 Fields
Fields
Updated: 2 Feb 2026
Updated: 2 Feb 2026
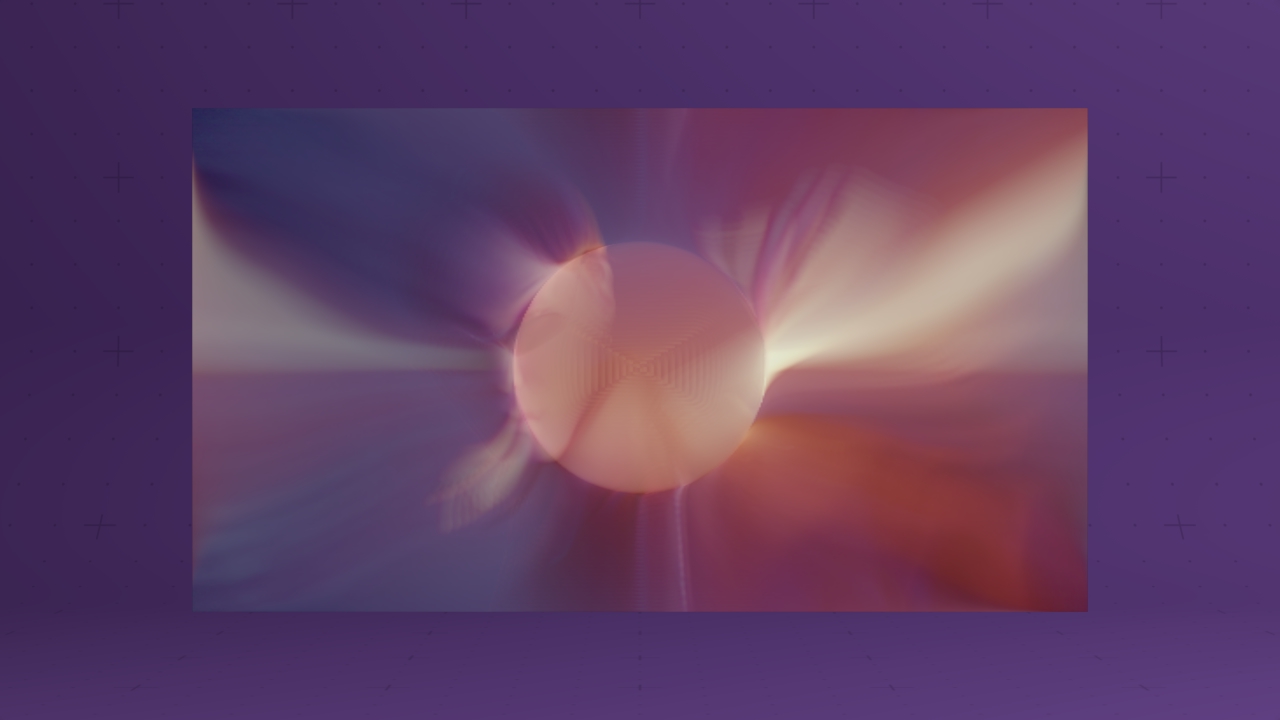
A field is a grid of voxels, which simulation smoke effects using a mixture of ink a motion vectors. A voxel is a 3D pixel that contains the following data:
By holding colour / “ink” information in the voxel, we can render it like a drop of ink suspended in a liquid or a puff of cloud. By holding a vector of movement we can simulate complex fluid-like motions through the grid.
With every newly rendered frame, the simulation of the field is stepped forward. During this simulation step, each voxel calculates it’s movement vector by understanding how the movement of the surrounding voxels are affecting it. For example, if a voxel to the left has a movement vector pushing to the right it will transfer some of its movement into the voxels to it’s right. In this way, it simulates the real world of motion in liquids or gases.
Likewise, in each step of the simulation, a portion of the ink follows the direction of the movement vector.
The way voxels are rendered can vary greatly, allowing smoke, clouds or more solid forms.
There are four primary types of field nodes:
You can also use the Movement Vector data from the field to affect particle systems using the Particle -> Affectors -> Field Affector node. This is very useful for fluid-like particle simulations.
Field systems starts with either a Field 2D Root or a Field 3D Root, and are built up with Emitter and Affector nodes, before finally being rendered to the camera with a Rendering node.
Fields are generally hooked into the Root node, although they can be applied to any node - they will still appear in the scene as long as there is a path to a Root node; they will inherit the transformation values of parent nodes.
Affector nodes modify the velocities of voxels in a field.
