Warping
Updated: 4 Dec 2023
Updated: 4 Dec 2023
These nodes take an image and stretch or squash them in different ways.
Warping nodes can be applied directly to all the same nodes as the rest of the post-fx nodes.
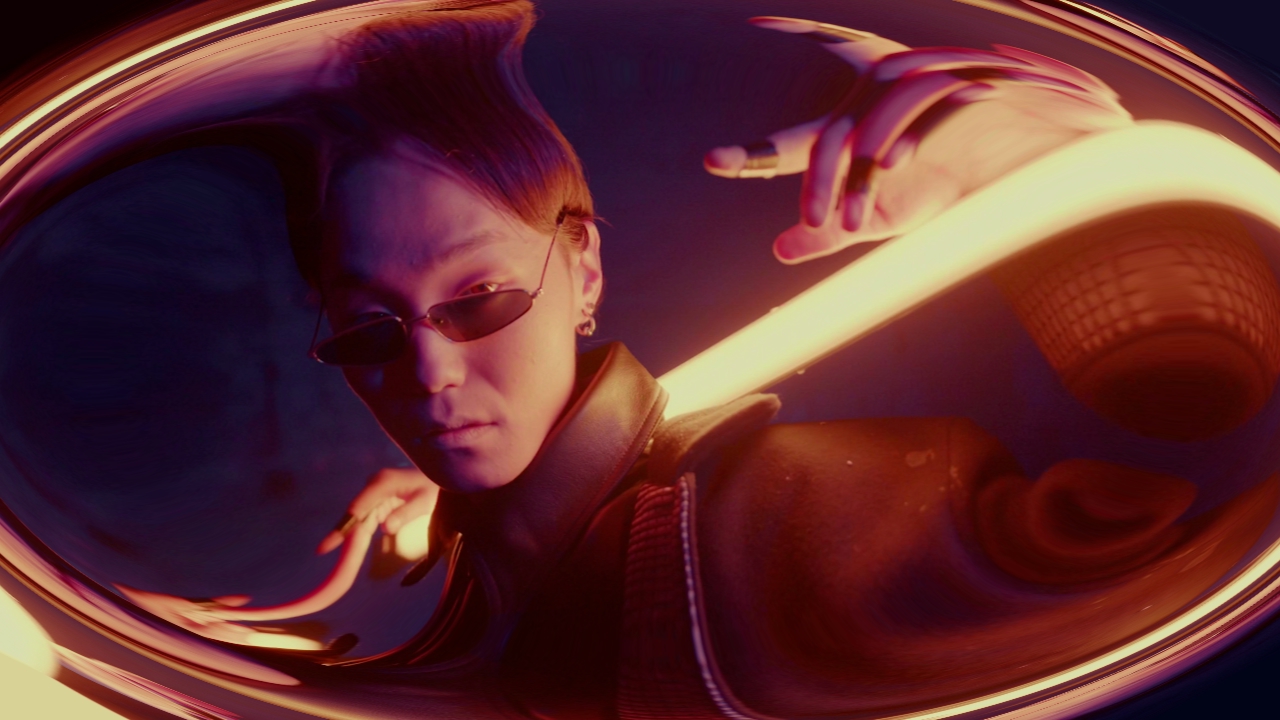 Barrel Distortion
Barrel Distortion
Simulate distortion of real-world camera lenses in an image.
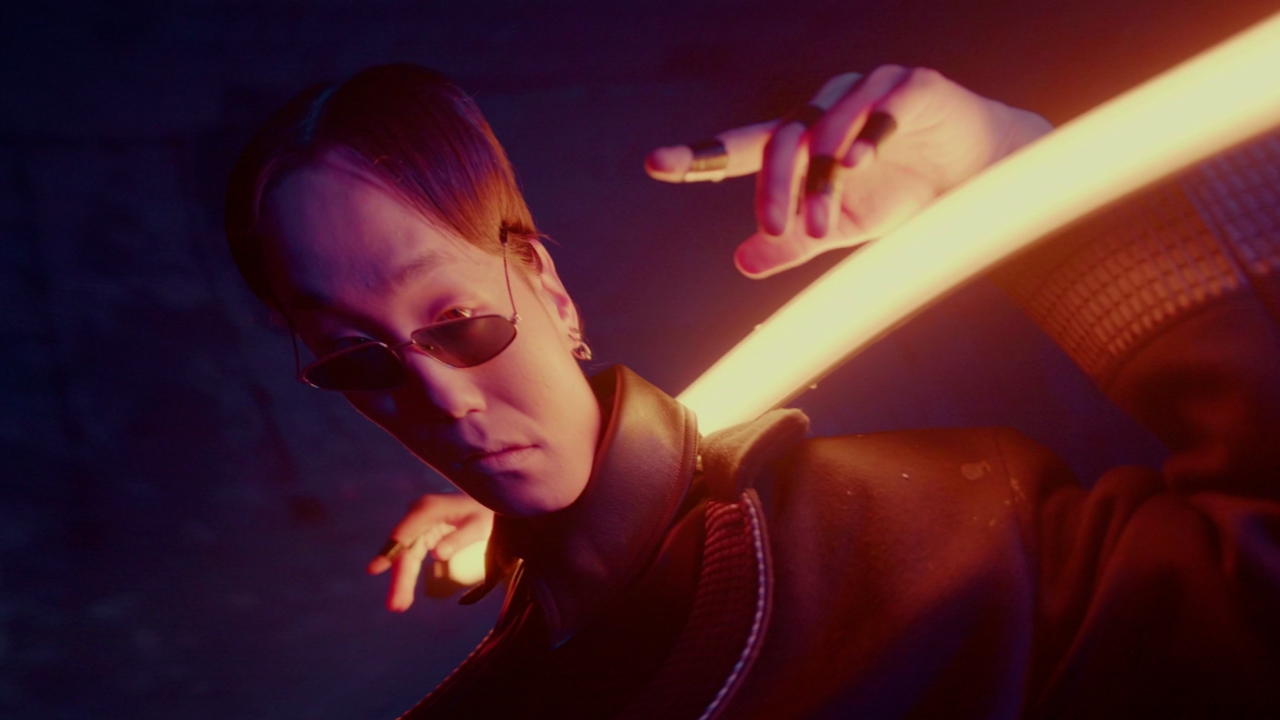 Bezier Warp
Bezier Warp
Warps using a bezier control grid and 8 control points.
