Falloff
Updated: 28 Jan 2026
Controls the falloff of other nodes.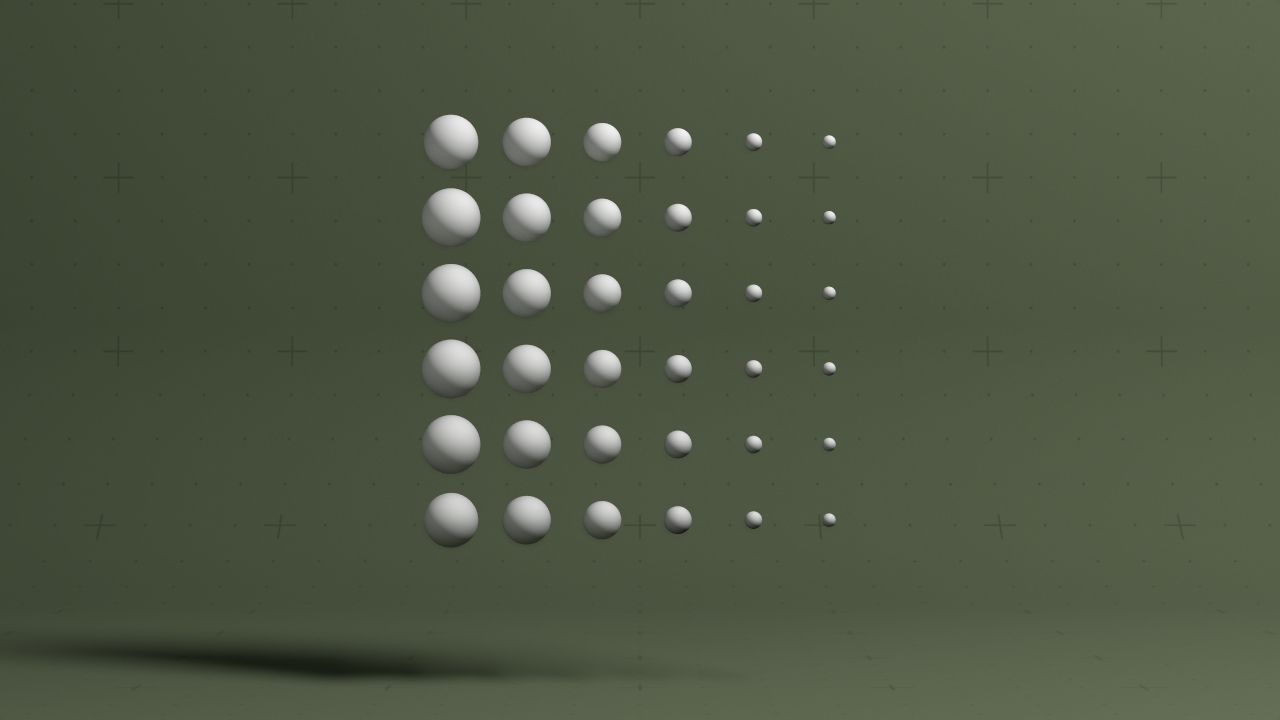
Updated: 28 Jan 2026
Controls the falloff of other nodes.

