Cloning nodes create instances of 3D objects and meshes, with each cloner node defining a method for where and how the clones are spawned. Clones are rendered using hardware instancing on the GPU, making it extremely performance efficient, but it requires each mesh to be an identical copy of one another. To clone an object it must be a child to the output of a Cloner node.
Cloners can be modified by using Effector nodes, which modify the transformation or the colour tint of each clone. By building up multiple of these nodes together, complex animations can be created. Effectors are also time independent, so jumping forward and back in time wont require any simulation or calculations, with the exceptions of the rigid body effector (which runs a physics simulation) and the Spring effector (which uses changes over time to calculate a simple spring simulation).
Cloners are generally hooked into the Root node, although they can be applied to any node – they will still appear in the scene as long as there is a path to a Root node; they will inherit the transformation values of parent nodes.
Effectors
Effector nodes modify the transformation values of clones in cloner node systems.
 Colour Ramp Effector
Colour Ramp Effector
Modifies a cloner system with colours from an input Colour Ramp.
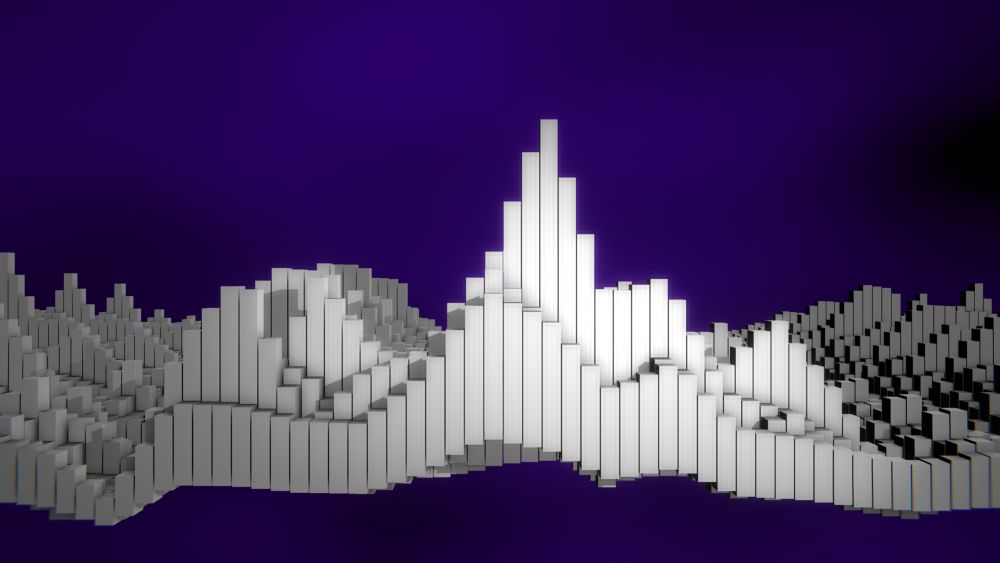 FFT Effector
FFT Effector
Modifies a cloner system using an audio input.
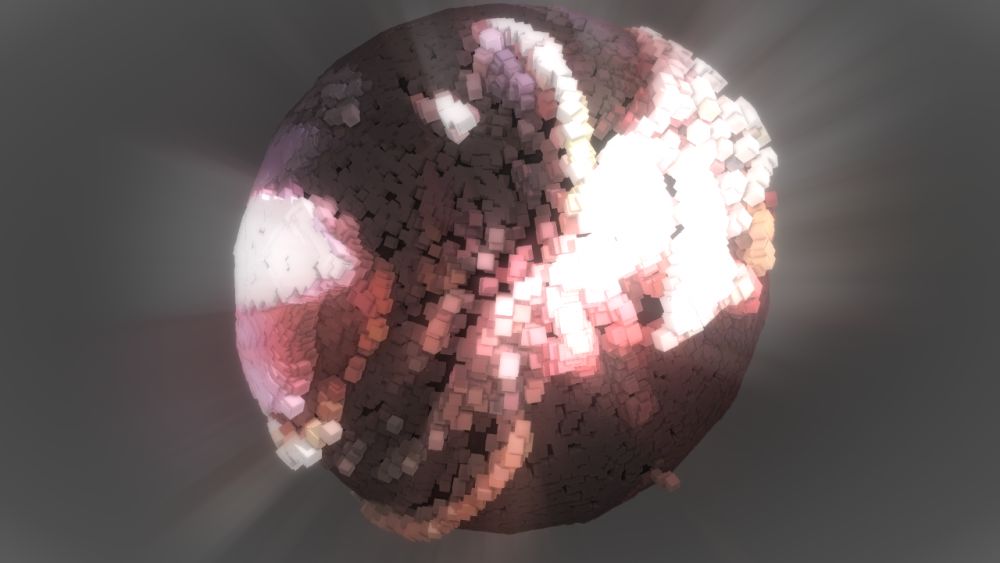 Image Effector
Image Effector
Modifies a cloner system using an input image or video.