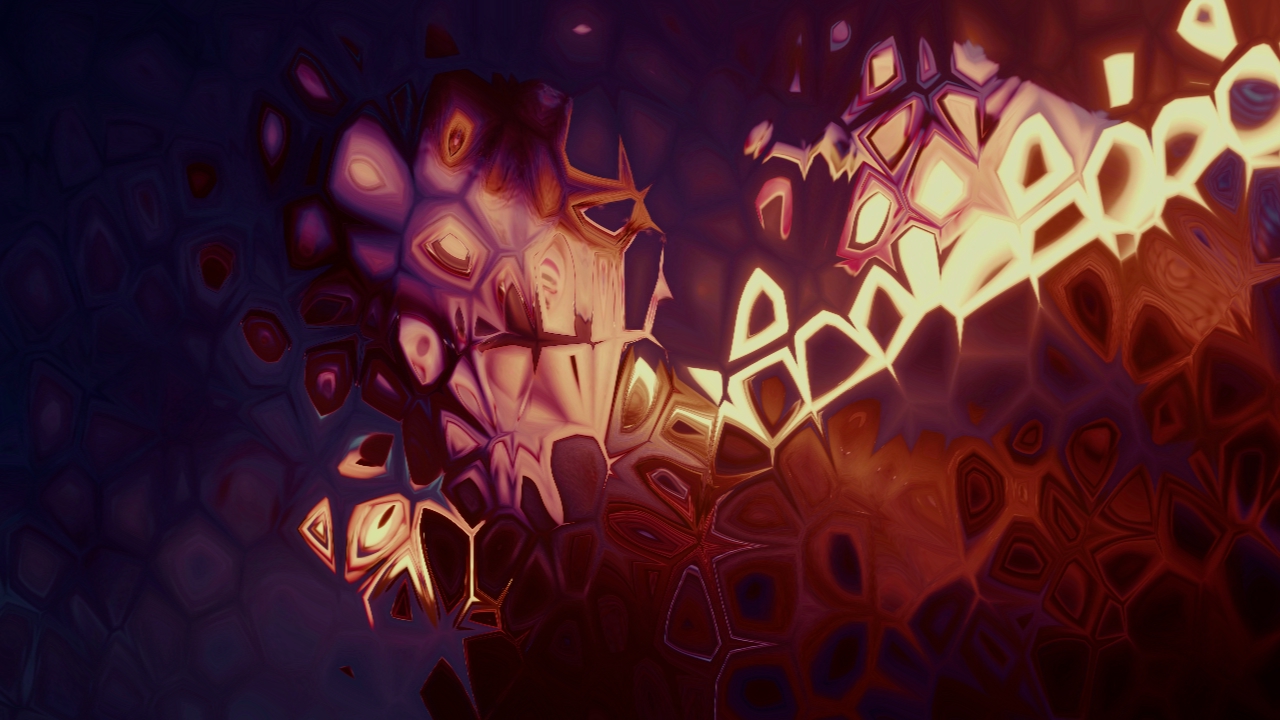 Bump Map Warp
Bump Map Warp
Warps an image based off of a bump map.
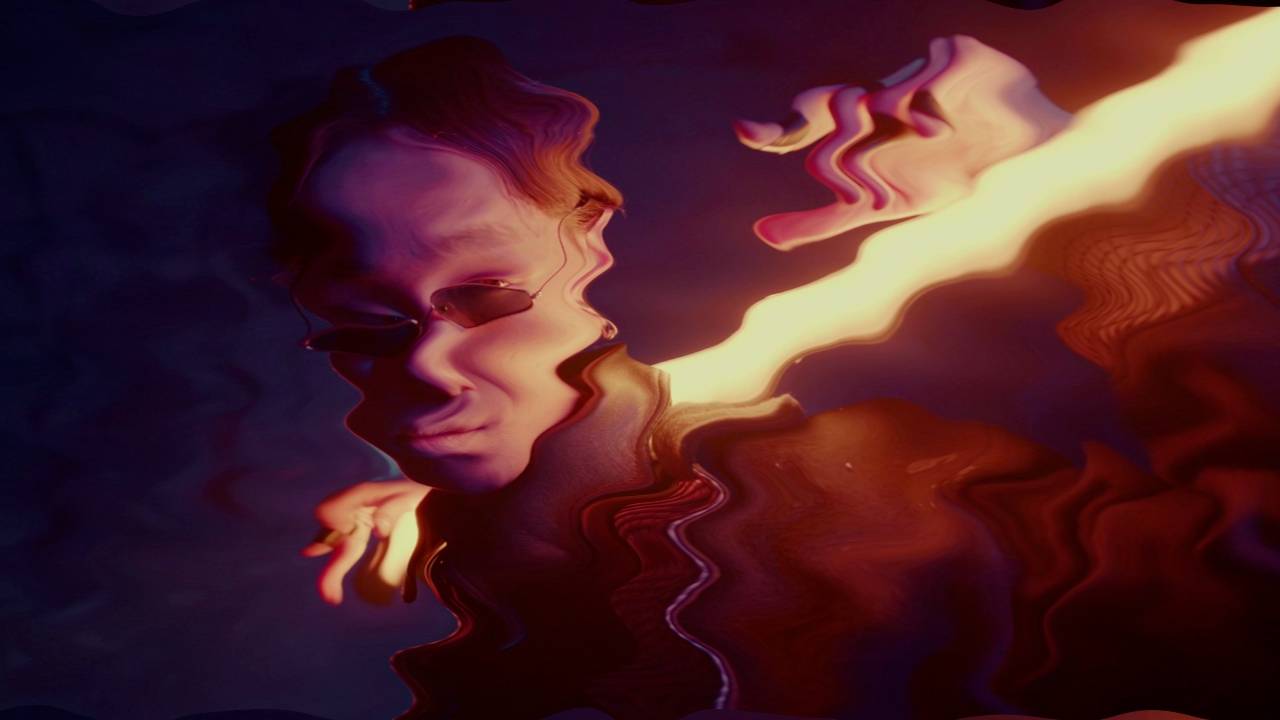 Curl Noise Warp
Curl Noise Warp
Warps using a curl noise function.
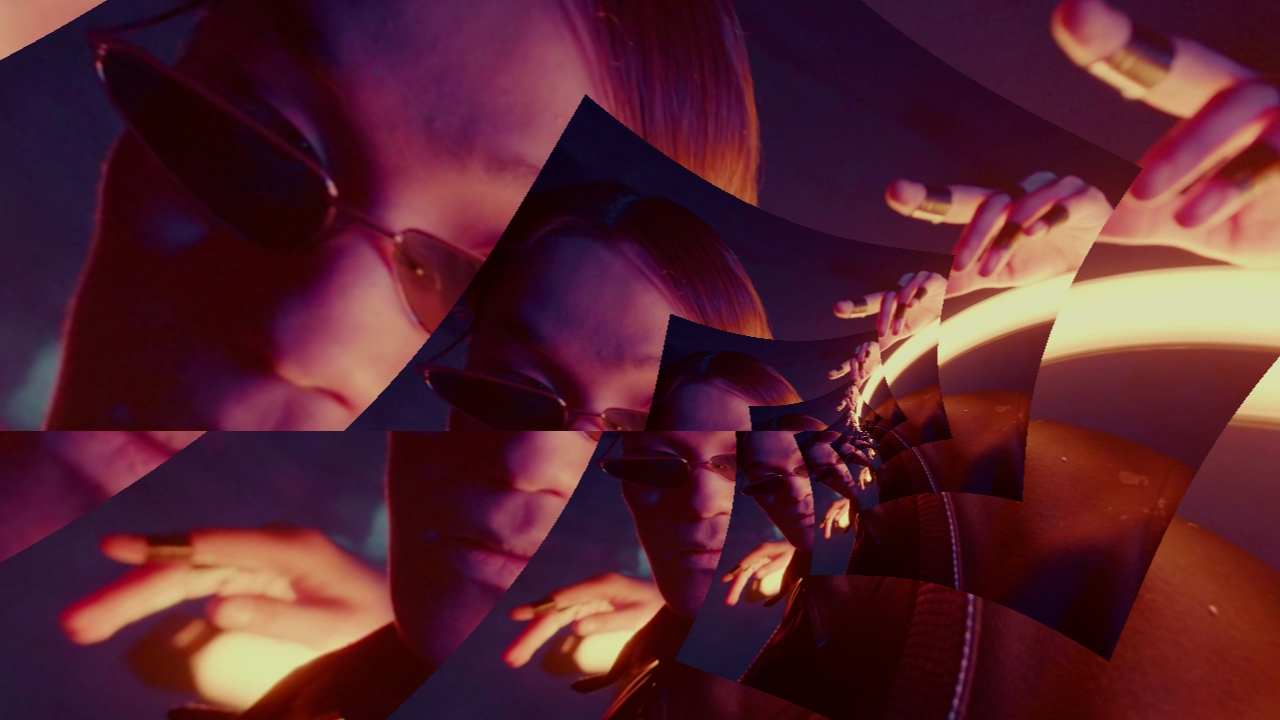 Droste Warp
Droste Warp
Applies a Droste function, creating an infinitely warping warp.
