 Particles
Particles
Updated: 10 Feb 2026
Updated: 10 Feb 2026
Particle nodes are nodes used in a particles system. This system starts with a Particle Root Node, and is built out with Emitter, Affector and Shader nodes, before finally being rendered to the camera with a Renderer node.
The Particle Root Node contains the particles themselves: their positions, velocities, colours and so on, in a pool waiting to be used. The number of particles in the pool is set by the Max Particle Count attribute on the root node. Particle Emitters take particles from the pool and bring them to life. Particle Affectors make them move; Particle Rendering Nodes control how particles are rendered to screen. When particles die they are returned to the pool until they are emitted again. It is possible that not all the particles in the pool are alive at any time. Even particles that are not currently alive in the pool carry some performance and memory overhead, so it is recommended that the maximum number of particles on the Particle Root node is limited to the amount actually needed by the emitters.
Multiple Particle Emitters may exist under one Particle Root node. Particle Affectors and Rendering nodes may be connected to the Particle Root directly, making them work on every particle under the root node; or they may be connected to individual Emitters, making them only affect the particles emitted by that Emitter.
Particles are generally hooked into the Root node, although they can be applied to any node - they will still appear in the scene as long as there is a path to a Root node.
Aside from the Particle Bounding Box, Particle Event and Particle Root, these nodes are split into 4 groups:
Particle Affector nodes modify particle motion.
 Angled Motion Affector
Angled Motion Affector
Moves particles via a noise field, with directions that are constrained to an angle.
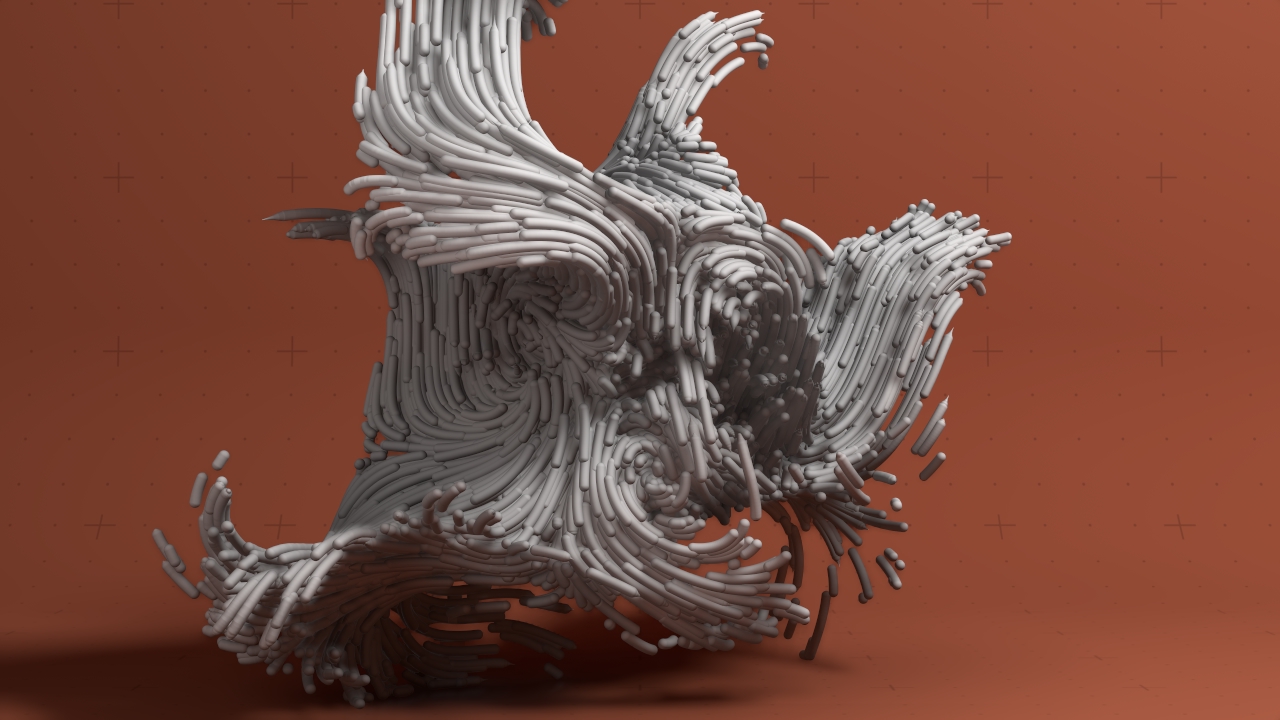 Curl Noise Fluid Affector
Curl Noise Fluid Affector
Applies curl noise velocities to Particles.