 Kill Box Effector
Kill Box Effector
Removes Clones from a cloner system within a specified area.
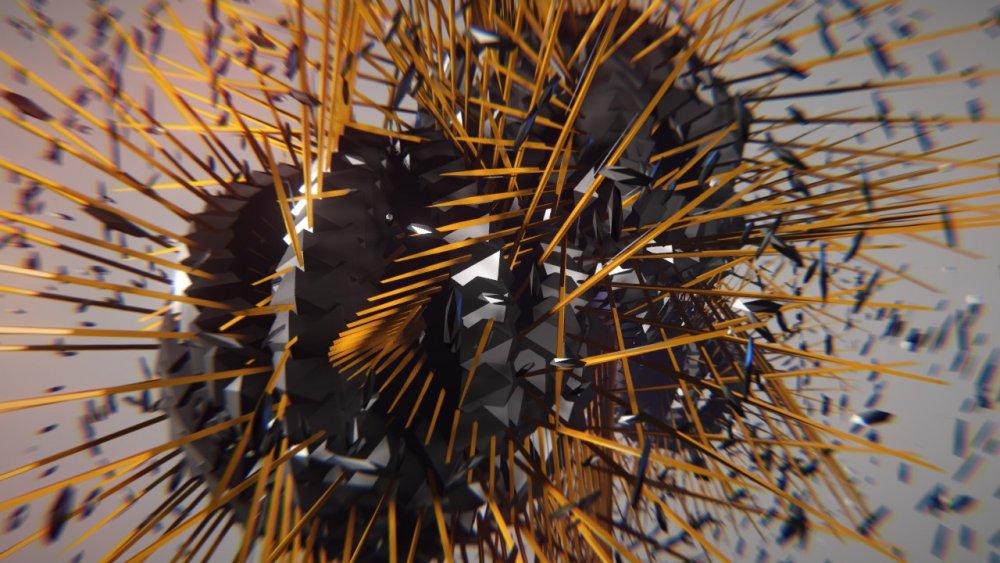 Plain Effector
Plain Effector
Modifies a cloner system with simple transforms.
 Quantise Effector
Quantise Effector
Modifies a cloner system by quantising all the clone positions.
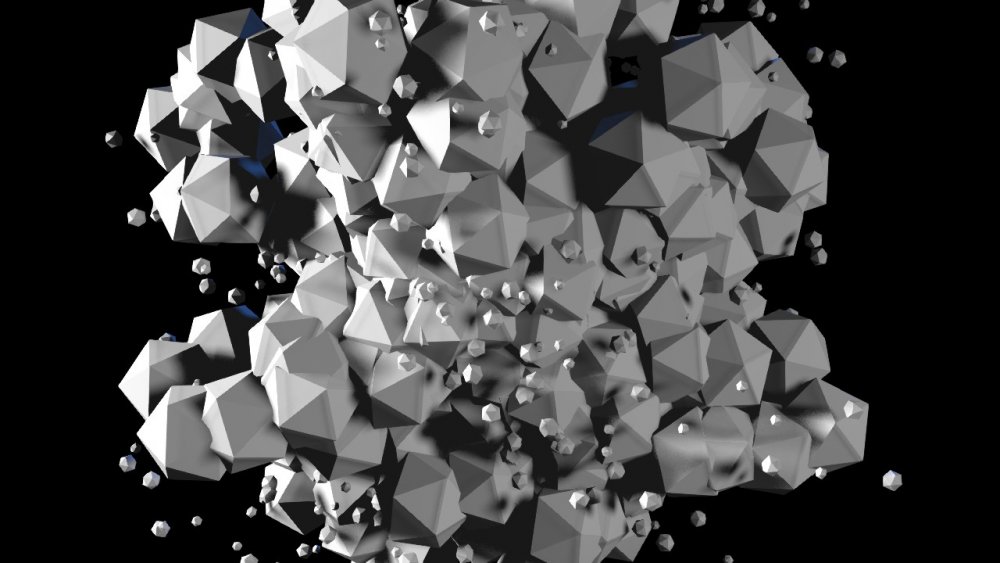 Randomise Effector
Randomise Effector
Modifies a cloner system with randomised transformations.