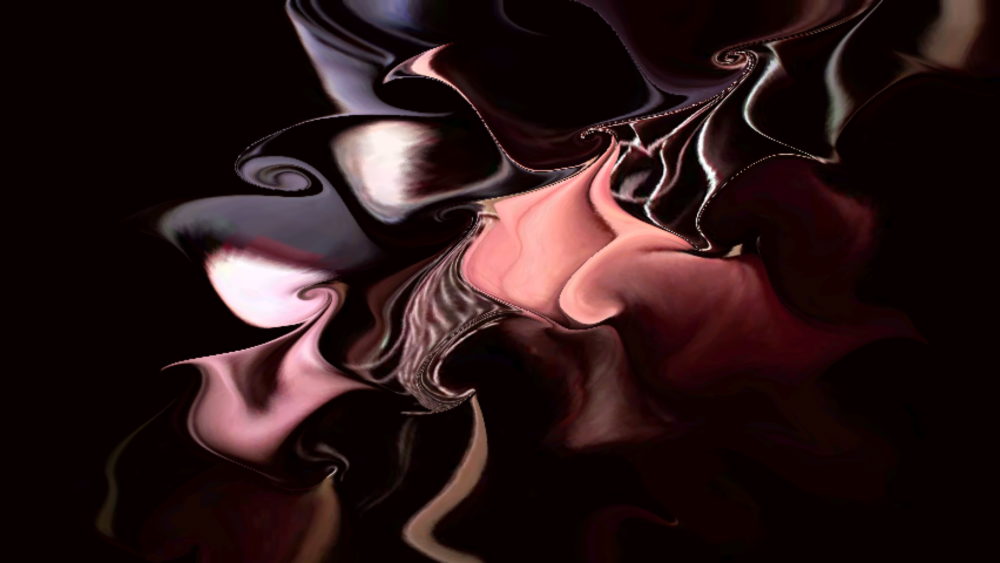 Field Position-Based Warp
Field Position-Based Warp
Warps an image based on the movement vectors of an input field.
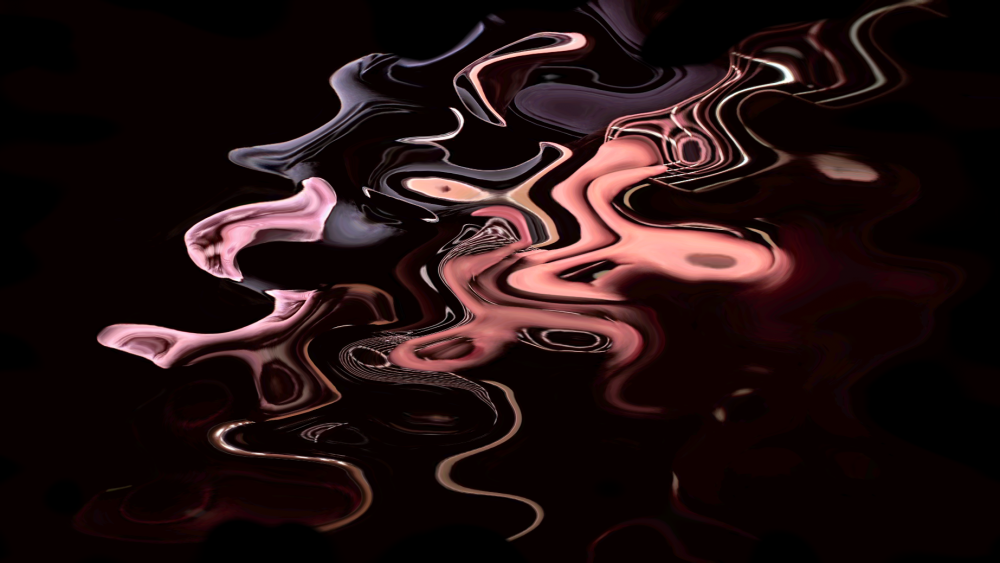 Field Warp
Field Warp
Warps an image based off of a field system.
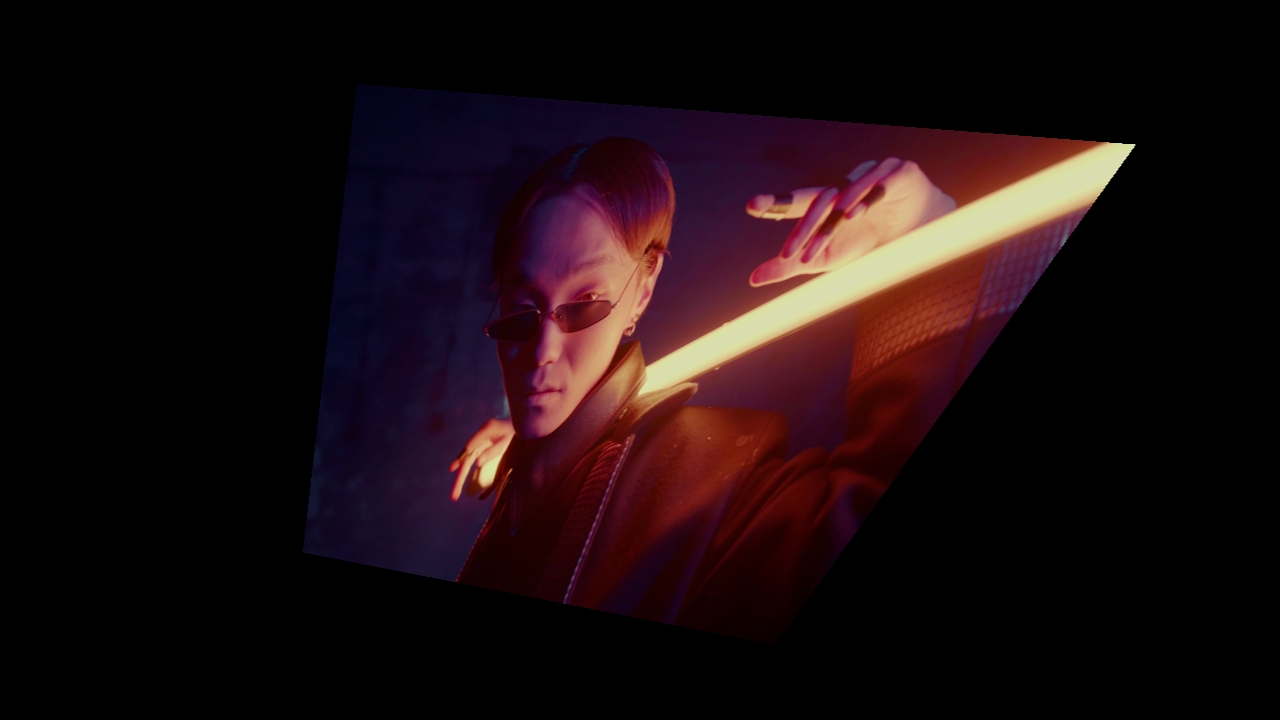 Four Point Warp
Four Point Warp
Warps from 4 cornered sections of the image.
