Everything in Notch 2026.1
Updated: 12 Feb 2026
Updated: 12 Feb 2026

The complete guide to what’s been added since 0.9.23
On 3rd February 2026, Notch v1.0 becomes Notch 2026.1. This release represents the culmination of the new features introduced in pre-1.0, 1.0 alpha, private-beta and public beta.
In total, it is a ground-up transformation of Notch, with major new systems, hundreds of new nodes, and fundamental improvements to every workflow.
A lot of people have been using Notch 1.0 since either private or public beta. To help see what is most recent, we’ve created badges that reflect when the feature was added:

The centrepiece of 2026.1 is NURA — the Notch Unified Rendering Architecture. NURA brings consistent results across four GPU renderers without changes to your materials, lighting, or render settings.
The key benefit is the ability to switch renderers at any time to suit your needs, whether that be real-time performance for live shows, high-quality path-traced renders for offline content creation, or a balance of both for interactive design workflows.
| Renderer | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Path Tracer | Native GPU-powered Monte Carlo path tracer with unbiased rendering algorithms. Fully interactive in the viewport with AI denoising from NVIDIA OptiX and Intel OIDN. | Highest quality offline renders, massive scalability, deterministic distributed rendering |
| Smart Tracer | Accelerated path tracer using spatio-temporal path guiding and ReSTIR. Reduces required passes from thousands to tens or even one. | High-quality renders without path tracing wait times, interactive path-traced workflows |
| Hybrid Renderer | Combines rasterisation with ray tracing for global illumination, multi-bounce reflections, and refractions. Scales across multiple machines and GPUs. | Real-time with advanced lighting features, multi-GPU deployment |
| Standard Renderer | Fastest renderer with complete material and shader support. Streamlined feature set for instant GPU response. | Live shows, 2D workflows, video effects, single-GPU installations |

Where different renderers in 0.9.23 had differing feature sets, all NURA renderers now support a common set of features, implemented in different ways depending on the renderer:
The Path Tracer and Smart Tracer always use ray tracing for primary rays. The Hybrid and Standard Renderers can optionally use ray tracing for primary rays. This can give a significant performance improvement in very high polygon scenes. Triangle, point and line primitives are all supported directly by the renderer, as are fields, procedurals and particles - allowing rays to pass through them correctly in order and for all of them to shadow each other.
Explore how the new rendering features work across all four NURA renderers:
Volumetric lighting has been completely reworked and is now handled directly by the rendering nodes. New features include:
Motion blur is now integrated into all rendering nodes and now features:
Depth of Field is now built into the rendering nodes:
Ambient Occlusion is now built into the rendering nodes:
These are now built into the rendering nodes.
Anti-aliasing is now built into the rendering nodes (instead of separate nodes):
All renderers now support transparency sorting per pixel via different methods.
Non-linear cameras (such as Fish Eye, VR 180, VR 360) can use ray tracing to render the exact output pixels, without needing to go via a cube map - improving quality and performance and reducing VRAM usage. β
Cameras now include controls for depth of field and motion blur.
Enhanced Shadow Catcher Material support across all renderer nodes with a Blend Amount parameter for controlling blending.

The number and quality of lights has been increased across all renderers. Lights are generated and culled on the GPU, allowing them to be cloned.
Omni Light and Spot Light — Dedicated nodes extracted from generic Light node. Support for ray traced cone-based soft shadows on Hybrid Renderer. Screen-Space shadows improve quality at contact points. β
Area Light — Now has Beam angle parameters (Light Cone Angle, Light Inner Cone Angle). Works in all renderers. Support for ray traced cone-based soft shadows on the Hybrid Renderer.
Sky Light — Works in all renderers. Improved direct sun shadow term. Works with new “Daylight Environment” node to generate procedural, dynamic skys.
Emissive Objects - Emissive geometry can light the rest of the scene, with shadows, in Hybrid/Smart/Path Tracer.
Decal — Improved version with blend modes and falloff support. β
The entire UI system has been rewritten. All panels can be moved and docked to create custom workspace layouts.