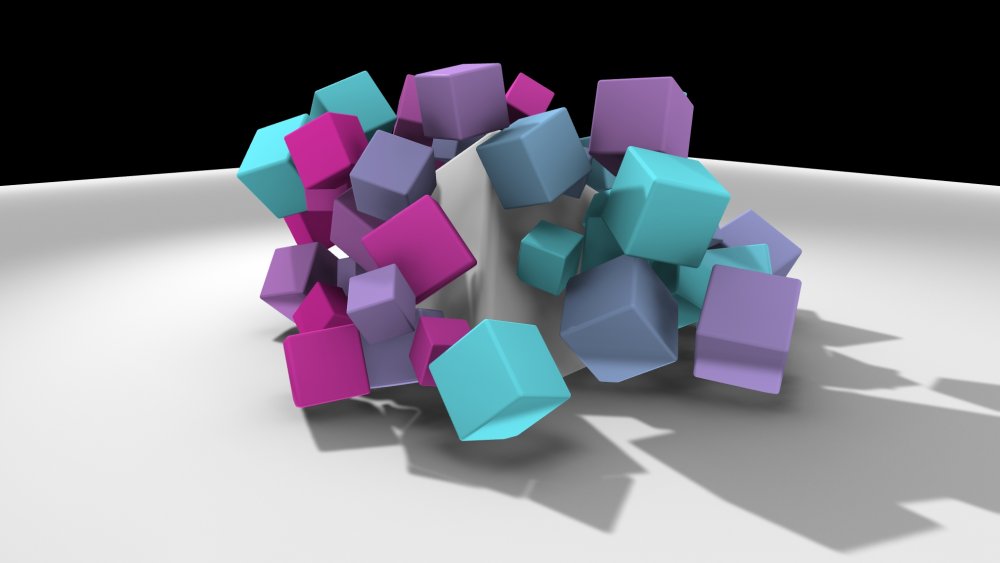 Rigid Body Effector
Rigid Body Effector
Applies a Rigid Body simulation to A cloner system.
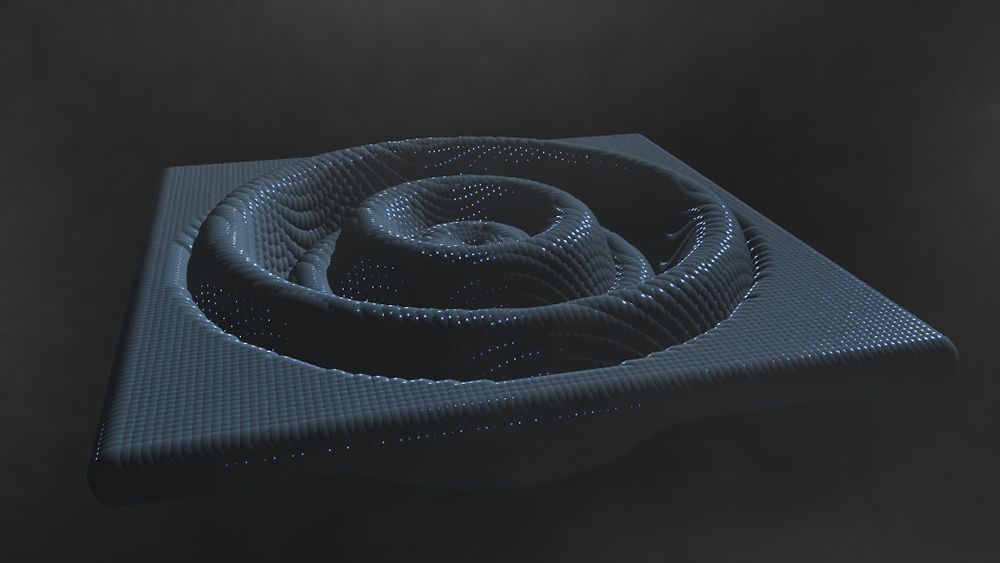 Ripple Effector
Ripple Effector
Modifies a cloner system with a ripple effect.
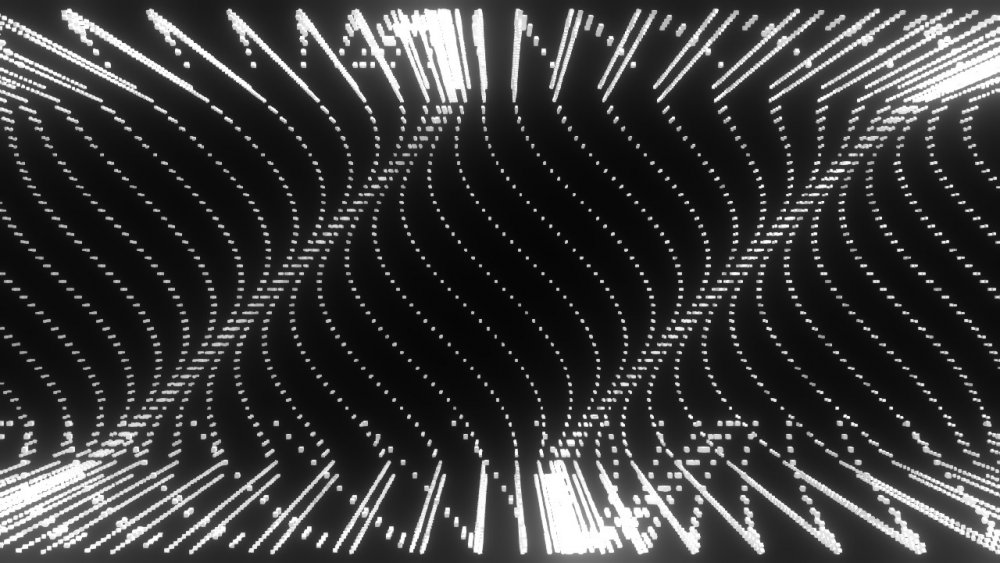 Sine Effector
Sine Effector
Modifiers a cloner system with a sine wave oscillations.