 Depth Image Collision Affector
Depth Image Collision Affector
Allows particles to collide with depth camera data.
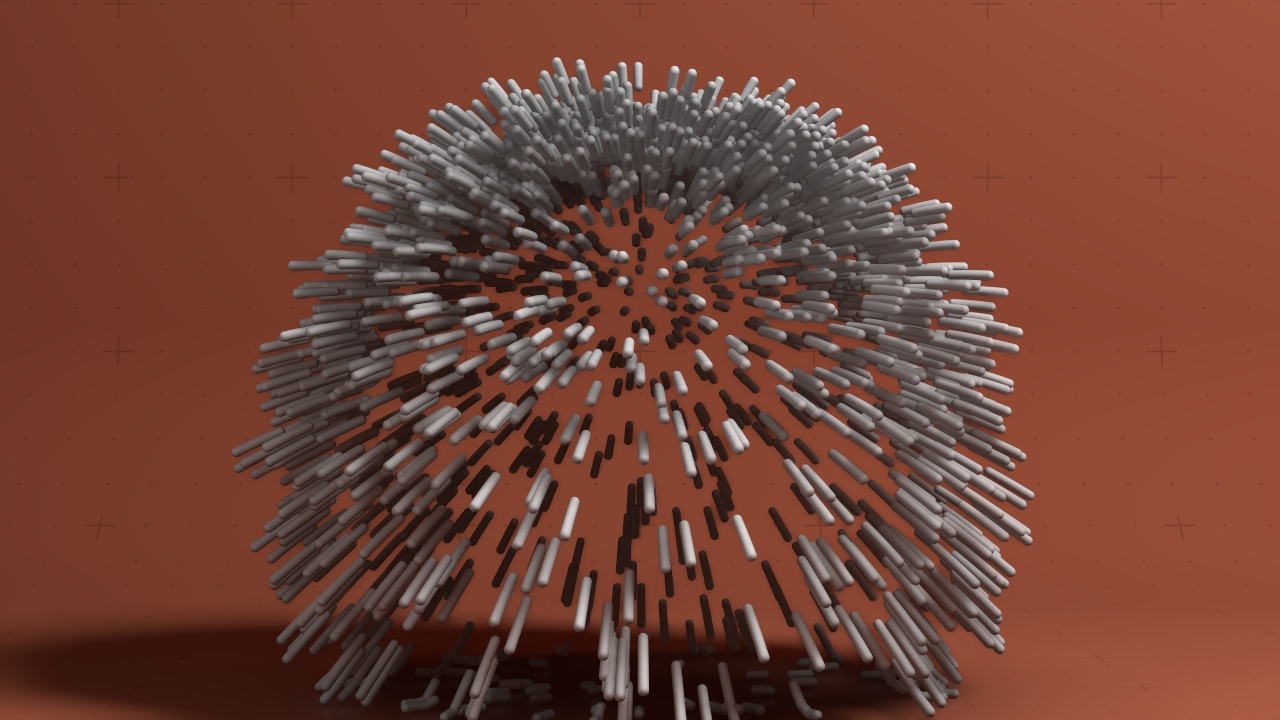 Explode Affector
Explode Affector
Applies an explosive force to particles at birth.
