Repeat
Updated: 30 Jan 2026
infinitely clone children in a Procedural system.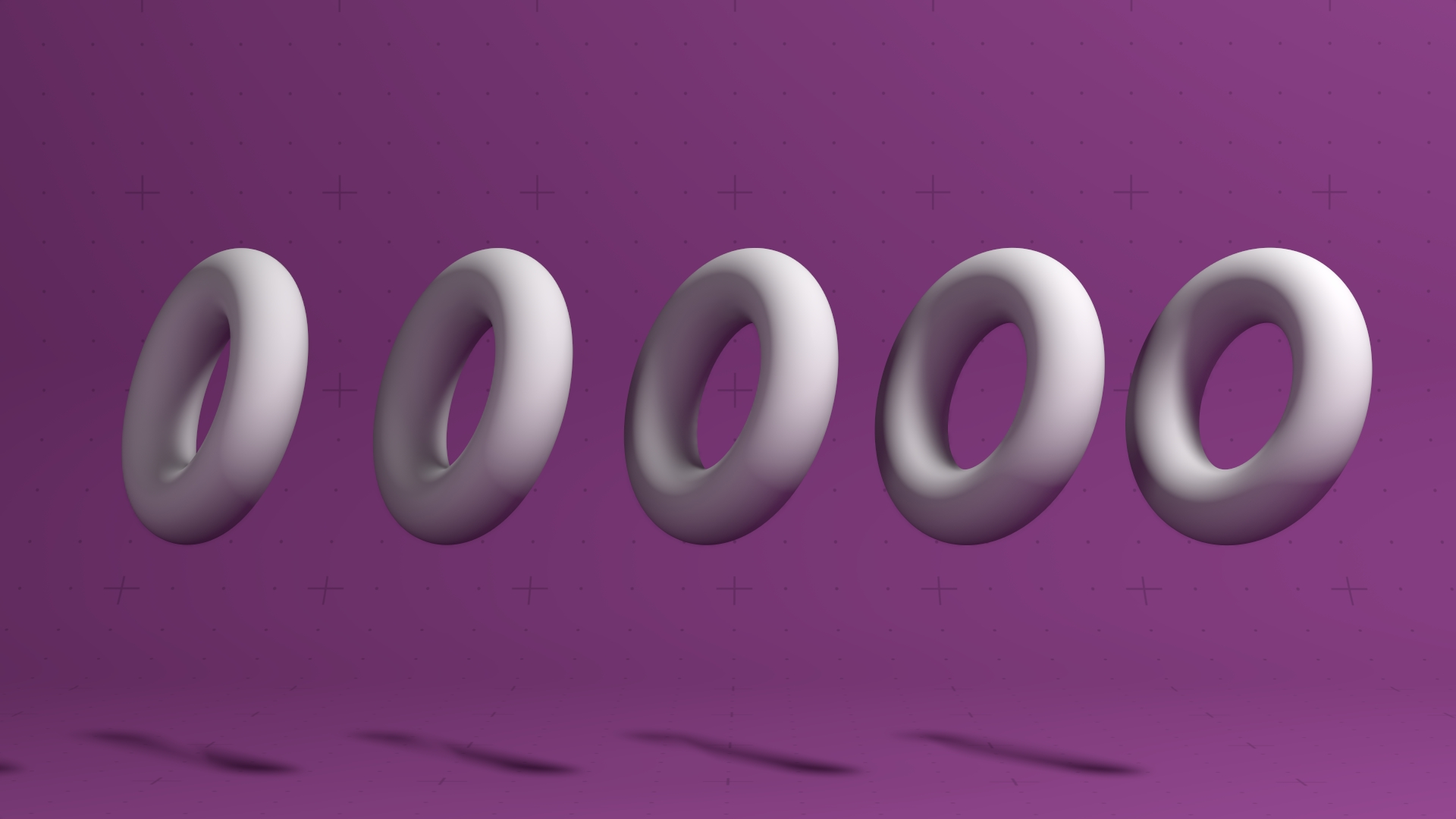
Updated: 30 Jan 2026
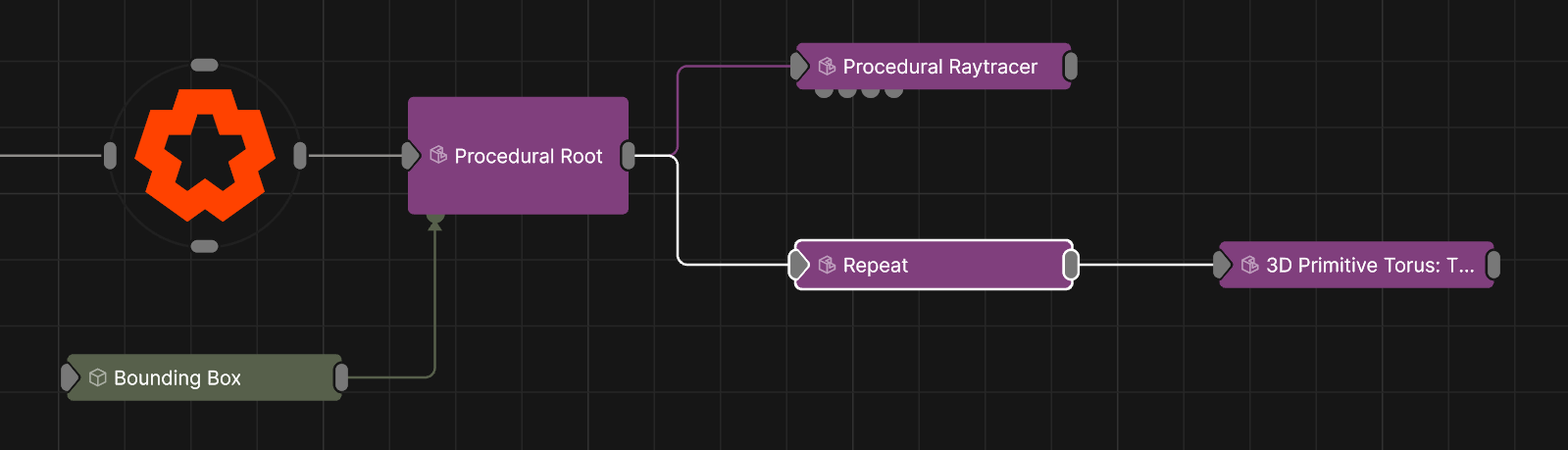
infinitely clone children in a Procedural system.

This node spatially replicates the children in a procedural system. This is a spatial operation, so the number of copies is potentially infinite, allowing for far more complex procedural effects.
Nodes that are to be cloned should be connected to the output of this node. Any Procedural node can be connected, although the render nodes cannot be cloned.
These properties control the 3D transforms of the node. Transforms will generally be inherited by child nodes, although they can be ignored through the Inherit Transform Channels attributes.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | The objects position along the local x-axis. |
| Position Y | The objects position along the local y-axis. |
| Position Z | The objects position along the local z-axis. |
| Rotation Heading | The objects rotation around the local y-axis. |
| Rotation Pitch | The objects rotation around the local x-axis. |
| Rotation Bank | The objects rotation around the local z-axis. |
| Scale X | The objects scale along the local x-axis. |
| Scale Y | The objects scale along the local y-axis. |
| Scale Z | The objects scale along the local z-axis. |
Control the inheritance of the transforms from the parent.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position | Toggle inheritance of the Position from the parent. |
| Rotation | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation from the parent. |
| Scale | Toggle inheritance of the Scale from the parent. |
| World Position Only | Inherit the world position from the parent only, rotation and scale will be ignored. Overrides above properties. |
| Inherit Time | Toggle inheritance of time from the parent. |
These properties control the core behaviours of the node.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| CSG Mode |