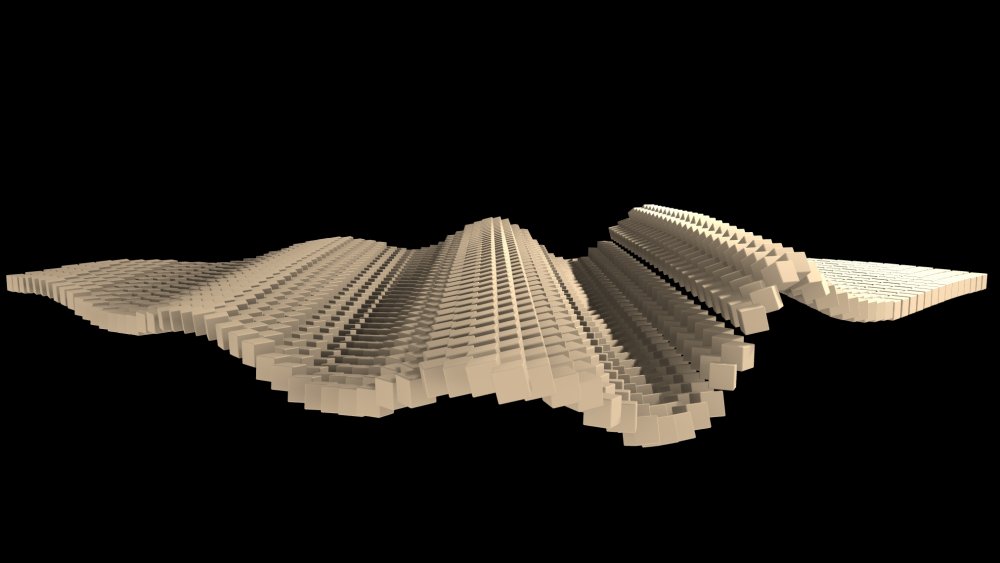 Spring Effector
Spring Effector
Modifiers a cloner system by adding a springiness to Clone transformations.
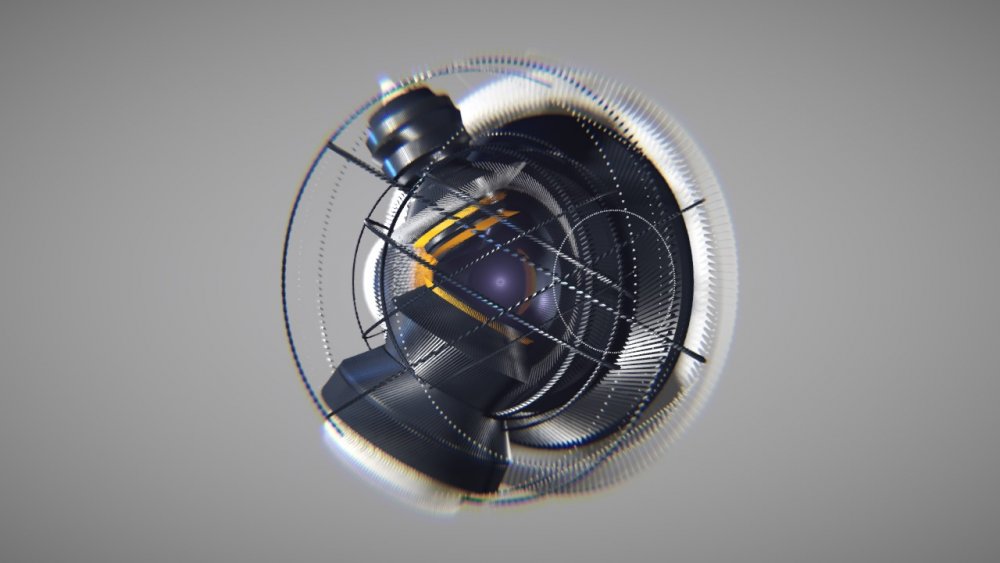 Target Effector
Target Effector
Rotates clones to target a point in space.