The nodegraph is your canvas, so we’ve spent a lot of time making it faster, more discoverable and enjoyable to use, with these new features:
CTRL+Space or Dbl-Click Nodegraph Background to β
CTRL+F β
P to toggle, Shift+P to pin selected, Ctrl+Shift+P to unpin selected) β
CTRL) to insert it between two nodes β
Ctrl+Shift+Click a node to remove it from its connection chain β
The addition of Embedded Nodes and Assets are foundational improvements to the Notch workflow.
Embedded nodes allow you to collapse a group of connected nodes down into a single node with it’s own exposed parameter surface. Beyond just cleaner nodegraphs, embedded nodes allow for multiple-instancing and re-use.
Assets build on embedded nodes by allowing you to save and load embedded systems with custom parameters for reuse across projects and sharing with your wider team. We now also ship a comprehensive library of production-ready assets to get you started - in the asset browser.


The Curve Editor is foundational to animation and has some significant upgrades:

A totally redesigned Property Editor that brings a host of usability improvements:

The utility & usability of the Viewport has been vastly increased for both 3D and 2D workflows.
Unified controls across all panels — Alt+LMB rotate, Alt+Shift+LMB pan, Alt+RMB zoom
Viewport HUD — Provides performance metrics and scene stats
Placement tool — Place objects directly onto surfaces
Viewport picking — Now select Nulls, Cameras, Lights, Splines directly in viewport
Snapping — Incremental, Viewspace, Worldspace, snap to grids or user defined snap lines (horizontal or vertical) created on the viewport ruler. [HOLD SHIFT while moving object]
Rulers — for precise alignment
Guides — Customise your own (DBL-CLICK on ruler), or use off the shelf: grid, center cross, thirds, quarters
Pickable viewport objects — for Lights, Cameras, and Nulls, Splines, Falloffs
Picture-in-Picture preview mode (Ctrl+F4)
Freeze UI button for more accurate performance readings
Material preview directly in viewport
Node Falloff visualisation in viewport
Viewport sidebar for Spline and Paint Clones interactions
Viewport axis labels option
Grid fades at distance
The Resource Browser has been entirely rewritten with:

The Resource Inspector is a new panel that significantly improves the workflow and preparation of imported resources.
Working with exposed parameters gets a major boost with the new Remote Panel. You can now view and interact with all exposed parameters in one place, emulating the end-user experience of using the VFX/media server blocks.
This is perfect for testing and setting up your projects without needing to deploy to a block for persistent validation.


A new Scopes window (View->Scopes) provides real-time colour analysis of the viewport: β
Save versioned snapshots of your project with File->Save Version (Ctrl+Alt+S): β
Brand new Log Panel, features error filtering, clearing of logs and quick file access for sending to support.

The new off the shelf materials & assets library can rapidly accelerate your creation process. 2026.1 includes a comprehensive library, but also the ability for your team to build and share your own custom assets.

Long requested, the new 2D Root Node brings a dedicated 2D workspace with its own rendering pipeline:
Cloning has been reimagined with:
New Cloner nodes:
| Node | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Grid Cloner | Regular 3D grid arrangements β |
| Radial Cloner | Circular and radial patterns β |
| Linear Cloner | Line-based distribution β |
| Iterative Cloner | Transform-based spiral/fractal effects β |
| Mesh Cloner | Clone onto mesh surfaces β |
| Paint Clones | Hand-place clones in viewport onto surfaces β |
| Volume Cloner | Fill 3D volumes β |
| Procedural Cloner | Voxel-based cloning from procedurals β |
| Image Cloner | Drive clones from image data β |
| Particle Cloner | Attach geometry to particle positions β |
| Spline Cloner | Clones follow spline curves β |
| Array Cloner | Clone from transform array elements β |
| Cloner Cache | Cache cloner states β |
New effector:
| Node | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Smoothing Effector | Smooths changes to position, rotation, and scale with separate controls and falloff. β |
Effector enhancements across the board: Effectors have received a variety of new features:

Points, lines and splines are now first-class geometry primitives, which can be rendered directly by all renderers. Deformers can be applied to them, and deformers exist to convert between types.
All geometry generation, including primitives, now runs on GPU - so properties can be animated efficiently. New primitive types have been added. Particles and clones can be converted to geometry.
All geometry generation is deterministic, and geometry is only regenerated on change - not per frame.
Combined with the new deformer system, complex geometry processing can now be performed directly in Notch.
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Primitive 2D | A 2D primitive type. |
| Duplicate Geometry | Take a copy of some geometry - for use in geometry processing chains. |
| Points From Clones | Extract clone positions as points. β |
| Falloff Node | Universal falloff that overrides falloff properties on any connected node. β |
A brand new pivot system allows you to intelligently set custom pivots per node.
Set Custom pivots per Node, either by:
All can set by using CTRL + P or using the Pivot node group properties.

The 3D Scene node has been rewritten:

The Text node now includes:

The spline system has been completely redesigned and expanded. No more chains of nulls!
The Spline node now features:
Two new nodes add powerful geometry generation capabilities:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Revolve Spline | Generate geometry by revolving a spline around Y-axis. β |
| Spline Extruder | New end caps, new extrude shapes, Ability to minimise twist. β |

The deformer system has been rewritten with support for complex, topology-changing deformers, and to allow complex deformer systems in processing chains to be built (like video nodes). Deformers are entirely deterministic, and only process when something in the deformer chain changes - making complex chains efficient. New weightmap nodes allow detailed control over deformers. Deformers can access and assign multiple materials on geometry. Cloth and rope physics now work as deformers.
There’s a large new set of deformers, including..
New Physics Deformers:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloth Deformer | Full cloth simulation with self-collision, friction, bounciness β |
| Rope Deformer | Rope physics with anchor constraints (first, last, or both points) β |
New Topology Deformers:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Voronoi Fracture | Shatter geometry with controllable Voronoi points β |
| Greeble | Procedurally generate complex surface detail β |
| Fertilize | Reveal geometry over time based on vertex index β |
| Cut | Slice meshes with UV control on cut faces β |
| Retopologise | Generate a reduced version of a mesh via conversion to an SDF. β |
| Spline Extend | Extrude a mesh along a spline path. β |
| Lines And Splines | |
|---|---|
| Connect With Lines | Create a line mesh connecting two meshes. β |
| Lines To Mesh | Convert a polygon mesh to lines. β |
| Object To Lines | Convert a polygon mesh to lines. β |
| Object To Points | Convert a polygon or line mesh to points. β |
| Spread Lines Deformer | Spread line geometry out along its length. β |
Weight Maps reimagined — Generate from nulls, attributes, noise, occlusion. Combine multiple maps. Control deformers, effectors, and shaders.
Particles have wide ranging new features across Weight Nodes, Emitters, Affectors, and Renderers.
Determinism — Particle simulations are now fully deterministic for multi-machine consistency.
Fixed Update Substeps — Multiple simulation substeps per frame to maintain a fixed update rate.
Stochastic Emission — Emission Interval options for interpolated emission between frames, eliminating gaps in fast-moving emitters.
Mesh Emitter — Emit particles directly from cloned geometry without needing Combine Geometry first.
New Weight Nodes:
New Affectors:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Fluid MPM Affector | Material Point Method for stable, detailed liquid simulation β |
| Particle-Particle Collision Affector | Particles collide with each other β |
| World Collision Affector | Particles collide with visible geometry β |
| Angled Motion Affector | Noise-driven motion constrained to angles β |
New Renderers:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Soft Ball Renderer | Particles as soft body spheres that interact β |
| Particles to Point Geometry | Renders particles as ray-traced spheres with full material support, and be used as geometry with deformers β |
| Line Connection Renderer | Lines between nearby particles, with option to render as 3D geometry β |