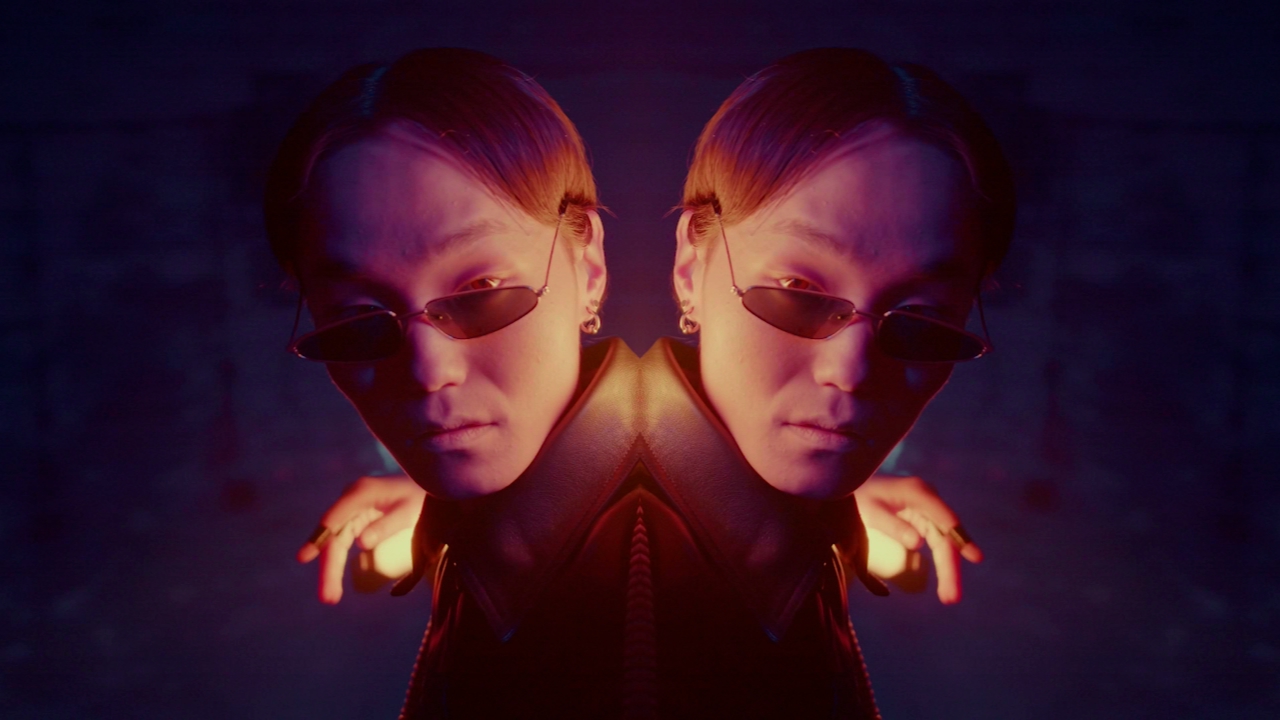 Mirror
Mirror
Mirrors one side of the image onto the other side.
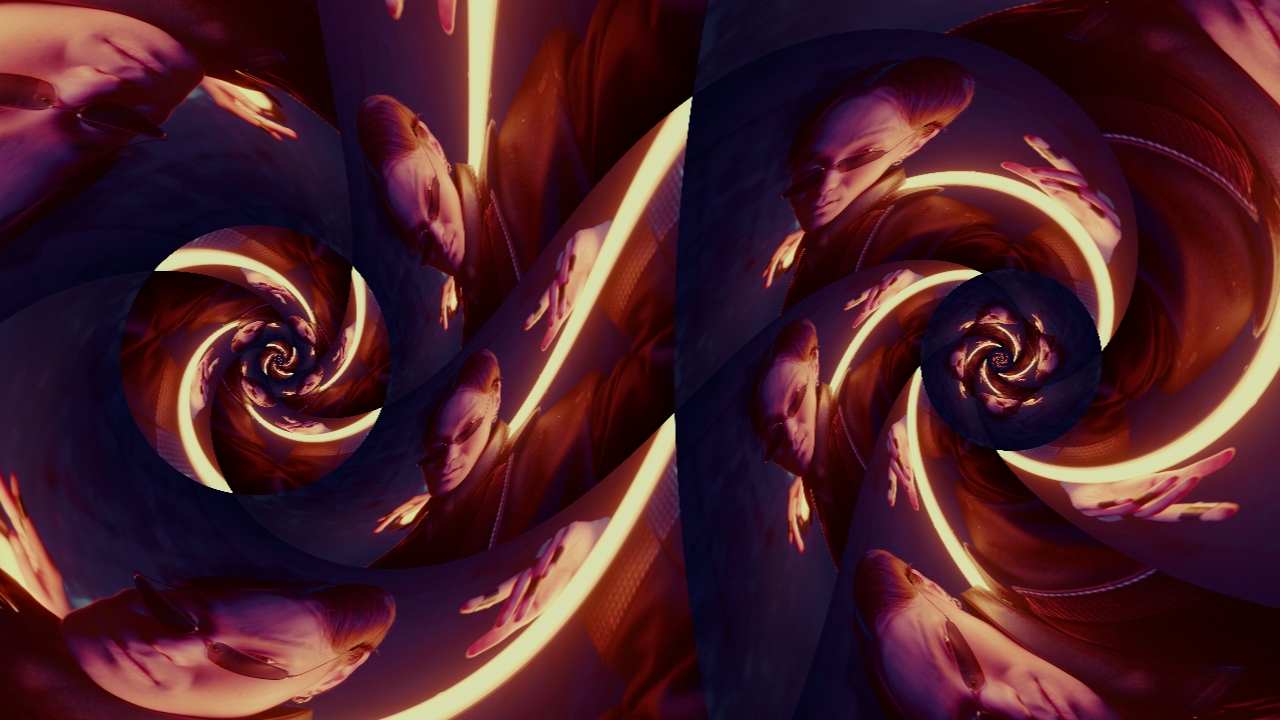 Moebius Warp
Moebius Warp
Applies a Moebius function, creating an infinitely warping warp.
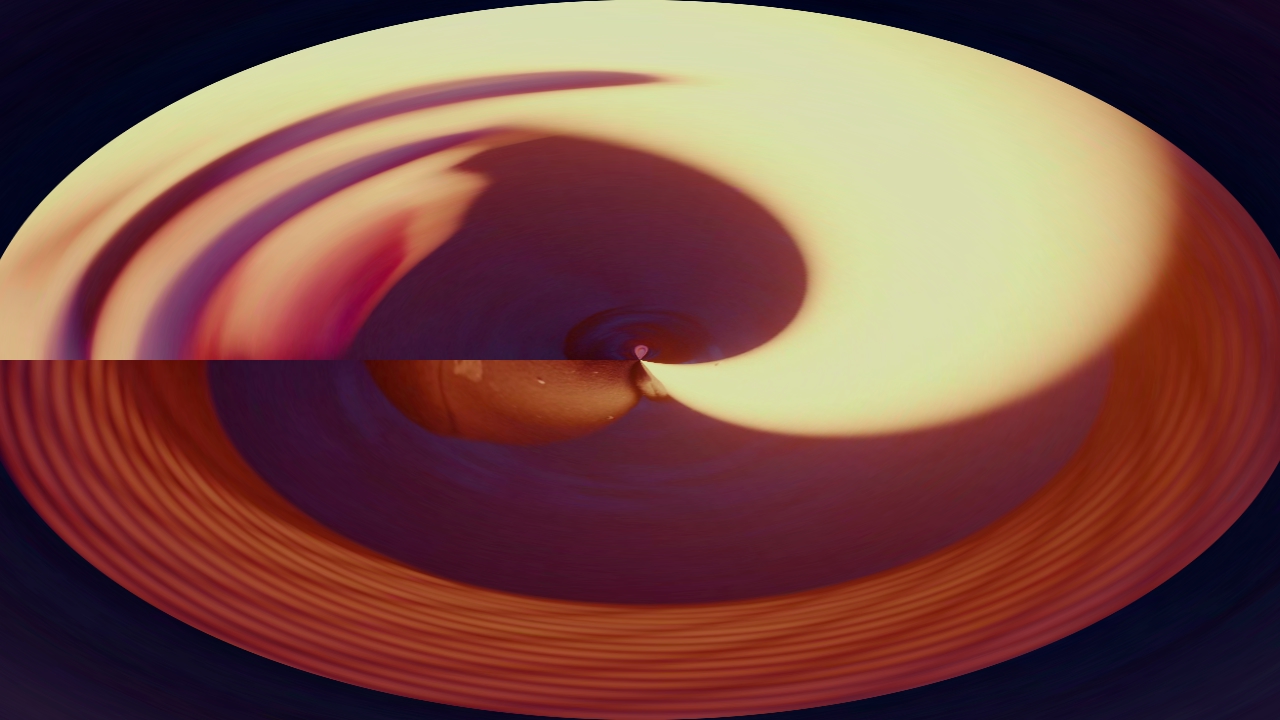 Polar Warp
Polar Warp
Warp the image using polar coordinates.