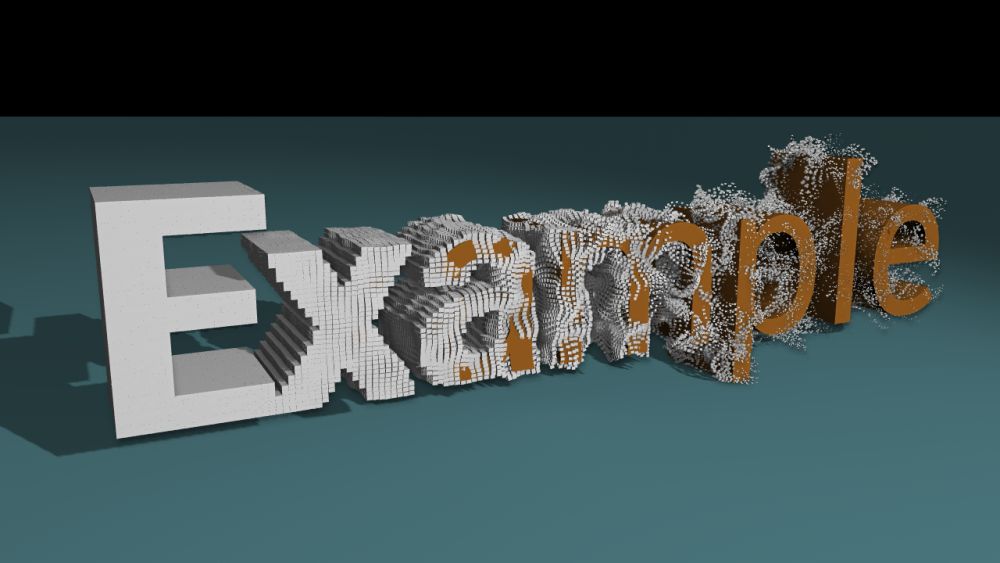 Turbulence Effector
Turbulence Effector
Modifies a cloner system with turbulent motion.
Nodes
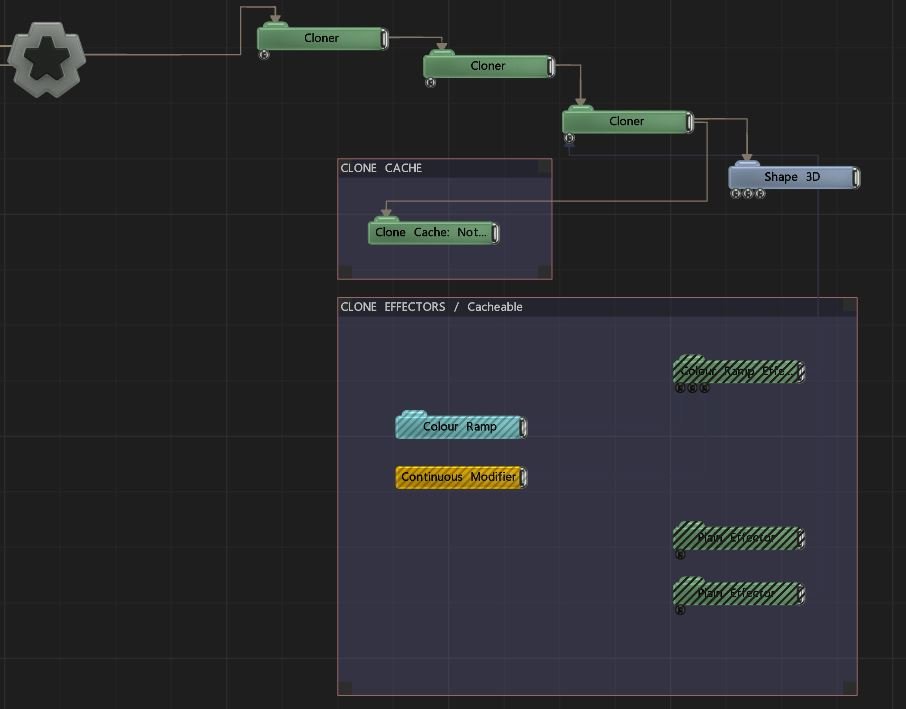 Clone Cache
Clone Cache
Caches a clone system for faster and repeatable results.
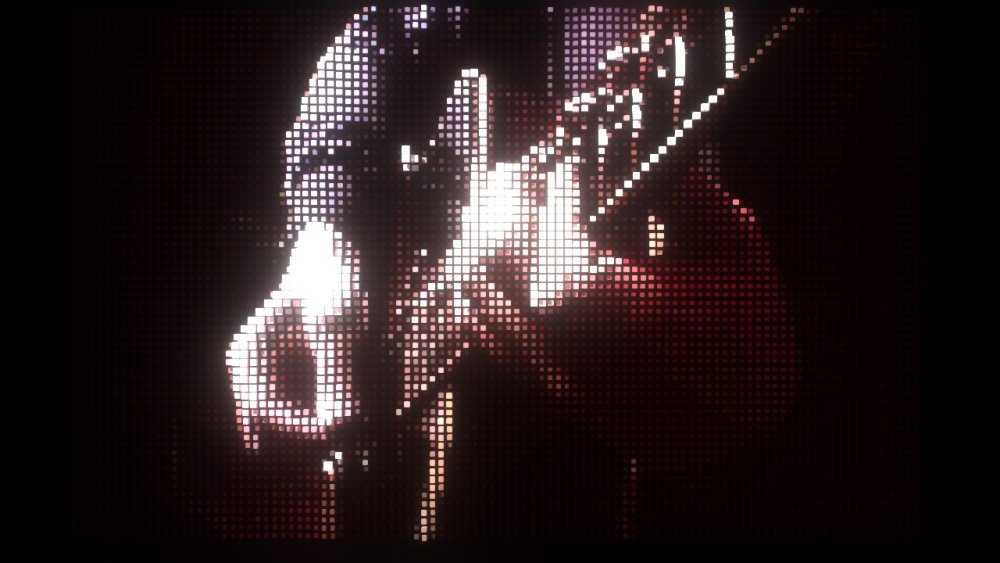 Clone To Image
Clone To Image
Generates Clones from an input image.