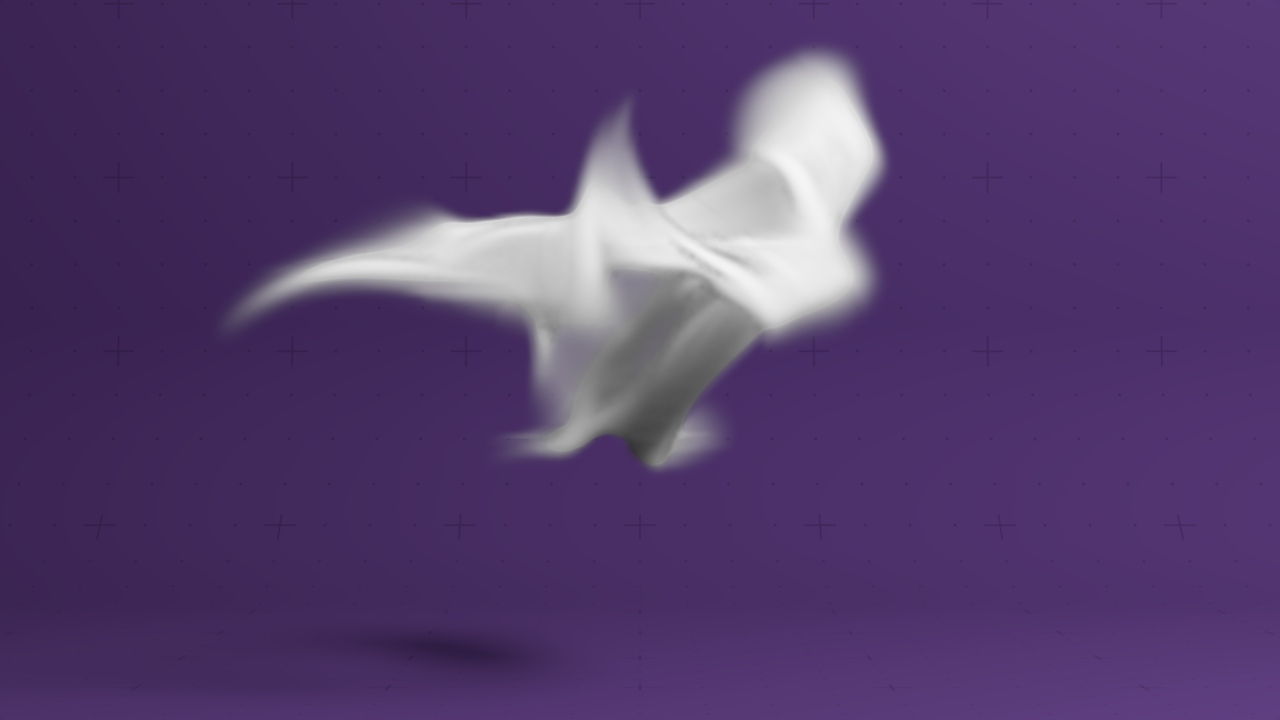 Curl Noise Affector
Curl Noise Affector
Applies curl noise velocities to a field.
 Derivative Feedback
Derivative Feedback
Applies a feedback effect to a 2D field.
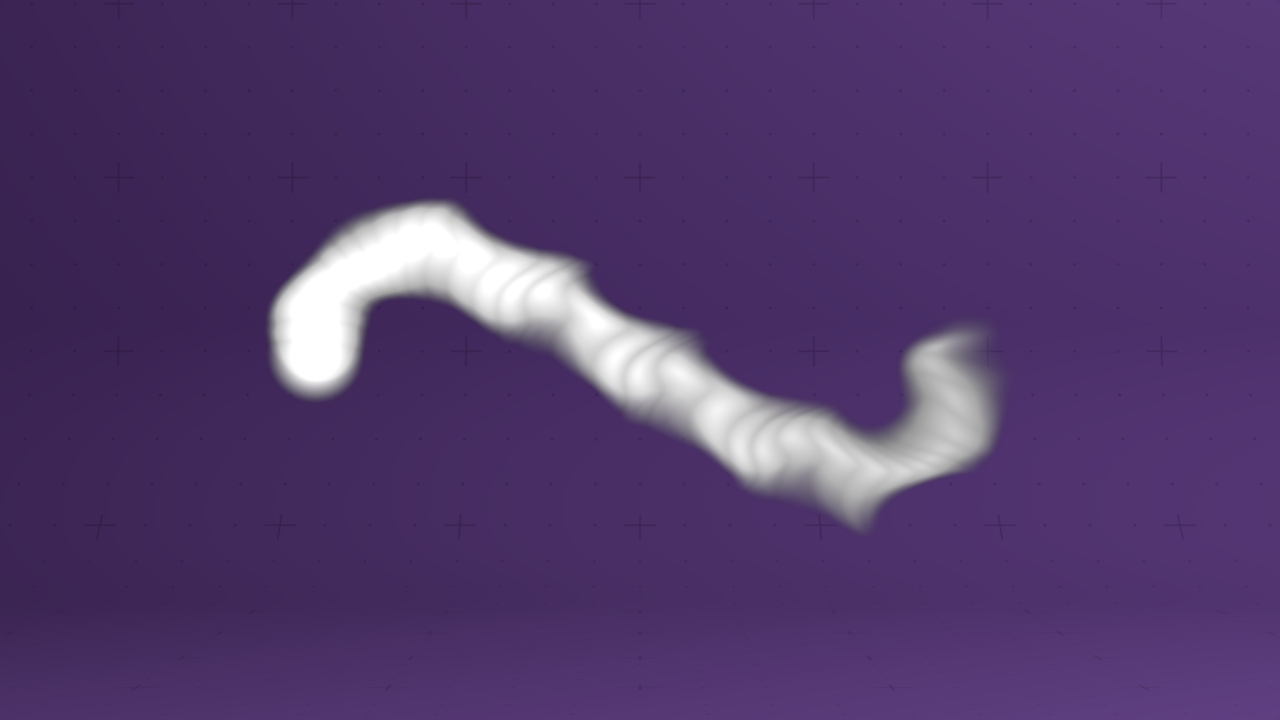 Field Affector
Field Affector
Applies a different field's velocities to a field.