Sparse Grid Architecture — The field system now stores only active cells:
OpenVDB Import and Export — Industry-standard volumetric data support. β
Cloning Fields - Fields can be cloned
Field Cache Renderer — Play back cached simulations with full material support, cloning, and transformation. β
Full NURA integration — Fields work across all four renderers.
Materials - Fields now support volumetric materials, and use of shading nodes - both for rendering and emitter/effector control.
The rigid body physics engine has been completely rewritten to provide a robust, stable, and high-performance simulation system:
Procedural Raytracer — Massive-scale worlds without bounding box constraints. Integrated with all the renderers.
New CSG Modes: Chamfer, Round, Stairs.
Fractal Node — Generate Mandelbulb, Mandelbox, Quaternion Julia fractals. Colour by iteration with gradient support. β
Spline Generator — Generate shapes from splines in procedural systems. β

Completely overhauled shading system:
New Nodes:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Tiles | Procedural brick/tile patterns |
| Randomise Colour | Randomise shading colours |
| Channel Sampler | Sample data from the surface or volume. |
| Cells generator | F2-F1 in 3D and 2D space |
No major Notch release would be complete without new Post-FX nodes:
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Glow | Realistic glow effects |
| Physical Lens Flare | Accurate lens flare simulation |
| Gaussian Blur | Resolution-independent blur with variable intensity β |
| Histogram Threshold | Threshold by percentage of pixels, not intensity β |
| Colour Reduce | Limit to chosen number of distinct colours β |
| Tritone | Remap colours for highlights, midtones, shadows β |
| Colour Curves | Precise control over brightness, contrast, and colour via editable curves β |
| Image Distance | Generate distance fields from images β |
| Block Glitch | Colour, greyscale, or no colour shift modes |
| Kuwahara Filter | Stylised oil-painting effect |
| Colour Correction | Per-channel gamma (power) curve parameters |
| Background Plate Subtract | Generate masks from difference with static plate β |
| Pixel Sort | Now with mask input |

Video Clips — Easy blending between multiple video clips with blend modes on the timeline. β
FFMPEG Support — Native playback without automatic transcoding. β
Video Loader — One Shot playback mode, Amount Played envelope for progress tracking, per-video Colour Space Conversion.

Subsurface Scattering Material — Light penetration for plastic, skin, wax. β Blend Materials — Blend multiple materials using blend channels/textures. β
Sound FFT Modifier — Visual interface to select frequency range and gain. β
Sound FFT Region Modifier — Add multiple detection regions to Sound FFT Modifier. β
Bake Modifier — Record input values as keyframes. β
Record Modifier — Record live input during playback. β
Compare Text String — String comparison including Levenshtein distance. β
Curve Remap — Remap modifier output values based on a customisable curve. β
Turbo mode stops the UI from updating during playback, boosting viewport playback performance. Useful for keeping smooth playback in the viewport while you’re reviewing a project.

The new Profiler takes a fresh approach to performance analysis, allowing different views to help identify bottlenecks in your project. β

DCI-P3, P3-D65, Rec.709, Rec.2020, sRGB Linear, ACEScg, P3-Display, sRGB 2.2 β
Reduces memory usage for large canvas sizes (8K, 16K).
The Render Queue now takes automations and batch rendering to the next level with:
Available in blocks and standalone with multiple resolution scaling options (50%, 66%, 75%, 100%).
Providing Render Nodes for rendering on spare workstations or render farms, has long been a requested feature. To enable this we have developed two new tools:
Both of these two tools use the same underlying rendering engine as Notch Builder and will be able to utilise a separate Notch Render Node license - so that your Builder licenses are not tied up.
New features have been added to the Sound FFT Modifier to give greater control and visual feedback when working with audio reactive projects:
| Format | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| OpenVDB | Volumetric | Single VDBs with multiple float channels. Sequence support and colour data planned for future. β |
| PLY | Point Cloud | Includes vertex colour import with automatic value scaling. |
| PSD | Image | Photoshop file support, updated to latest SDK. |
FFMPEG support was added for video playback within Builder, eliminating the need for automatic transcoding of formerly unsupported file formats. Previously, non-native formats required conversion to NotchLC before playback.
This update allows direct playback of a wider range of video formats, including:
These formats were already supported but received notable improvements:
| Format | Improvement |
|---|---|
| EXR | 32-bit export, improved colour space handling, fixed pitch/skewing issues |
| FBX | Per-polygon smoothing, FPS override via Resource Inspector, improved camera import |
| C4D | Redshift camera/light import, cloner node import, improved spline import |
| Alembic | Improved animated topology handling, multiple animation set support |