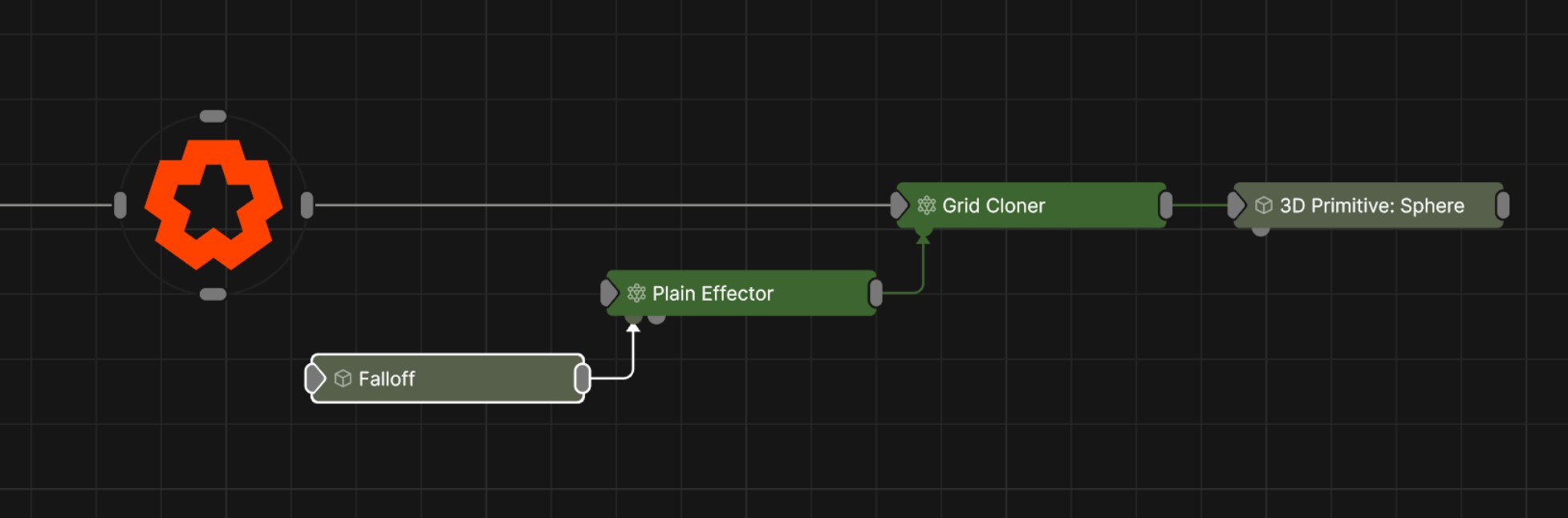
This node is used as a universal falloff node which can be connected to and control any other node with a falloff input, such as Deformers, Cloner Effectors, Fields Affectors and Physics Affectors. This allows you to control multiple node’s of different types falloff properties from a single point.
These properties control the 3D transforms of the node. Transforms will generally be inherited by child nodes, although they can be ignored through the Inherit Transform Channels attributes.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | The objects position along the local x-axis. |
| Position Y | The objects position along the local y-axis. |
| Position Z | The objects position along the local z-axis. |
| Rotation Heading | The objects rotation around the local y-axis. |
| Rotation Pitch | The objects rotation around the local x-axis. |
| Rotation Bank | The objects rotation around the local z-axis. |
| Scale X | The objects scale along the local x-axis. |
| Scale Y | The objects scale along the local y-axis. |
| Scale Z | The objects scale along the local z-axis. |
Control the inheritance of the transforms from the parent.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position | Toggle inheritance of the Position from the parent. |
| Rotation | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation from the parent. |
| Scale | Toggle inheritance of the Scale from the parent. |
| World Position Only | Inherit the world position from the parent only, rotation and scale will be ignored. Overrides above properties. |
| Inherit Time | Toggle inheritance of time from the parent. |
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Transform Modifier Apply Mode |
Select how this node applies its own transformation changes to other nodes when connected to their transformation modifiers input.
|
These properties used to set the falloff of other nodes.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Falloff Mode |
Which shape to use to calculate the falloff.
|
| Falloff Axis | Which axis the falloff should be oriented on. |
| Falloff Direction |
When using Planar mode, which directions to use to calculate the falloff.
|
| Falloff Easing Mode |
Interpolation method used to calculate the falloff within its range of influence.
|
| Falloff Size X | Size of the falloff range along the X axis. |
| Falloff Size Y | Size of the falloff range along the Y axis. |
| Falloff Size Z | Size of the falloff range along the Z axis. |
| Outer Range | Outer range of the falloff, outside of which the falloff is no longer effective. |
| Inner Range | Inner range of the falloff, inside of which the falloff is fully effective. |
| Curve Power | Controls the rate of change for the falloff between the inner and outer range. |
| Invert | Inverts the effect of the falloff. |
The properties control the time at which the node is active. See Timeline for editing time segments.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Duration |
Control the duration of the node’s time segment.
|
| Node Time | The custom start and end time for the node. |
| Duration (Timecode) | The length of the node’s time segment (in time). |
| Duration (Frames) | The length of the node’s time segment (in frames). |
| Time Segment Enabled | Set whether the node’s time segment is enabled or not in the Timeline. |
| Name | Description | Typical Input |
|---|---|---|
| Transform Modifiers | Apply the transforms of another node to this node. | Null |
| Target Node | Modifiy the rotations of the node to always direct the z axis towards the input. | Null |
| Local Transform Override | Apply the transforms of another node to this node, relative to its parent. | Null |