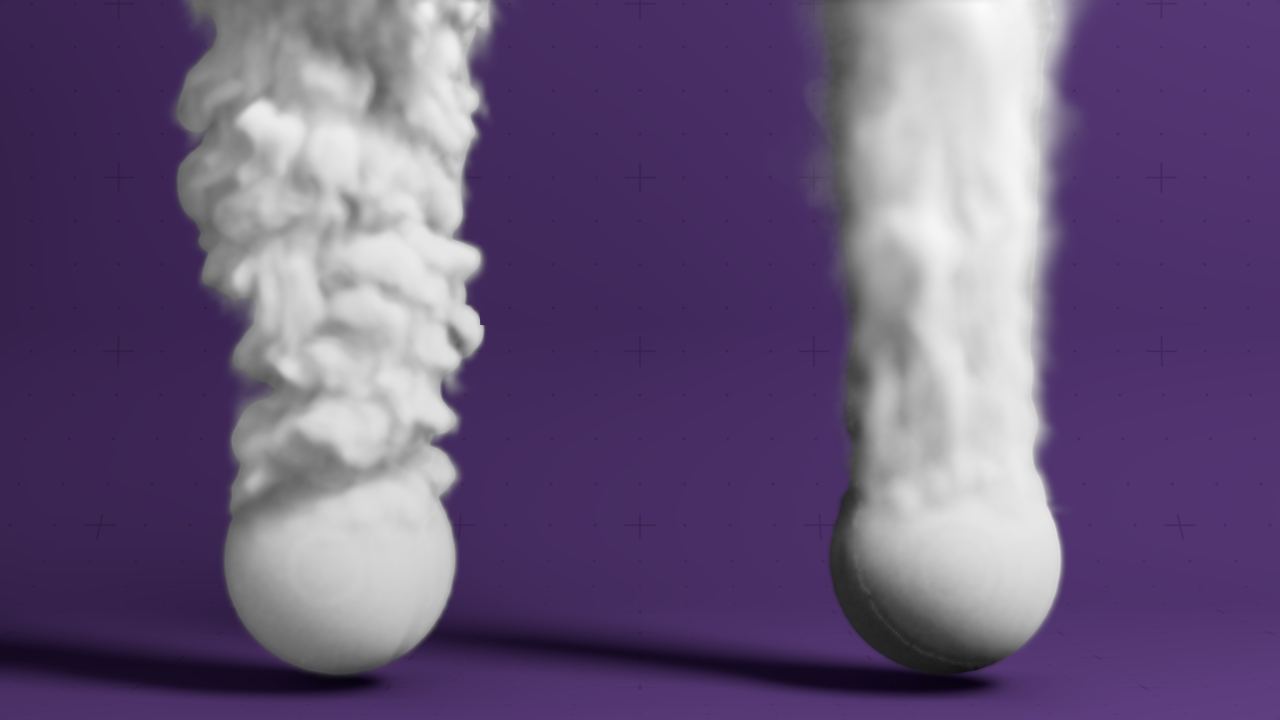 Field Feedback
Field Feedback
Blends the ink of a Field over time.
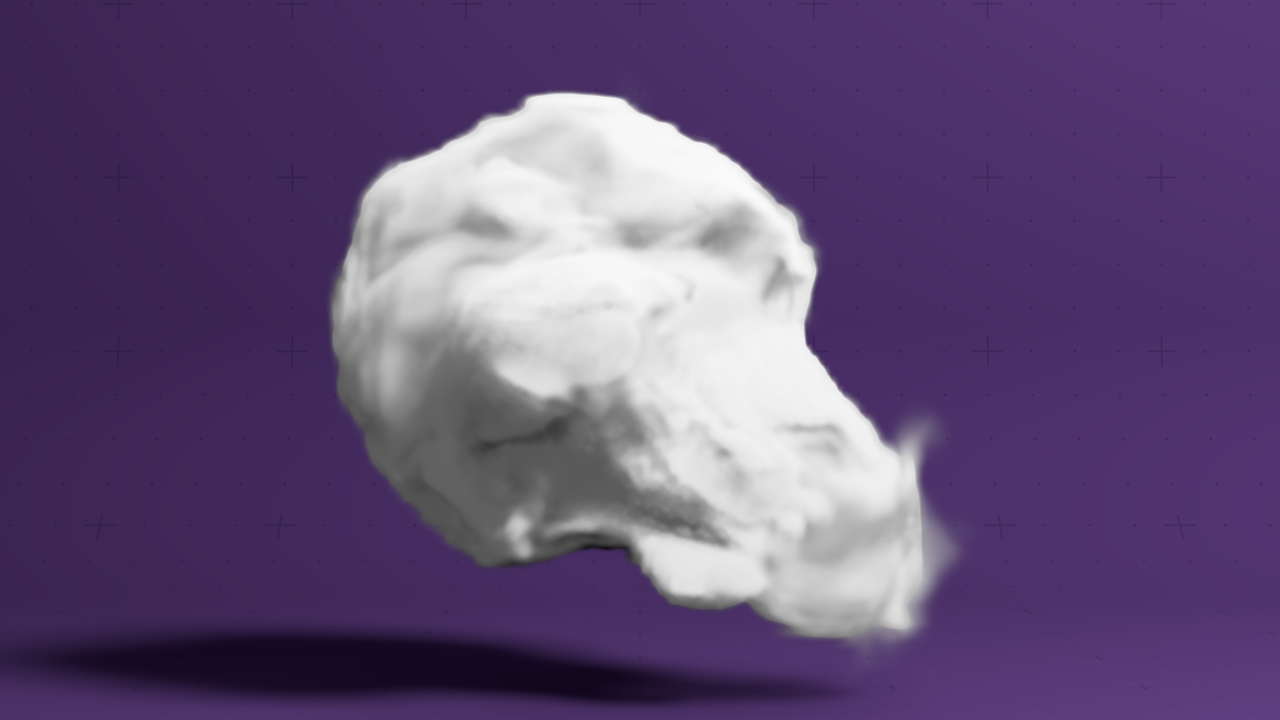 Field Procedural Affector
Field Procedural Affector
This node affects a field's velocities by attracting or repelling it using a procedural's surface.
 Fluid 2D Affector
Fluid 2D Affector
Applies a fluid simulation to a field.
 Image Affector
Image Affector
Uses an image to affect a field.