MOVIN Mocap Skeleton — New support for MOVIN real-time motion capture. β
OptiTrack and XSens — Added recording and playback support via Devices menu. β
Completely rewritten:
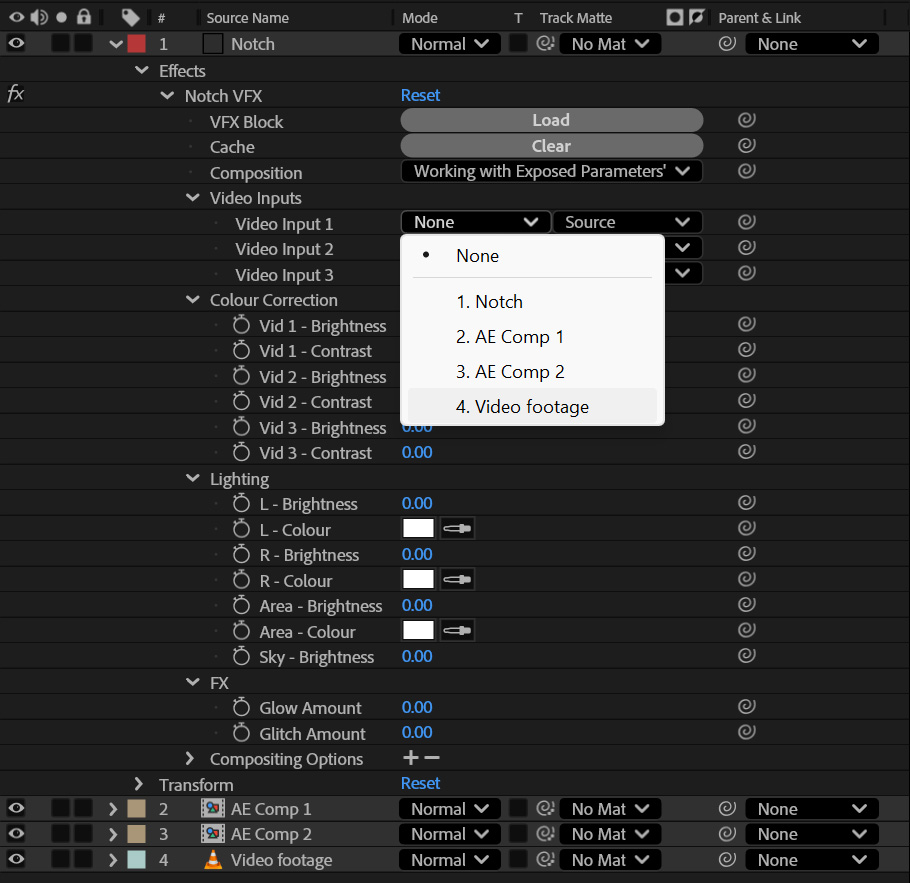
VFX Blocks allow you to embed, manipulate and render Notch content directly in DCCs (Digital Content Creation tools) such as Adobe After Effects. VFX Blocks can also receive video and image inputs from the host application and use them within the Notch scene, enabling a huge range of effects and 3D workflows directly in After Effects. β
This allows teams of non-Notch users to utilise Notch content without needing to understand the underlying Notch system, and enables use of Notch content within pre-existing Adobe workflows.
New scripting functions for the JavaScript Node expand automation and dynamic scene control:
| Shortcut | Action |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+Space | Floating node search |
| Ctrl+F | Floating find |
| P | Toggle node pinning |
| Shift+P | Pin selected nodes |
| Ctrl+Shift+P | Unpin selected nodes |
| K | Insert Comment node |
| Shift+K | Insert Region node around selection |
| / | Split time bar at current time |
| C | Cut time segments |
| Alt+H | Toggle all viewport tools β |
| Ctrl+F4 | Picture-in-Picture preview |
| Ctrl+Shift+V | Paste maintaining material connections |
| Ctrl+Alt+S | Save incremental version |