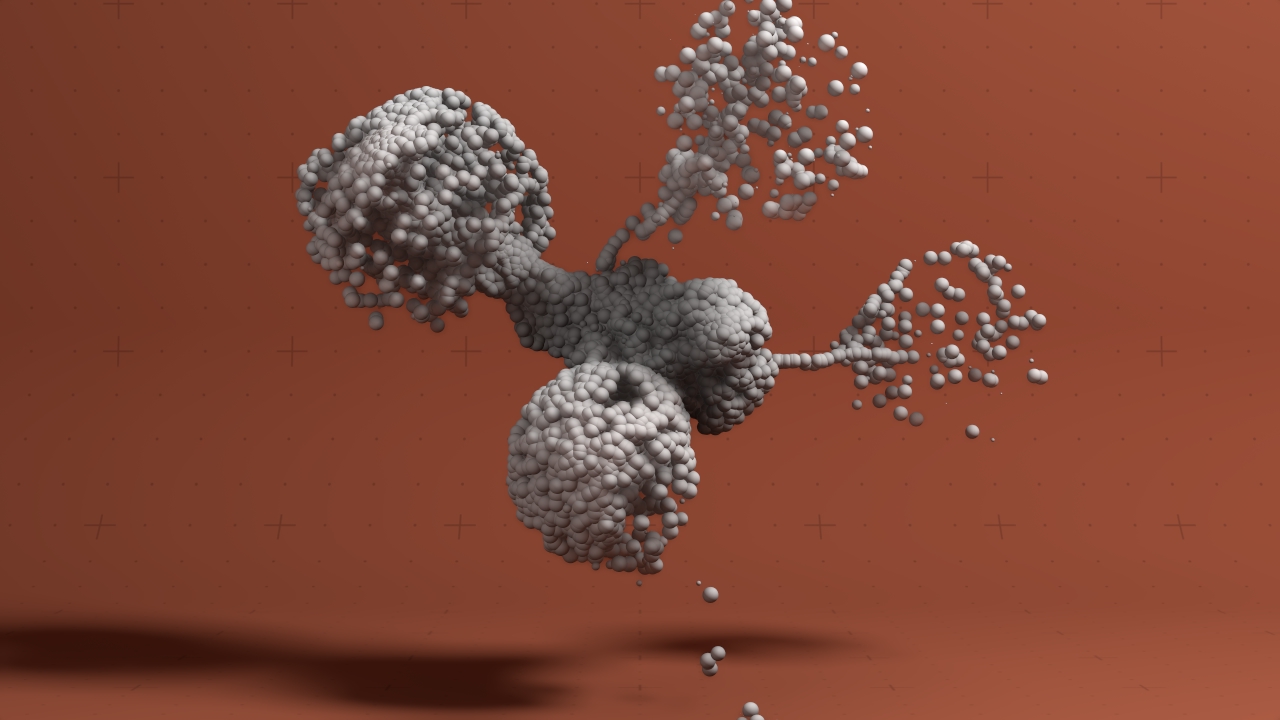 Field Affector
Field Affector
Allows particles to be affected by forces from a field.
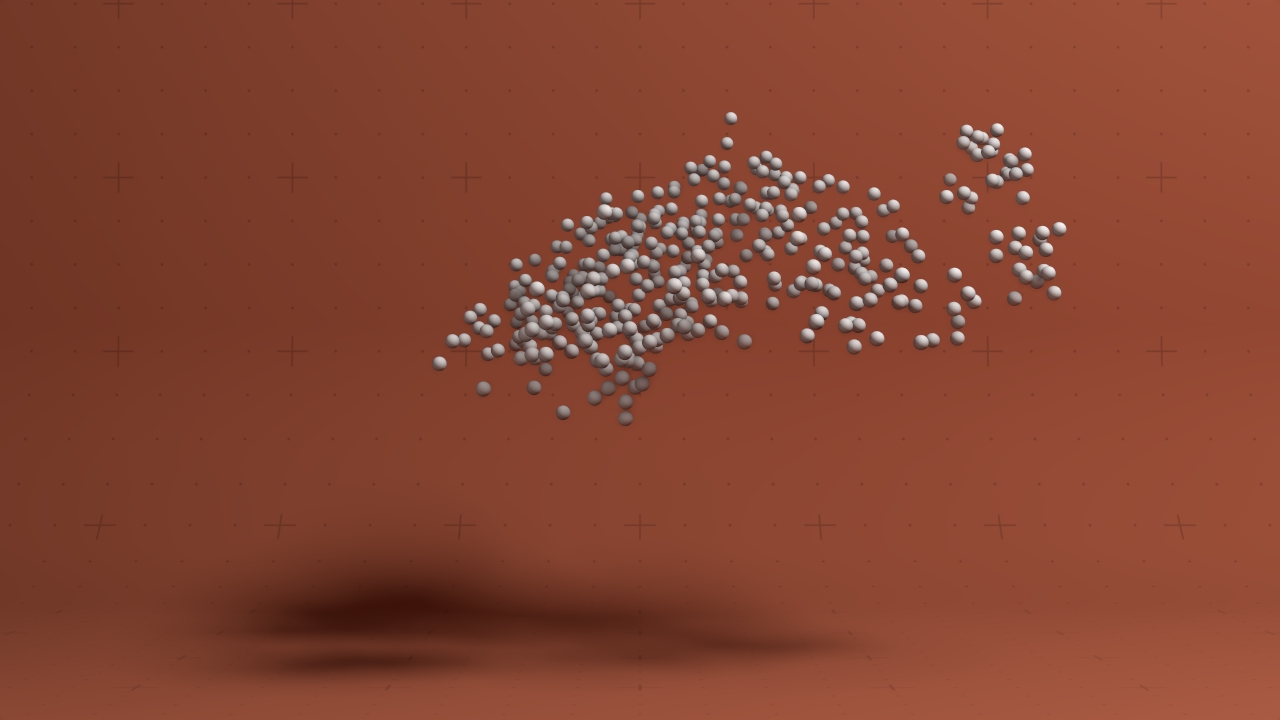 Flocking Affector
Flocking Affector
Simulates flocking behaviour with particles.