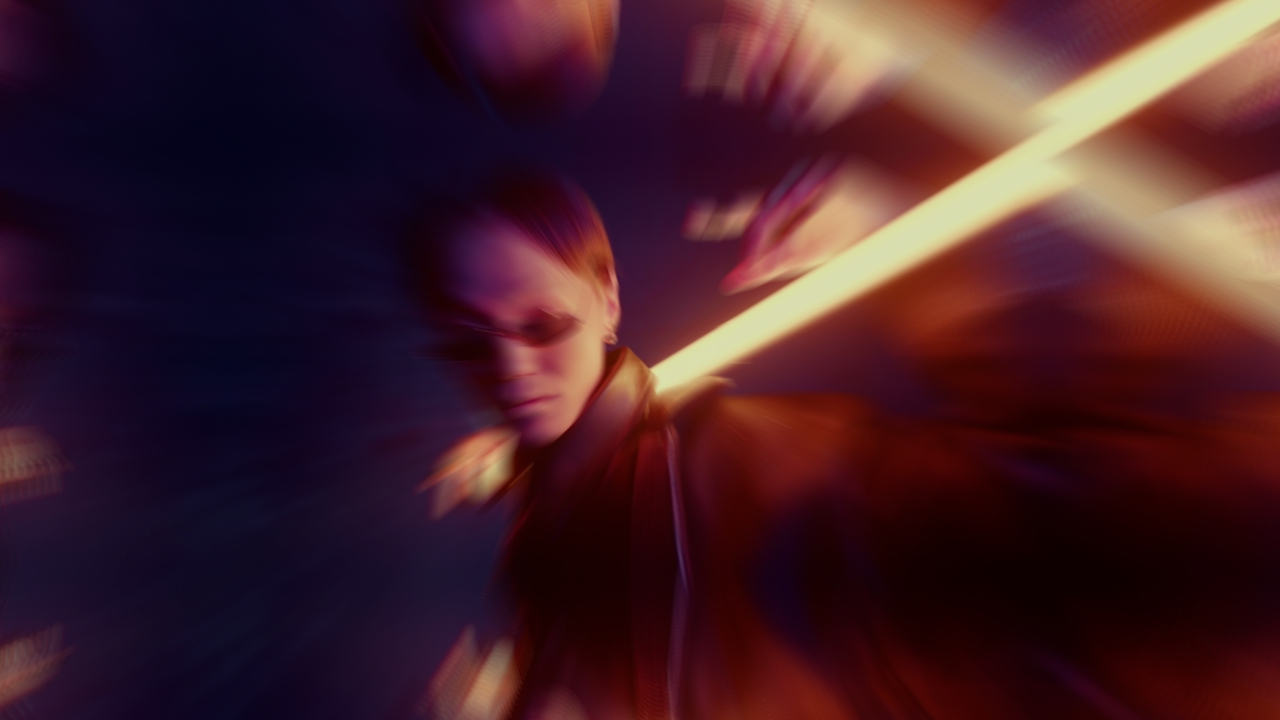 Radial Warp
Radial Warp
This node warps the screen radially around the center point.
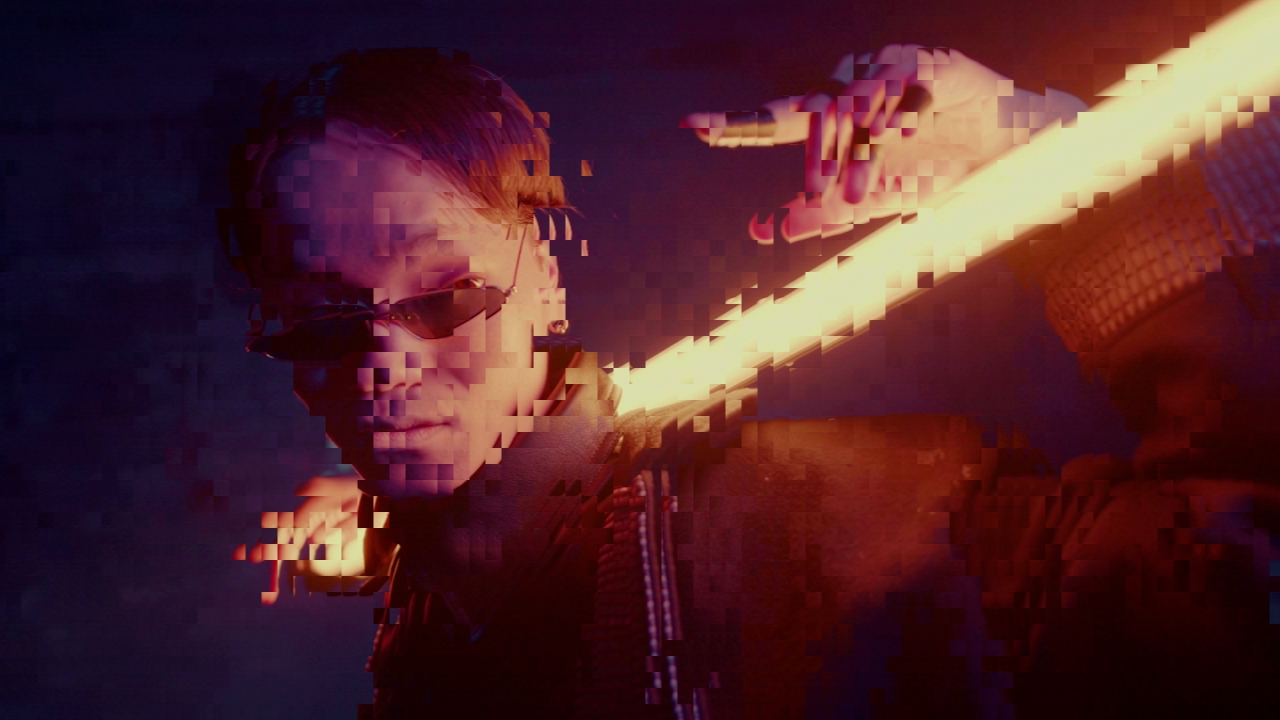 Randomise Tiles
Randomise Tiles
Randomise parts of the image based on an input image.