 Points Affector
Points Affector
Use points to disturb a field.
 Primitive Affector
Primitive Affector
Use basic primitives to affect the field.
 Turbulence Affector
Turbulence Affector
Applies turbulent velocities to a field.
 Velocity Affector
Velocity Affector
Applies a directional velocity to a field.
 Vortex Affector
Vortex Affector
Applies a rotational velocity to a field.
Add collision surfaces to a Field.
 Mesh Collision Affector
Mesh Collision Affector
Allows fields to collide with 3D Meshes.
 Primitive Collision Affector
Primitive Collision Affector
Allows fields to collide with primitive shapes.
 Procedural Collision Affector
Procedural Collision Affector
This node allows fields to collide with procedurals.
Emitter nodes spawn the colour/Ink that can be manipulated in a field system.
 Field - Field Emitter
Field - Field Emitter
Emits ink into a field from another input field.
 Image Emitter
Image Emitter
Emits ink into a field from an input image.
 Mesh Emitter
Mesh Emitter
Emits ink into a field based on an input Mesh.
 Particle 2D Emitter
Particle 2D Emitter
Emits ink into a field from particles.
 Particle 3D Emitter
Particle 3D Emitter
Emits ink into a field from particles
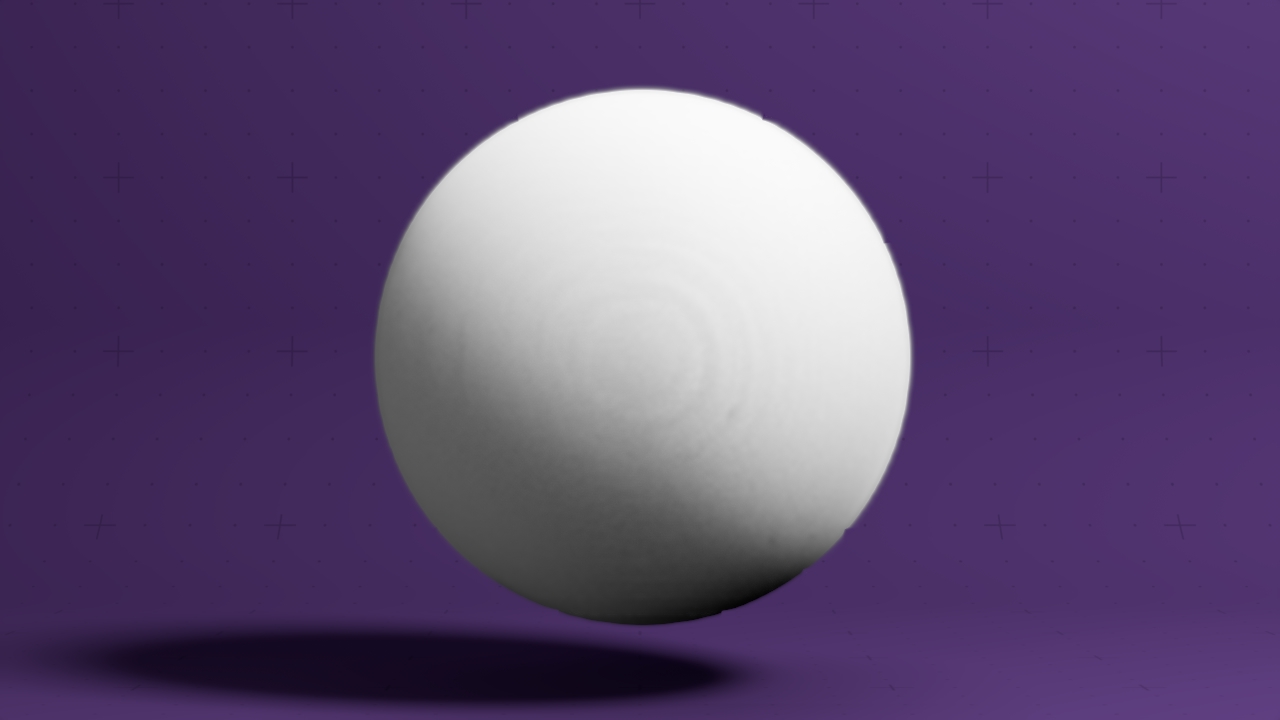 Primitive Emitter
Primitive Emitter
Emits ink into a field using a primitive shape.
