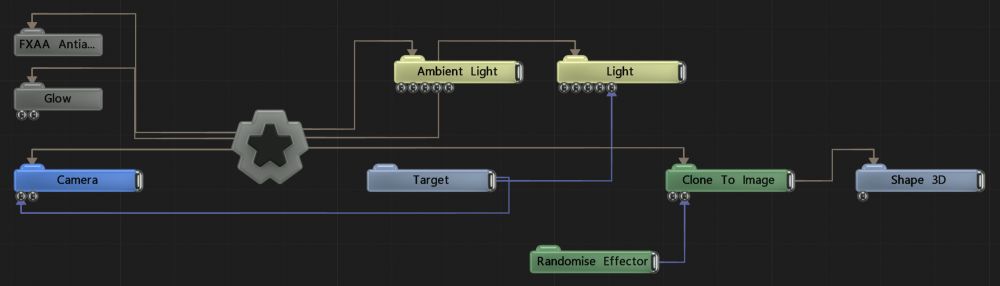


This node renders a 3D primitive mesh that has been generated according to various attributes. As well as being rendered directly, Shape 3D nodes may also be used as an input for various other nodes, including Particle Mesh Emitters, Field 3D Object Emitters, Clone To Mesh, Clone To Volume, Collision Affectors and numerous others. A Material Node can also be input to control the shapes material properties.
The Shape 3D node may be used as a rigid body in a physics system via the Physics Attributes properties. It must be parented under a Rigid Body Root node for physics to be applied.
Smoothing and subdivision is interleaved with deformation so deformers may be applied to a certain subdivision level.
Subdivision, smoothing and deformation may have a noticeable memory and processing overhead.
This node outputs the normal transformation and translation values, but it also outputs geometry which can be modified with Deformer nodes, or used as a mesh sources for nodes which accept mesh connections, such as the Field 3D Object Emitter or the Procedural 3D Object.
These properties control the 3D transforms of the node. Transforms will generally be inherited by child nodes, although they can be ignored through the Inherit Transform Channels attributes.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | Move along the local x-axis. |
| Position Y | Move along the local y-axis. |
| Position Z | Move along the local z-axis. |
| Rotation Heading | Rotate around the local y-axis. |
| Rotation Pitch | Rotate around the local x-axis. |
| Rotation Bank | Rotate around the local z-axis. |
| Scale X | Scale along the local x-axis. |
| Scale Y | Scale along the local y-axis. |
| Scale Z | Scale along the local z-axis. |
Toggle which transform channels should be inherited from the parent node. By default, all transforms will be inherited.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | Toggle inheritance of the X Position from the parent. |
| Position Y | Toggle inheritance of the Y Position from the parent. |
| Position Z | Toggle inheritance of the Z Position from the parent. |
| Rotation Heading | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation Heading from the parent. |
| Rotation Pitch | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation Pitch from the parent. |
| Rotation Bank | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation Bank from the parent. |
| Scale X | Toggle inheritance of the X Scale from the parent. |
| Scale Y | Toggle inheritance of the Y Scale from the parent. |
| Scale Z | Toggle inheritance of the Z Scale from the parent. |
| World Position Only | Inherit the world position from the parent only, rotation and scale will be ignored. Overrides above properties. |
| Inherit Time | Toggle inheritance of time from the parent. |
These properties control the core behaviours of the node.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Shape Type | Choose which 3D shape is rendered. |
| Radius | The radius of the primitive, where appropriate. |
| Size X | The size of the primitive in the X axis, where appropriate. |
| Size Y | The size of the primitive in the Y axis, where appropriate. |
| Size Z | The size of the primitive in the Z axis, where appropriate. |
| Subdivisions X | How many subdivisions along the objects X axis. |
| Subdivisions Y | How many subdivisions along the objects Y axis. |
| Axis | Select which axis you want the shape to aligned to upon creation. |
| Line Thickness | Thickness of lines, if “Line” or “Line Array” is selected in the “Shape Type” attribute. |
These properties control how the geometry is rendered into the scene.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Visible | Control whether the node is visible or not to the scene. |
| Seen By Rays | Allow the mesh to be seen by the raytracer. When set to 0, the mesh will still render in camera but will be ignored by any raytracing nodes. |
| Tessellation Enabled | Enables hardware tessellation, which subdivides the mesh efficiently at render time on the GPU. Tessellation does not consume memory resources and is more efficient than subdivision. |
| Max Tesselation Factor | The maximum tessellation factor for hardware tessellation. Controls the maximum number of polygons generated from each source polygon in the mesh. |
| Subdivision Near Distance | The near distance from the camera at which tessellation is at its highest. |
| Subdivision Distance | The distance from the camera at which tessellation falls off to the original mesh polygons. |
| Reveal | Controls the Fertilizer value, used to grow vertices from specified source points. Easiest used with the Generate Fertilizer Times Deformer. |
| Reveal Back | Controls the back Fertilizer value, used to grow vertices from specified source points. Easiest used with the Generate Fertilizer Times Deformer. |
| Render Z Only | When enabled, the 3D object is only rendered to the depth buffer in the main camera render. No colour data is rendered. |
| Render to Shadows Only | When enabled, the object is only rendered to shadow map passes, not to the main camera render. |
| Per Object Composite Alpha | Overwrites the alpha channel beneath the object, giving simple effect of transparency. Best used when the mesh won’t overlap with other objects, as other meshes will not be seen through the mesh. |
These properties control how the UVs of the mesh are transformed when output for the UV camera. Useful for arranging multiple objects to be output for the same UV Camera.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| UV Scale X | Scale the mesh UV along the x axis. |
| UV Scale Y | Scale the mesh UV along the y axis. |
| UV Offset X | Move the mesh UV along the x axis. |
| UV Offset Y | Move the mesh UV along the y axis. |
These properties control the behavious of the object in a Physics System.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Friction | The friction of the rigid body. |
| Bounciness | The bounciness of the rigid body. |
| Density | The density of the rigid body. The density is scaled by the area of the shape to determine the mass of the body. |
| Spin X | The spin of the rigid body in the X axis. This scales the inertia tensor on the X axis, making the body spin faster in that direction when torque is applied. |
| Spin Y | The spin of the rigid body in the Y axis. This scales the inertia tensor on the Y axis, making the body spin faster in that direction when torque is applied. |
| Spin Z | The spin of the rigid body in the Z axis. This scales the inertia tensor on the Z axis, making the body spin faster in that direction when torque is applied. |
| Dynamics Mode | How the object is used in a physics simulation. Parenting to a Physics Root node node must be done for any physics simulations to occur.
|
| Dynamics Transform For Rendering Only (Faster) | If selected, the transform of the body is maintained on GPU only. This reduces latency and increases performance but means that parenting to the object, e.g. using it to transform lights or emitters, will not work. |
| Rigid Body Shape | The shape of the rigid body
|
| Rigid Body Sphere Radius | The radius of the rigid body sphere shape if applicable |
| Rigid Body Box Size X | The size of the rigid body box shape if applicable |
| Rigid Body Box Size Y | The size of the rigid body box shape if applicable |
| Rigid Body Box Size Z | The size of the rigid body box shape if applicable |
| Rigid Body Convex Hull Mode | If the Convex Hull shape is used, determines the convex hull mode used - which will be wrapped around the node’s geometry |
See Materials
| Name | Description | Typical Input |
|---|---|---|
| Transform Modifiers | Apply the transforms of another node to this node. | Null |
| Target Node | Modifiy the rotations of the node to always direct the z axis towards the input. | Null |
| Local Transform Override | Apply the transforms of another node to this node, relative to its parent. | Null |