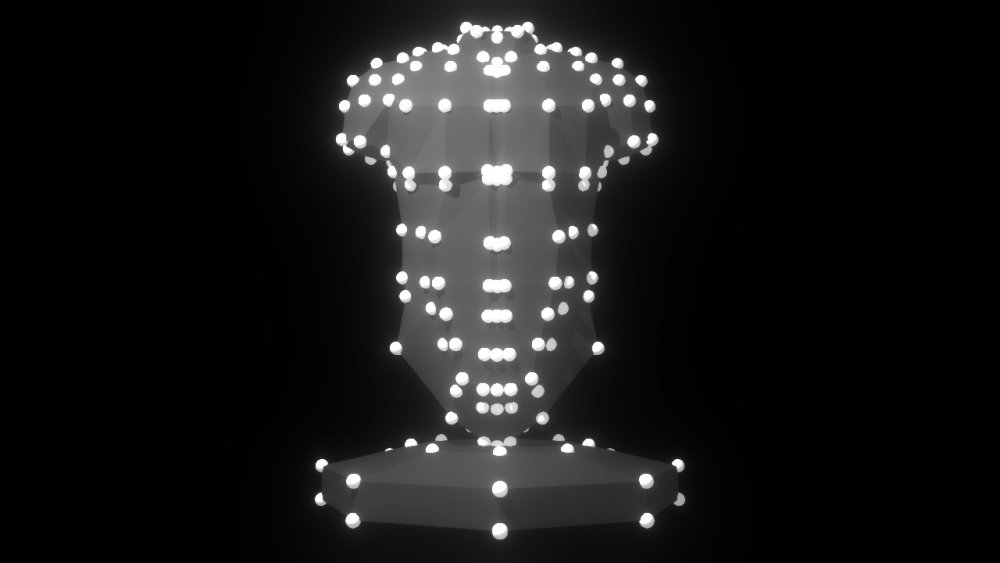 Clone To Mesh
Clone To Mesh
Generates Clones from an input geometry
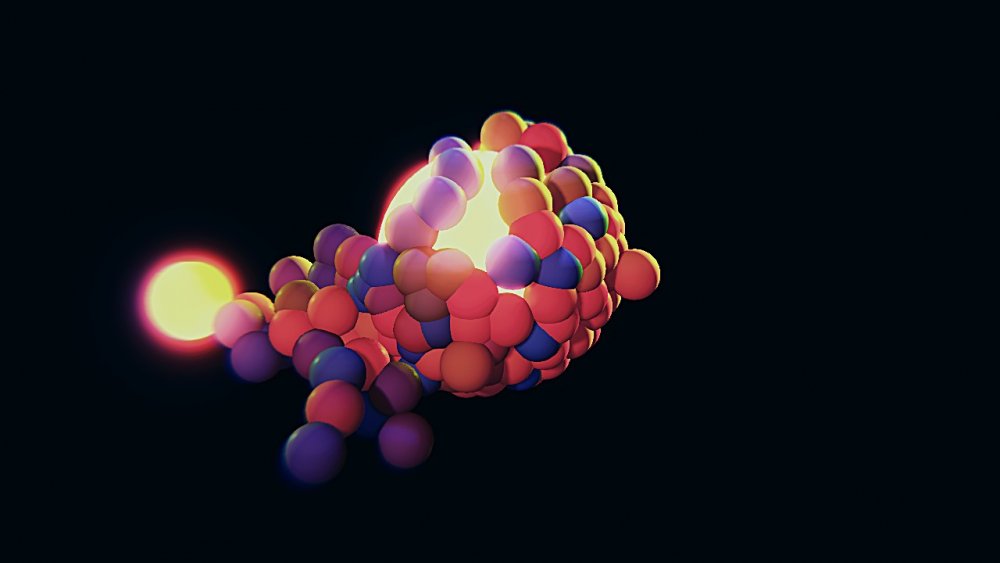 Clone To Particles
Clone To Particles
Generates Clones from an input Particle system
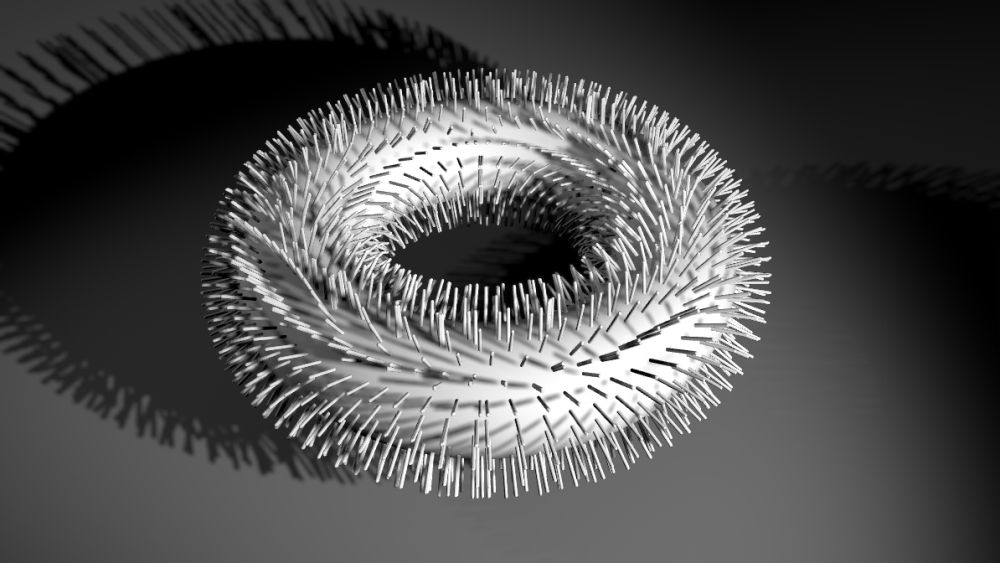 Clone To Point Cache
Clone To Point Cache