 Fluid FLIP Affector
Fluid FLIP Affector
Simulates fluid dynamics on Particles with FLIP simulations.
 Fluid MPM Affector
Fluid MPM Affector
Simulates fluid dynamics on Particles with an MLS-MPM simulation.
 Fluid SPH Affector
Fluid SPH Affector
Simulates fluid dynamics on Particles with an SPH simulation.
 Force Affector
Force Affector
Applies a force to particles.
 Image Affector
Image Affector
Attract or repel particles from an image.
 Kill Box Affector
Kill Box Affector
Remove particles from inside or outside a zone.
 Mesh Attractor
Mesh Attractor
This node is used to attract or repel particles from the surface of a given 3D object, affect them by the velocity of the mesh, or make them flow along the surface of a mesh.
 Mesh Collision Affector
Mesh Collision Affector
Allows Particles to collide with Meshes.
 Mesh Distance Field Affector
Mesh Distance Field Affector
Apply forces to particles from mesh surfaces.
 Particle-Particle Collision Affector
Particle-Particle Collision Affector
Allows particles to collide with each other.
 Points Affector
Points Affector
Uses points sources to disturb the particles.
 Primitive Affector
Primitive Affector
Apply forces to particles from primitive shapes.
 Primitive Collision Affector
Primitive Collision Affector
Allows particle collisions with simple 3D primitives.
 Procedural Affector
Procedural Affector
Allows particles to interact with procedurals.
 Rigid Body Collision Affector
Rigid Body Collision Affector
Allows particle collisions with active rigid bodies.
 Scale Affector
Scale Affector
Apply changes to the scale of particles.
 Shockwave Affector
Shockwave Affector
Apply a shockwave through particles.
 Spline Attractor
Spline Attractor
Attracts particles towards a spline.
 Spring Affector
Spring Affector
Applies a spring simulation on particles.
 Turbulence Affector
Turbulence Affector
Applies turbulence to particles.
 Velocity Affector
Velocity Affector
Applies a constant velocity to particles.
 Vortex Affector
Vortex Affector
Applies a rotational velocity to particles.
 World Collision Affector
World Collision Affector
Allows particle collisions with all 3D object in the scene.
Emitter nodes spawn particles that can be manipulated in a particles system.
 Field Emitter
Field Emitter
Emit particles from a Field system.
 Image Emitter
Image Emitter
Emit particles from an image.
 Mesh Emitter
Mesh Emitter
Emit particles from a mesh.
 Particle Cache
Particle Cache
Caches a particle system for potentially faster and repeatable results.
 Primitive Emitter
Primitive Emitter
Emit particles from a primitive shape.
 Procedural Emitter
Procedural Emitter
Emit particles from a Procedural system.
 Screen Emitter
Screen Emitter
Emit particles from objects within the screen space.
 Spline Emitter
Spline Emitter
Emits particles from a spline.
 Trail Emitter
Trail Emitter
Emits particles from other particles.
 Video Feature Emitter
Video Feature Emitter
Emits particles from feature points of a video.
 Volume Emitter
Volume Emitter
Emit particles that fill the volume of a mesh.
Rendering nodes visualise the particles by spawning images, meshes or trails.