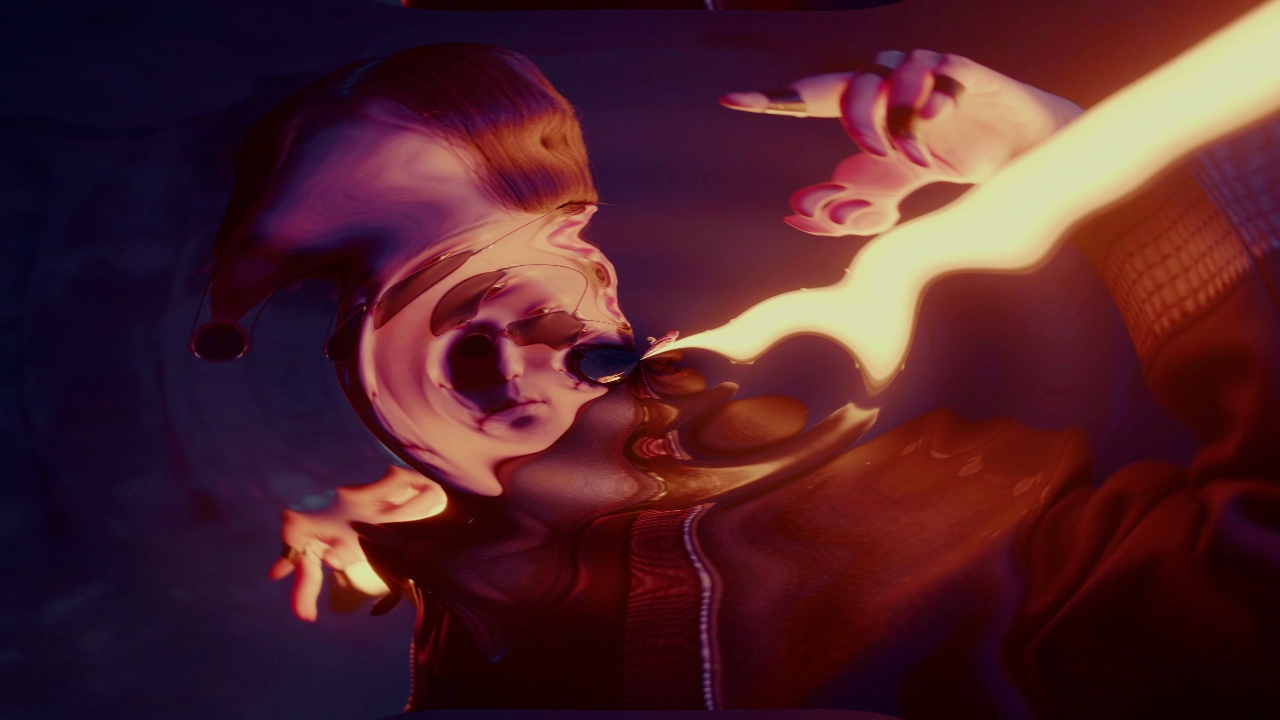 Ripple
Ripple
Warps an image a ripple emanating from the center of the screen.
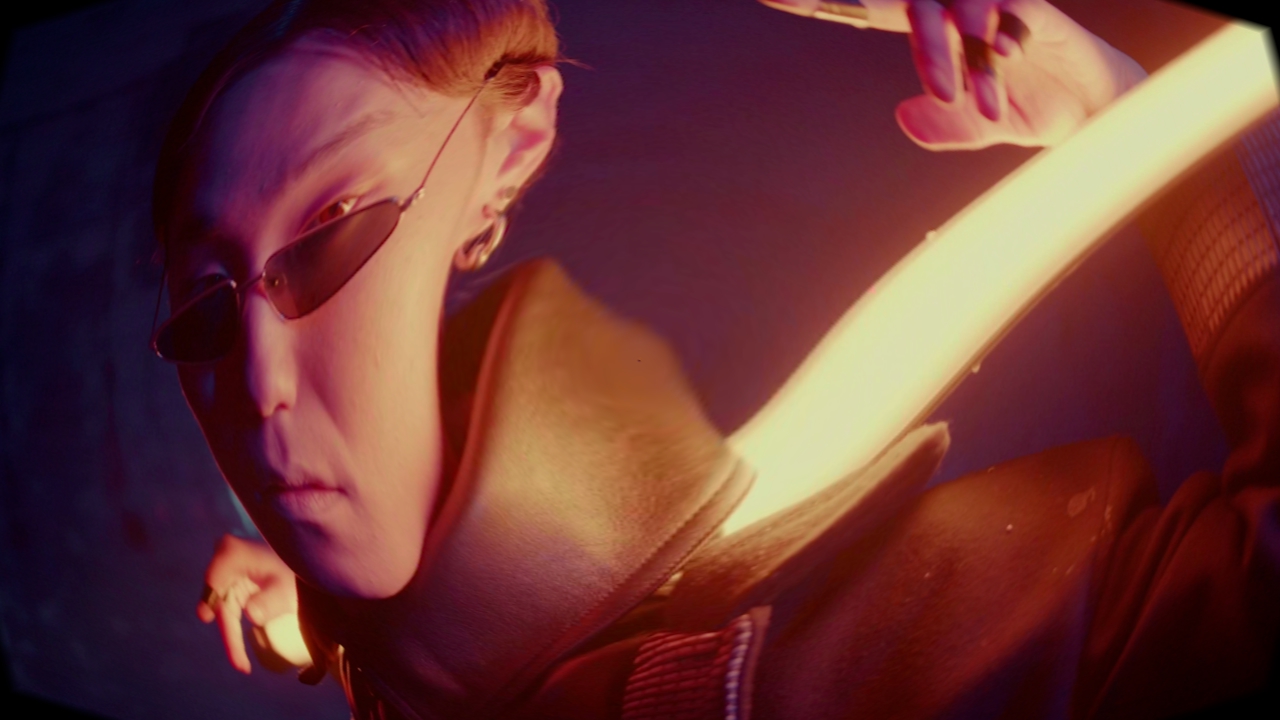 Screen Warp
Screen Warp
Adds a bulge effect to the image.
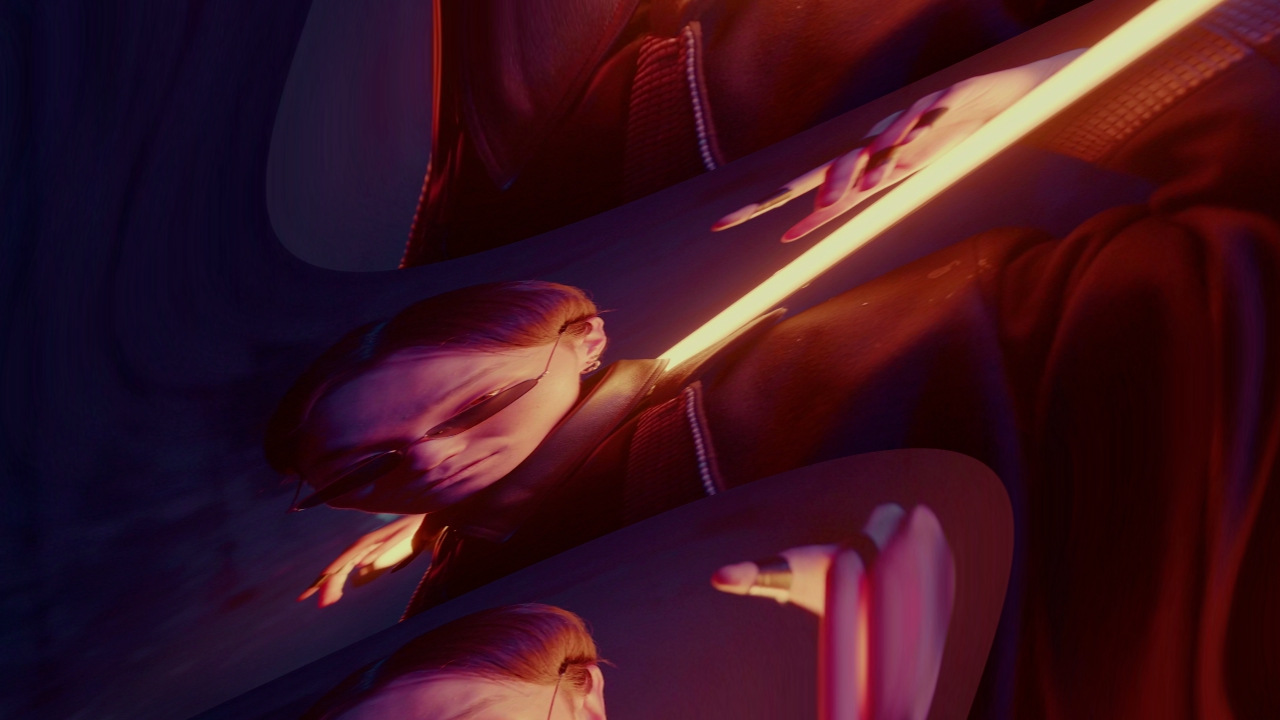 Sine Warp
Sine Warp
Warps an image with a ripple emanating from the centre of the screen.