Generates Clones from the positions defined by a Point Cache node.
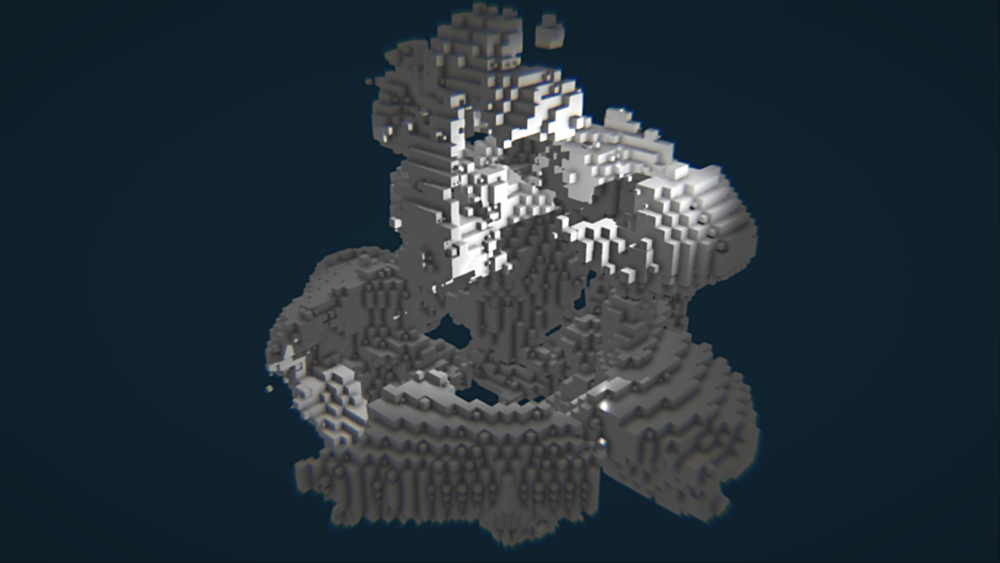 Clone To Procedurals
Clone To Procedurals
Generates Clones from an input Procedural system.
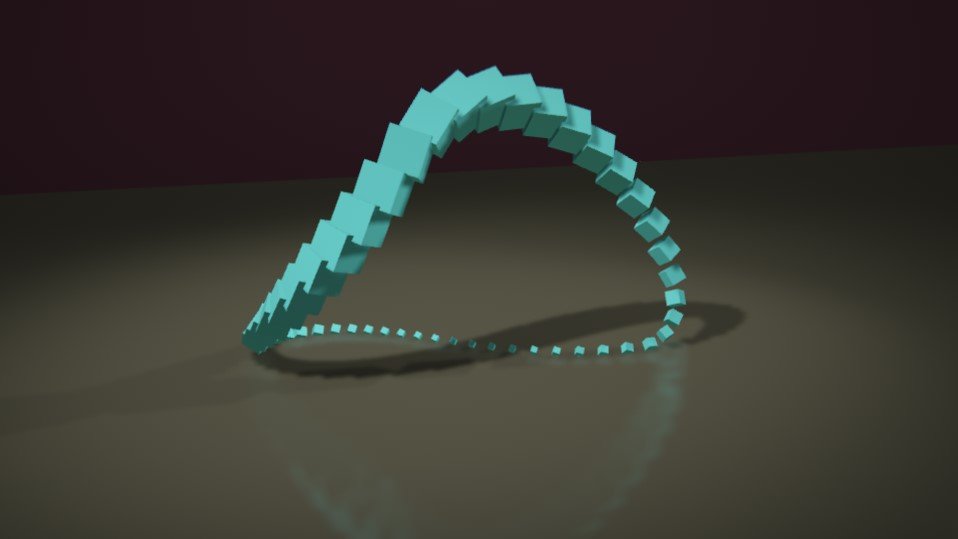 Clone To Spline
Clone To Spline
Generates a clones which follow the curve of a spline.