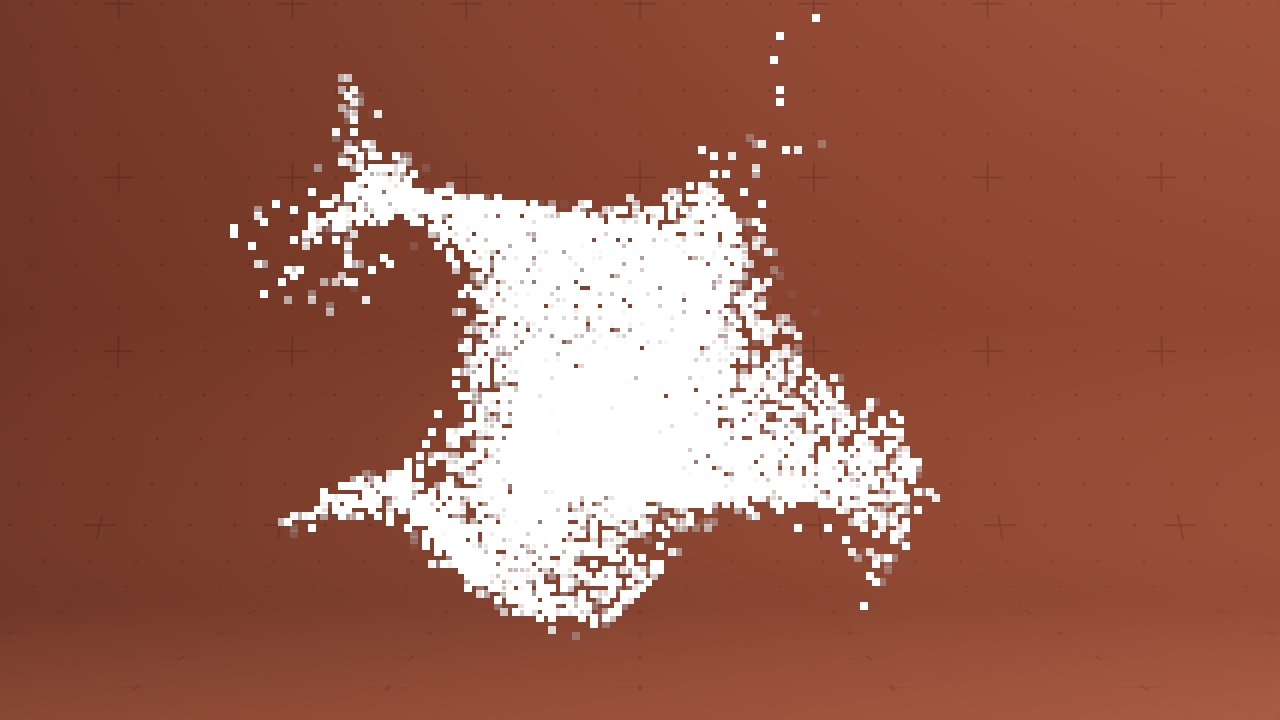 Dot Matrix Renderer
Dot Matrix Renderer
Renders particles as a dot-matrix in screen space.
 Geometry Connection Renderer
Geometry Connection Renderer
Renders particles as connected geometry and lines.
 Gradient 2D Renderer
Gradient 2D Renderer