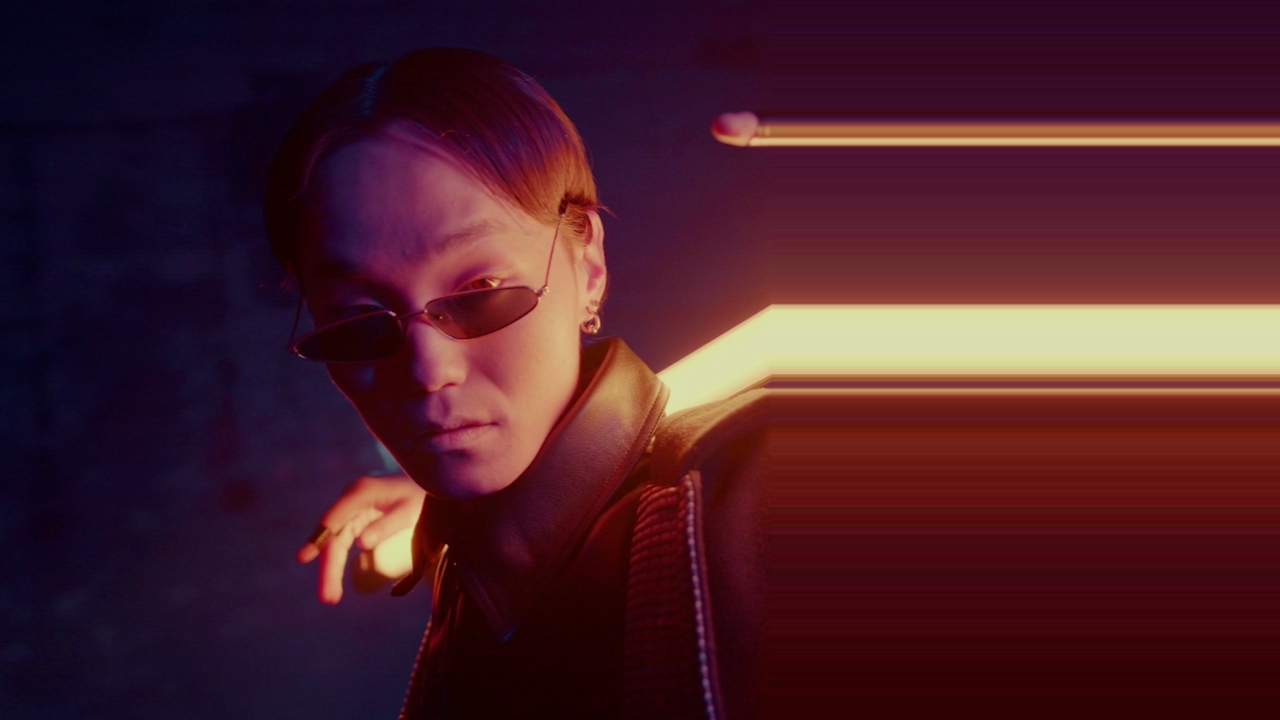 Stretch
Stretch
Stretches a cross section of the image.
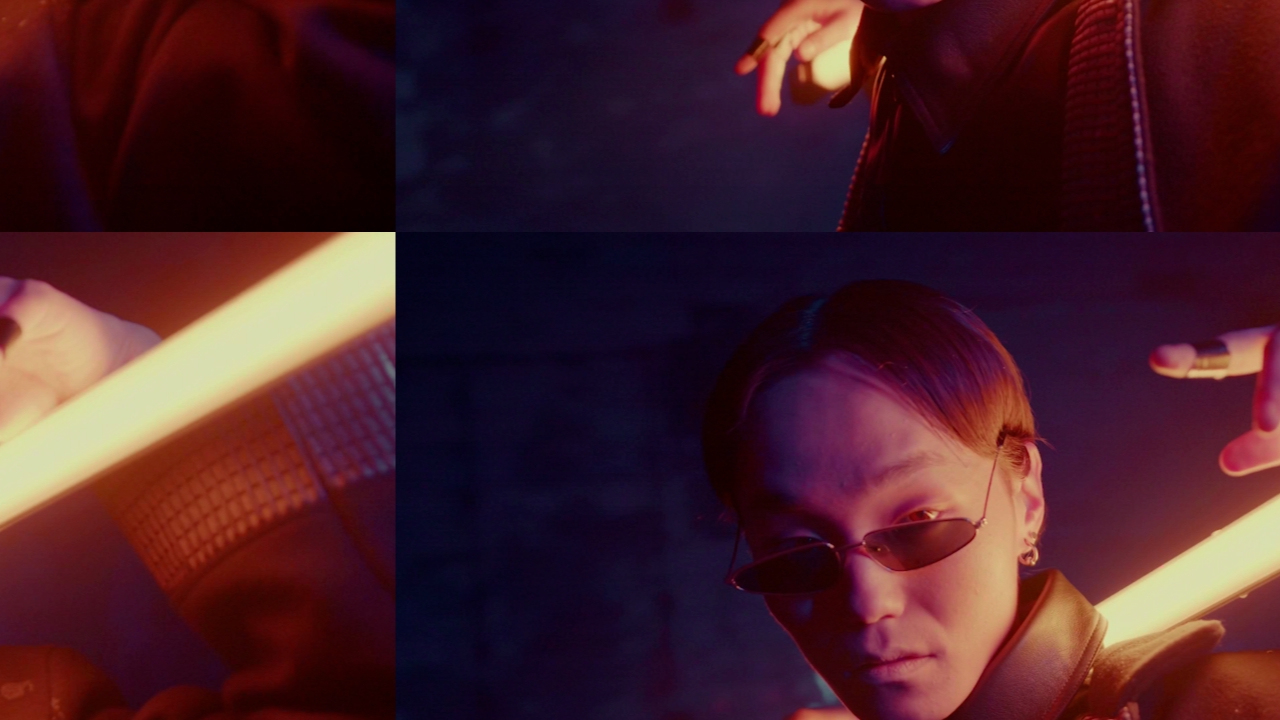 Transform Image
Transform Image
Apply a transform to the image.