 Clone To Transform Array
Clone To Transform Array
Generates Clones from an input Array node.
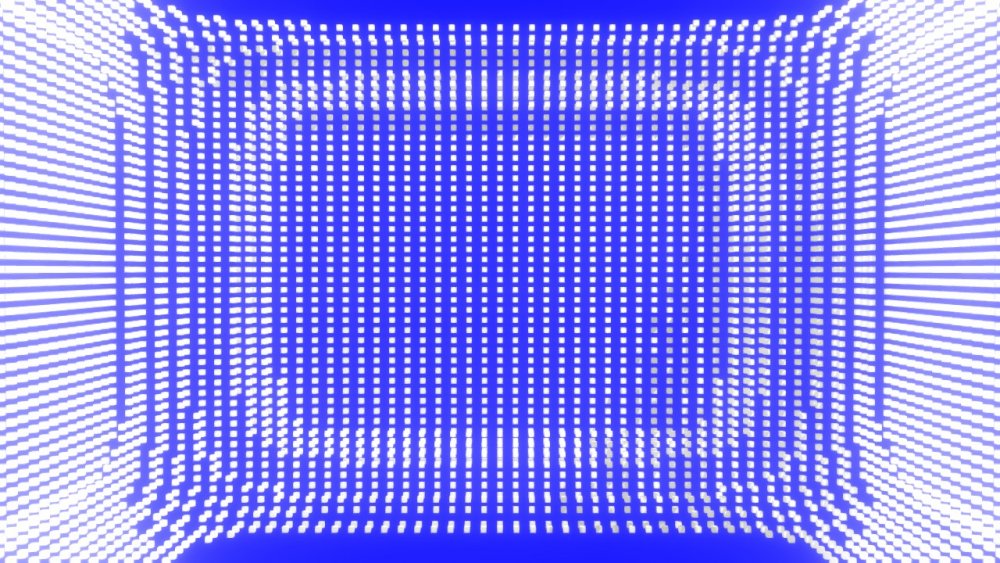 Clone To Volume
Clone To Volume
Generates Clones which fill the volume of input geometry.
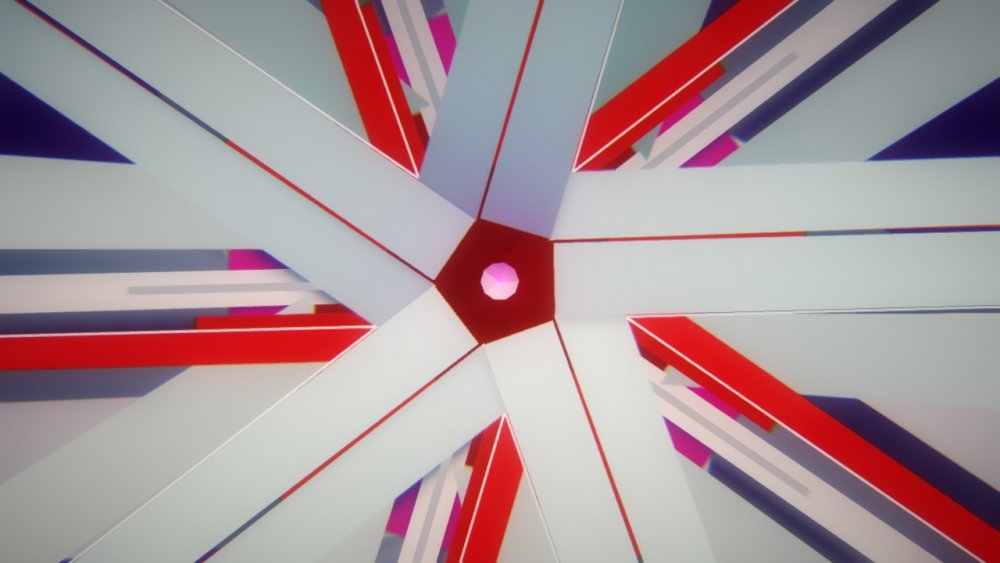 Cloner
Cloner
Generates Clones in a regular pattern.
 Random Cloner
Random Cloner
Generates Clones with random transformations.