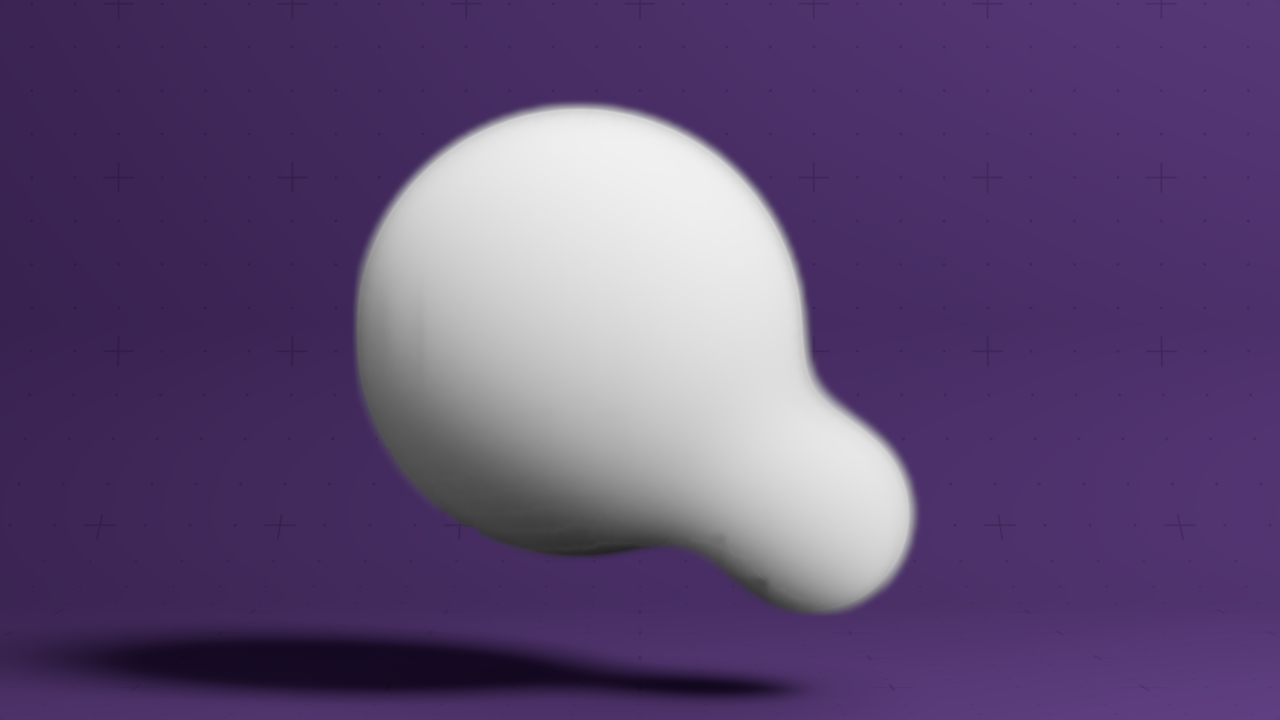 Procedural Emitter
Procedural Emitter
Emits ink into a field from procedurals.
 Reaction-Diffusion
Reaction-Diffusion
Generates a reaction-diffusion simulation for a field.
Materials for field systems.
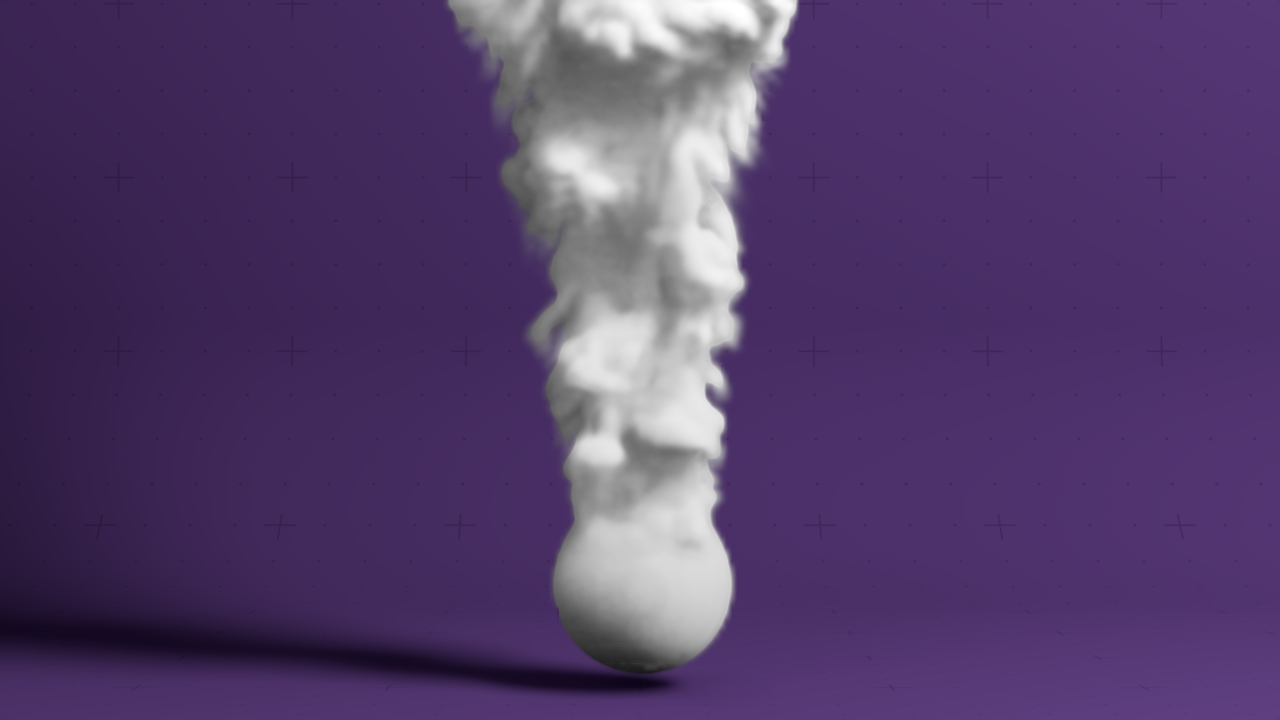 Field Cloud Material
Field Cloud Material
A 3D field material suitable for smoke and cloud volumes, which shades solely based on density.