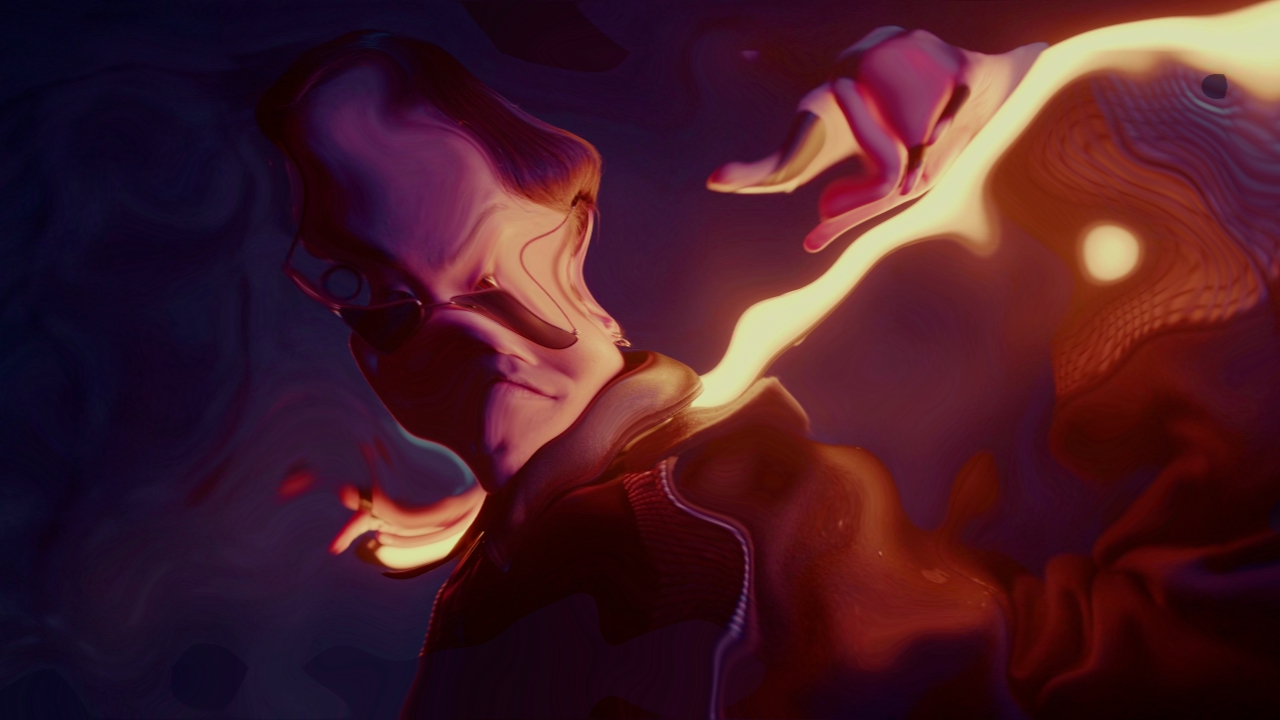 Turbulence Warp
Turbulence Warp
Warps an image with a turbulence.
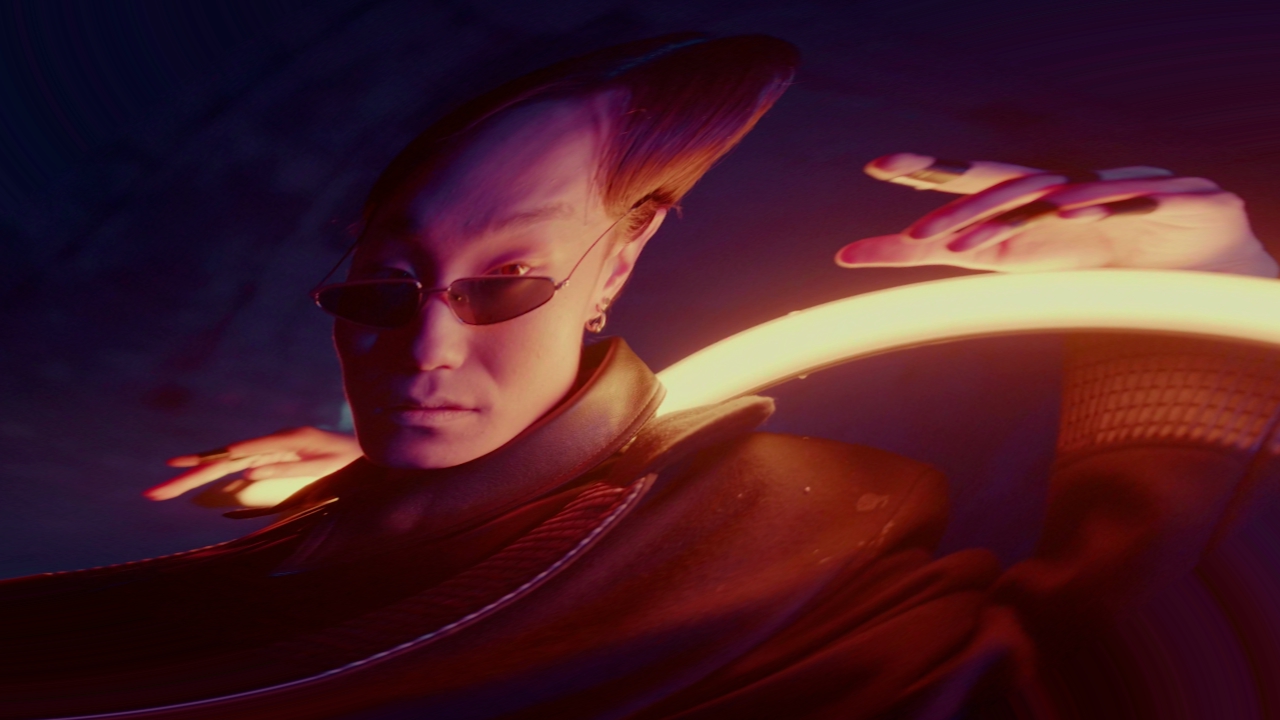 Twirl Image Warp
Twirl Image Warp
Warps the image in a twist around the center.
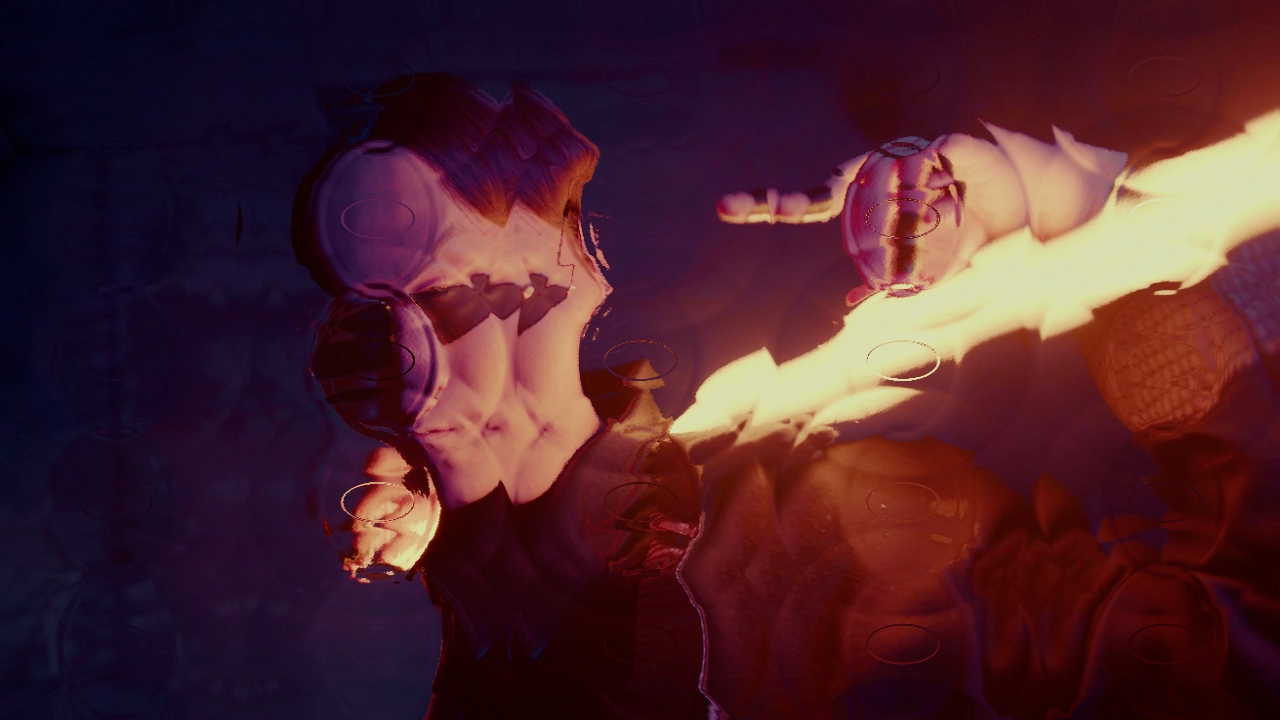 Water Ripples
Water Ripples
Simulate water on an image.