These options change how a this procedural node combines with the existing of the procedural system.
|
| CSG Blend Weight | How much the new procedural blends with the old procedurals, depending on the CSG Blend Weight. |
| Custom CSG Code | Type your Custom code here, using the HLSL language. Read more on Editable Code. |
| Repeat Mode | Selects the axis along which to repeat the procedural. |
| Repeat Positive Direction Only | Only repeat clones in the positive axes. |
| Limit Repeat Count | Uses the repeat count x/y/z to limit the child generators. |
| Repeat Spacing X | The distance each of the clones is spaced out along the X axis. |
| Repeat Spacing Y | The distance each of the clones is spaced out along the Y axis. |
| Repeat Spacing Z | The distance each of the clones is spaced out along the Z axis. |
| Repeat Count X | The number of clones repeated along the X axis. |
| Repeat Count Y | The number of clones repeated along the Y axis. |
| Repeat Count Z | The number of clones repeated along the Z axis. |
The properties control the time at which the node is active. See Timeline for editing time segments.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Duration |
Control the duration of the node’s time segment.
|
| Node Time | The custom start and end time for the node. |
| Duration (Timecode) | The length of the node’s time segment (in time). |
| Duration (Frames) | The length of the node’s time segment (in frames). |
| Time Segment Enabled | Set whether the node’s time segment is enabled or not in the Timeline. |
| Name | Description | Typical Input |
|---|---|---|
| Transform Modifiers | Apply the transforms of another node to this node. | Null |
| Target Node | Modifiy the rotations of the node to always direct the z axis towards the input. | Null |
| Local Transform Override | Apply the transforms of another node to this node, relative to its parent. | Null |