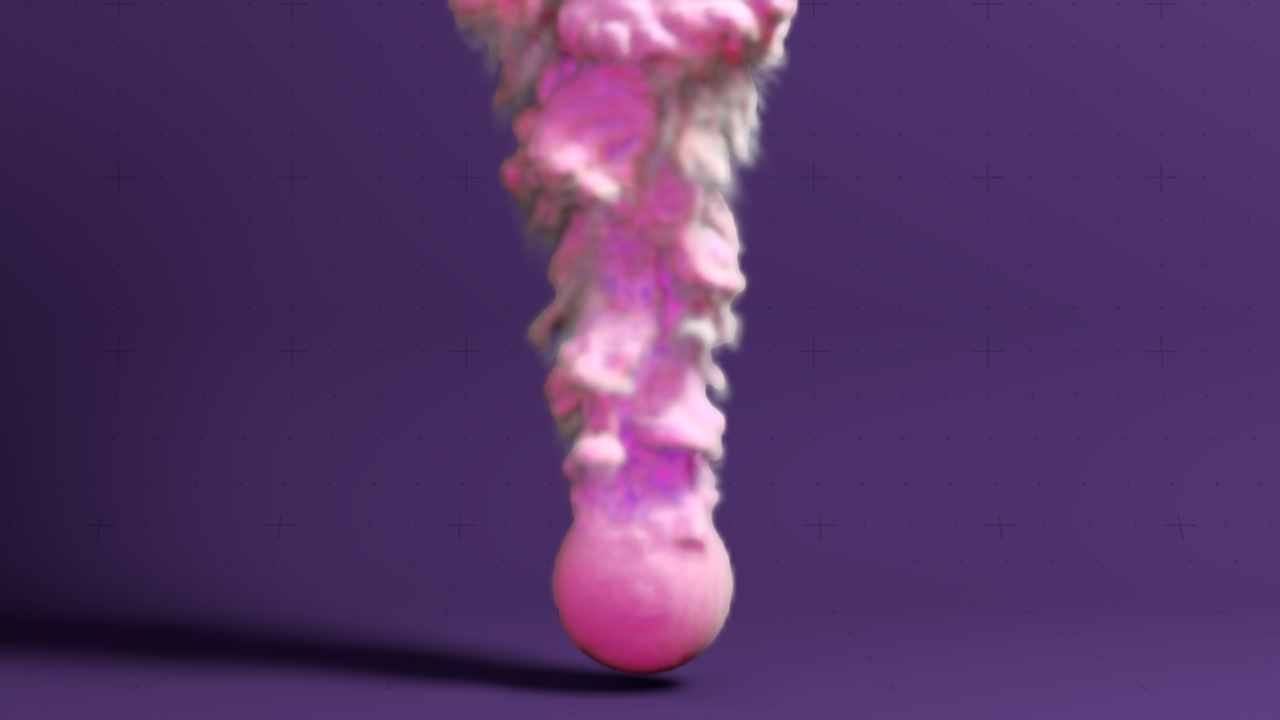 Field Colour Ramp Material
Field Colour Ramp Material
Uses a colour ramp to colour a field system based on density or temperature. The field will fade through the colours in the ramp as the density/temperature get higher or lower.
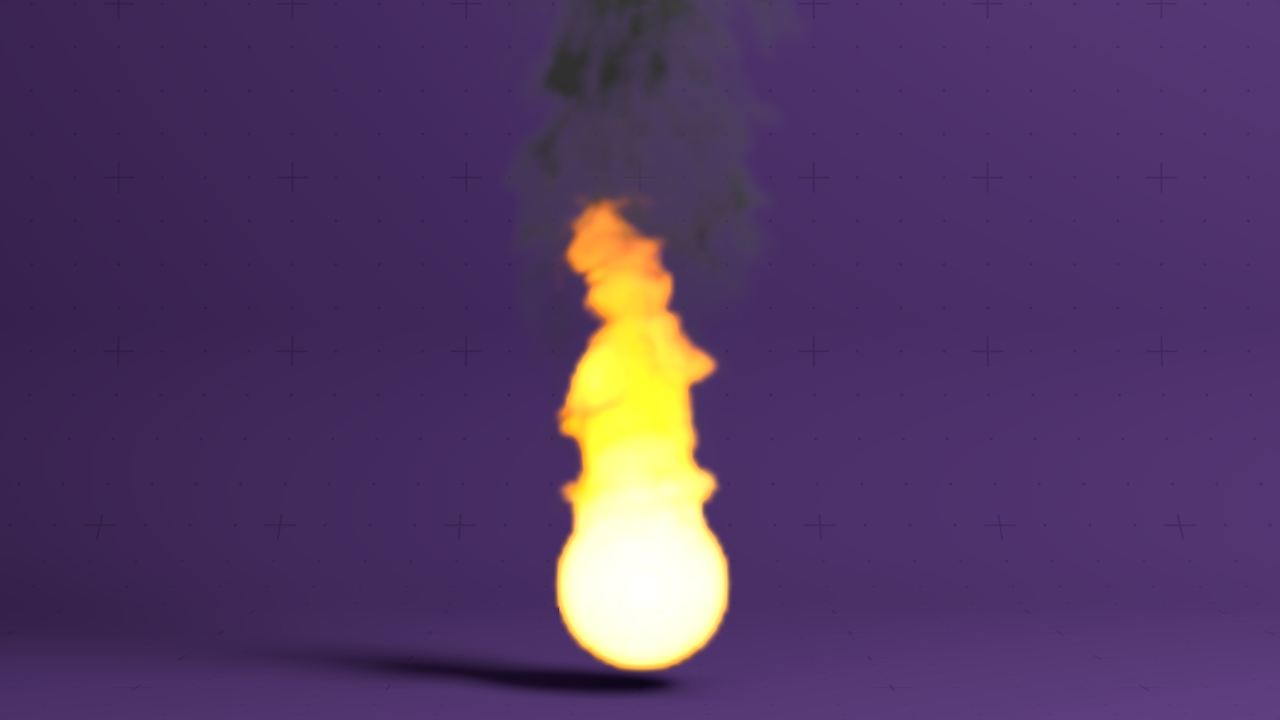 Field Flame Material
Field Flame Material
A 3D field material suitable for fire / flames.
