Procedural Raytracer
Updated: 30 Jan 2026
Renders a procedural system as a raytraced surface.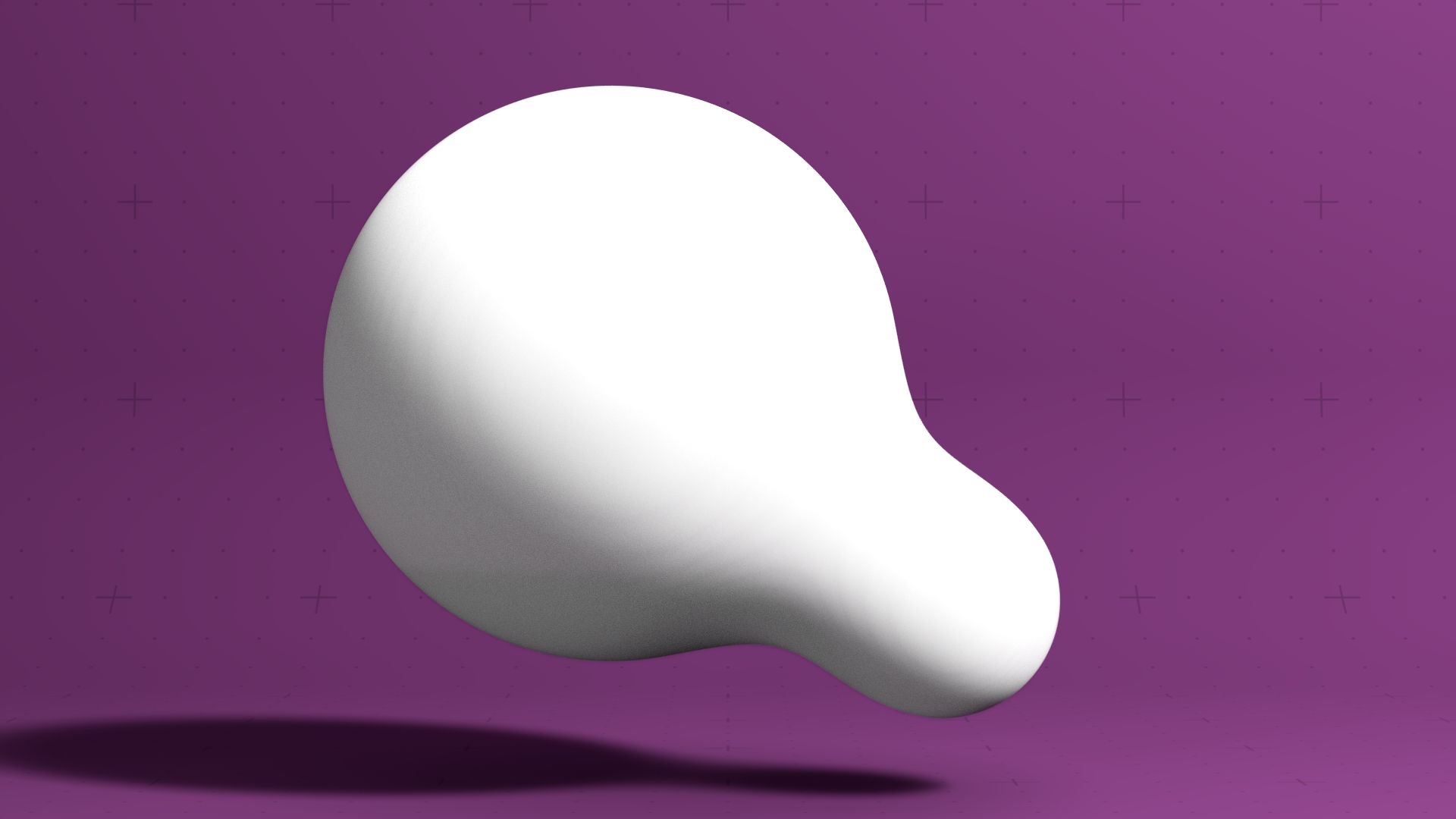
Updated: 30 Jan 2026
Renders a procedural system as a raytraced surface.

This node renders a procedural system as a raytraced surface using ray marching, allowing for significantly more detail and complexity to be rendered.
Ray Marching is a technique for rendering signed distance fields (SDFs) by drawing a ray from the camera and stepping through the SDF using the step size. If the distance to the closest surface (which easily calculable using an SDF) is lower than the step distance, then we know the surface has be hit and the system can be calculated. If the step size is too high, the ray can pass through surfaces it should hit, or hit surfaces it should miss. Lowering the step size can improve this, but can heavily impact perfomance. Complexity of the procedural system can also impact the surface detail, so simplifying the procedural where possible can also improve both accuracy and performance.
The Volumetric mode is a great way to generate clouds, and supports Field Materials.
These properties control the 3D transforms of the node. Transforms will generally be inherited by child nodes, although they can be ignored through the Inherit Transform Channels attributes.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | The objects position along the local x-axis. |
| Position Y | The objects position along the local y-axis. |
| Position Z | The objects position along the local z-axis. |
| Rotation Heading | The objects rotation around the local y-axis. |
| Rotation Pitch | The objects rotation around the local x-axis. |
| Rotation Bank | The objects rotation around the local z-axis. |
| Scale X | The objects scale along the local x-axis. |
| Scale Y | The objects scale along the local y-axis. |
| Scale Z | The objects scale along the local z-axis. |
Control the inheritance of the transforms from the parent.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position | Toggle inheritance of the Position from the parent. |
| Rotation | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation from the parent. |
| Scale | Toggle inheritance of the Scale from the parent. |
| World Position Only | Inherit the world position from the parent only, rotation and scale will be ignored. Overrides above properties. |
| Inherit Time | Toggle inheritance of time from the parent. |
These properties control the core behaviours of the node.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Render Mode |
Control how the procedural is rendered after being traced.
|
| Step Size | How far the raytracer steps each iteration while finding the surface of the procedural. |
| Bounds Size | Sets an outer bound for the volumetrics. Lower values can improve performance and limit the expansion of the procedural, while higher values may lose quality and impact performance - but allows for massive procedural systems to be rendered. |
| Visible | Control whether the node is visible or not to the scene. |
The properties control the time at which the node is active. See Timeline for editing time segments.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Duration |
Control the duration of the node’s time segment.
|
| Node Time | The custom start and end time for the node. |
| Duration (Timecode) | The length of the node’s time segment (in time). |
| Duration (Frames) | The length of the node’s time segment (in frames). |
| Time Segment Enabled | Set whether the node’s time segment is enabled or not in the Timeline. |
| Name | Description | Typical Input |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Override the default material with a material node. | Material |
| Affecting Lights | Lights that will be used in the raytracer. | Light |
| Excluded Lights | Lights that will be excluded from the raytracer. | Light |
| Colour Texture | Input Colour Texture Map | Video Loader |
| Diffuse Texture | Input Diffuse Texture Map | Video Loader |