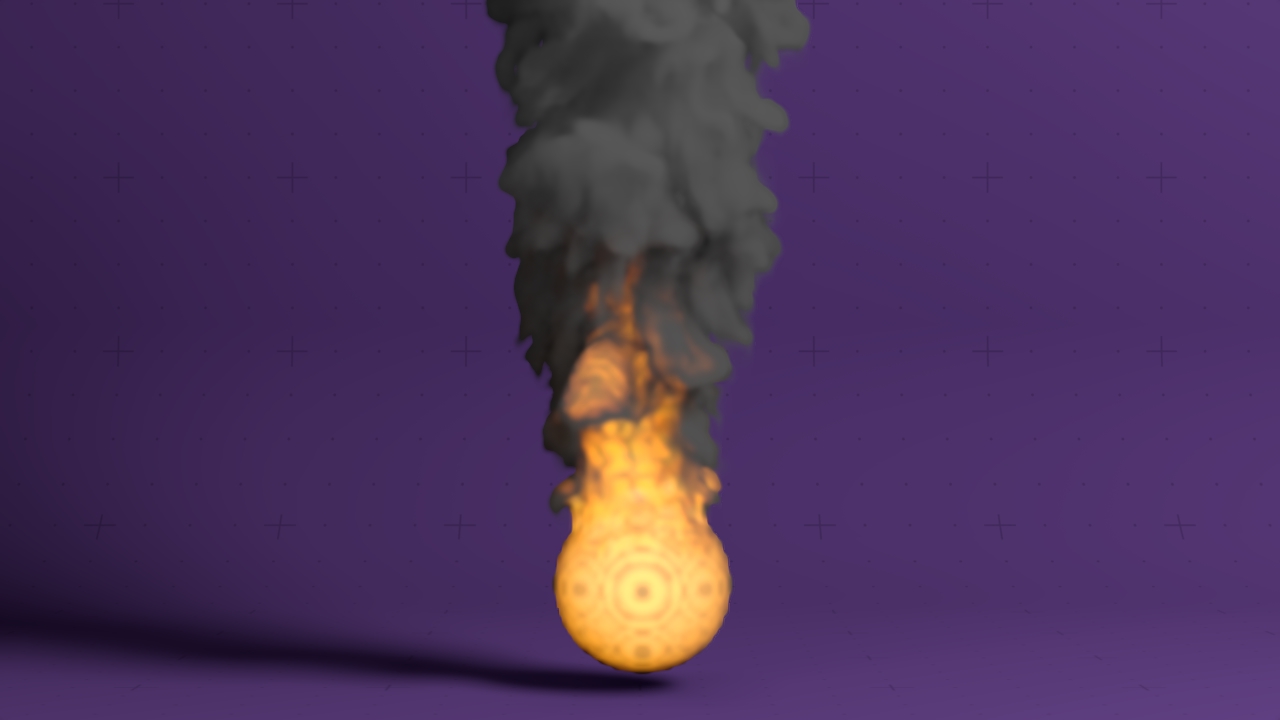 Field Pyro Material
Field Pyro Material
A 3D field material suitable for pyro / explosions.
Rendering nodes visualise the field or control how it is rendered and shaded.
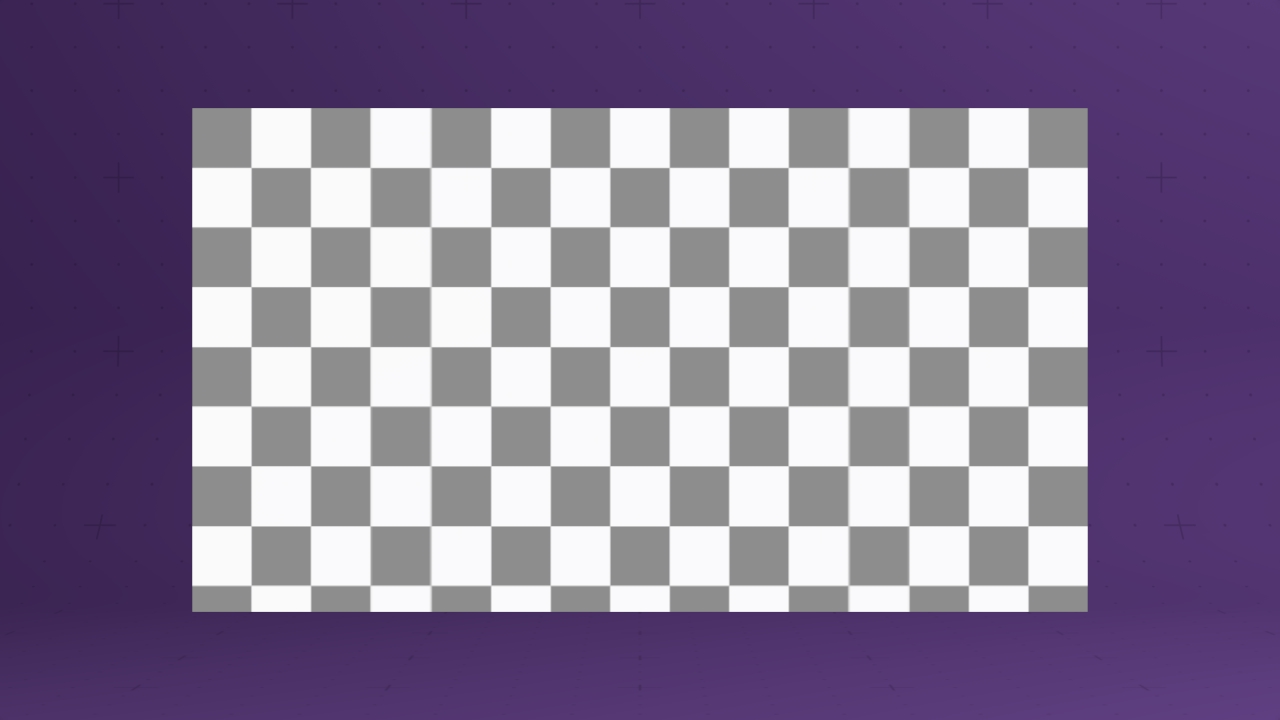 Field 2D Renderer
Field 2D Renderer
Renders a field system as a volume.
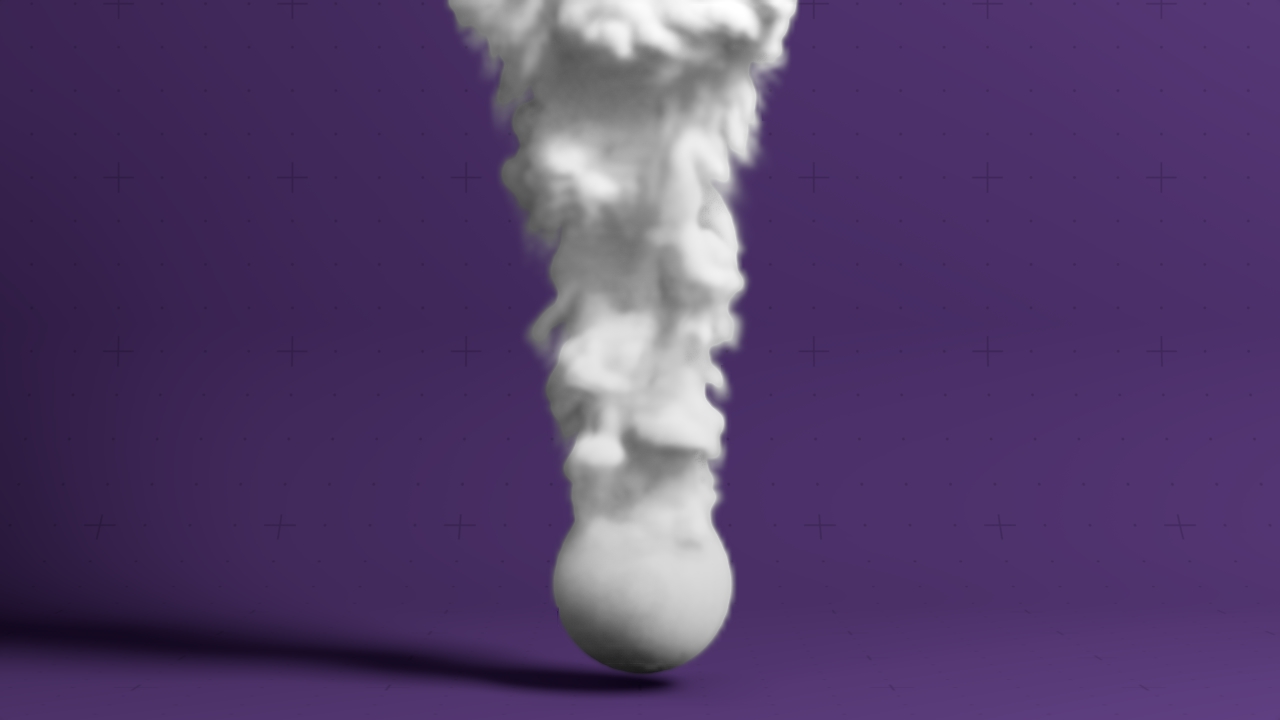 Field 3D Renderer
Field 3D Renderer
Renders a 3D field via path tracing.
 Render To Object Surface
Render To Object Surface
Apply the field to the surface of geometry.
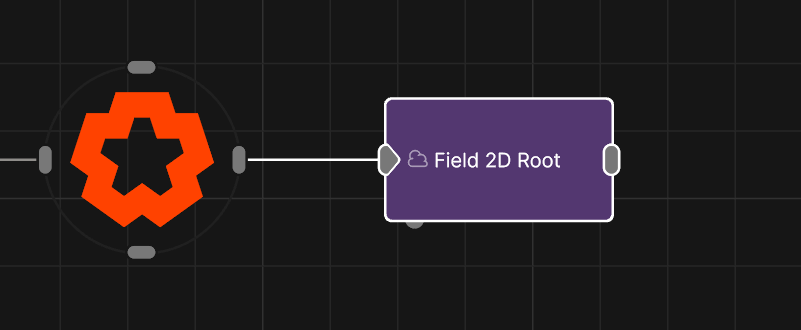 Field 2D Root
Field 2D Root
The root node for a 2D Field system
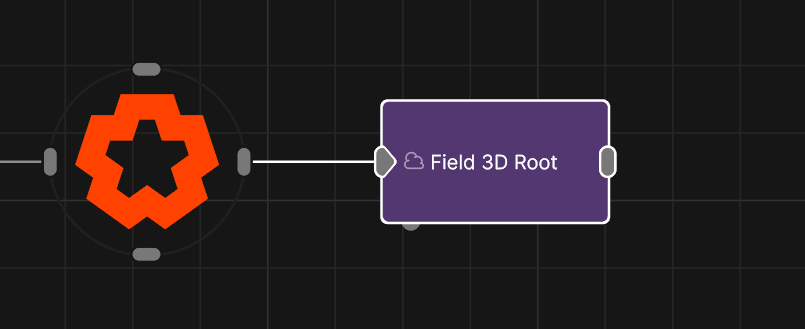 Field 3D Root
Field 3D Root
The root node for a 3D Field system
 Field Cache
Field Cache
Caches a Field system to disk for consistent results.
 Field Cache Renderer
Field Cache Renderer
Playback a cached field simulation.