This node generates a 2D Gradient based on the positions and colours of active particles.
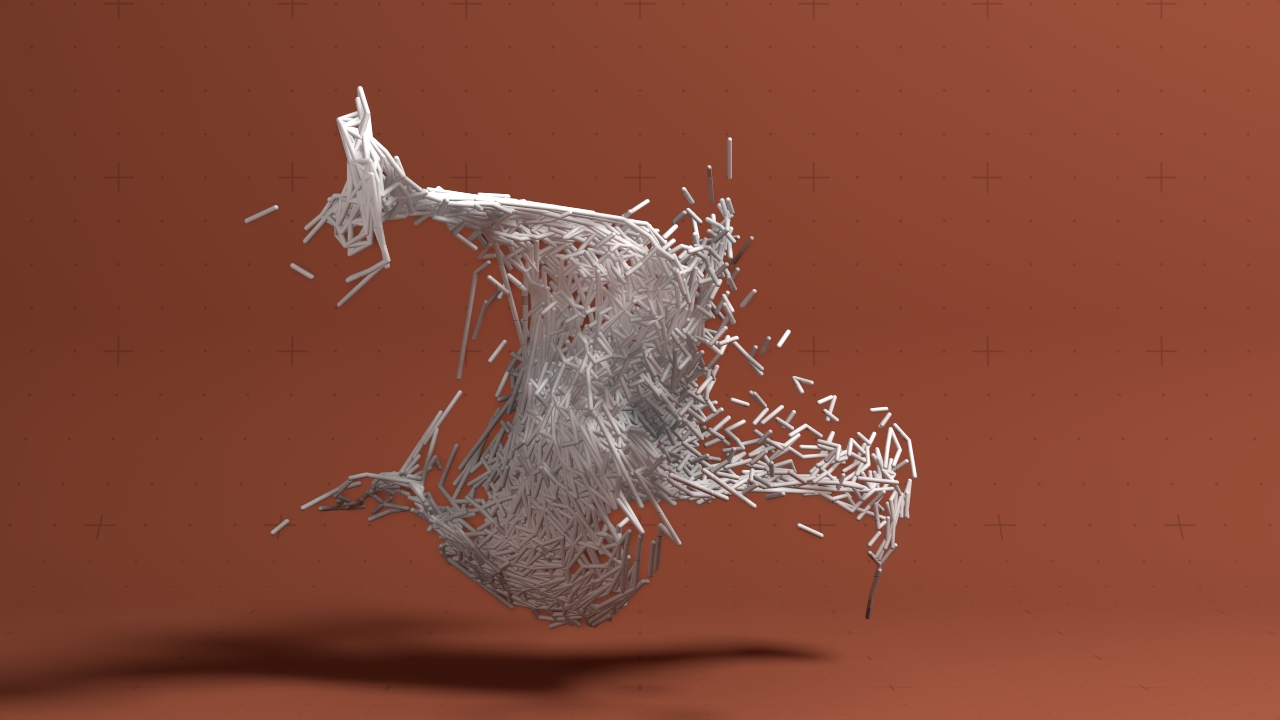 Line Connection Renderer
Line Connection Renderer
Renders lines between nearby particles.
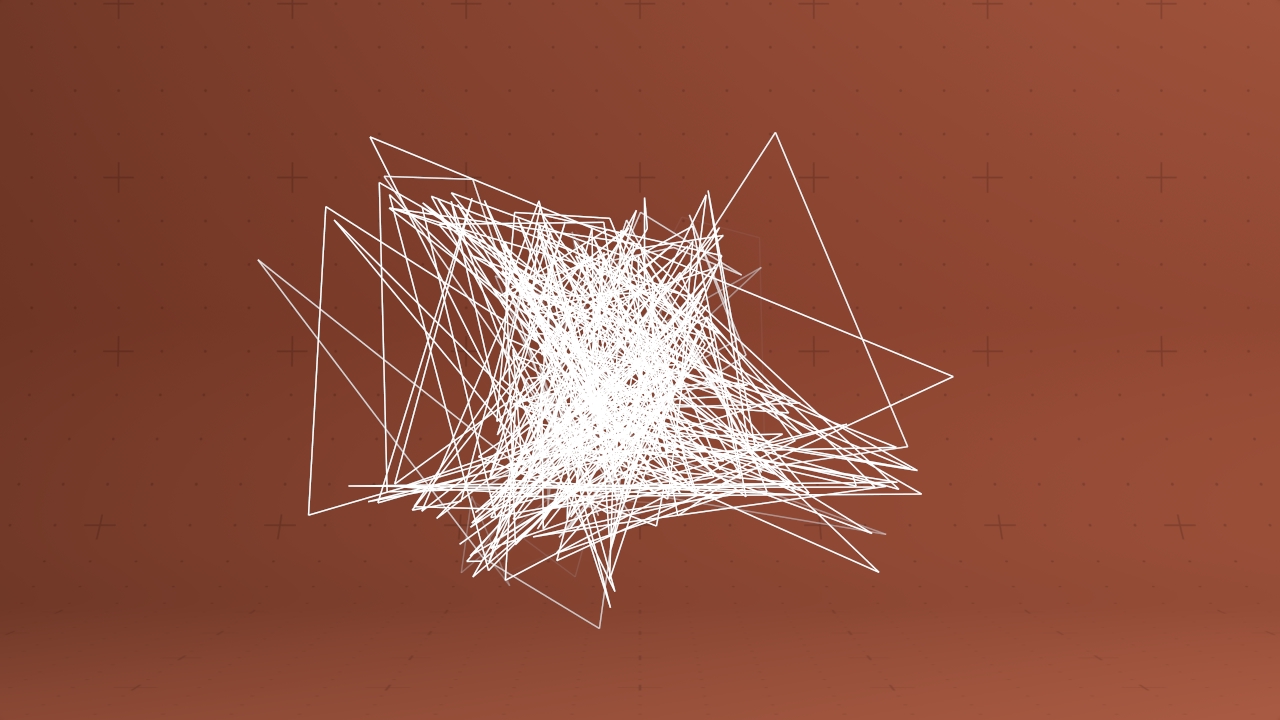 Line Renderer
Line Renderer
Renders lines between pairs of particles.
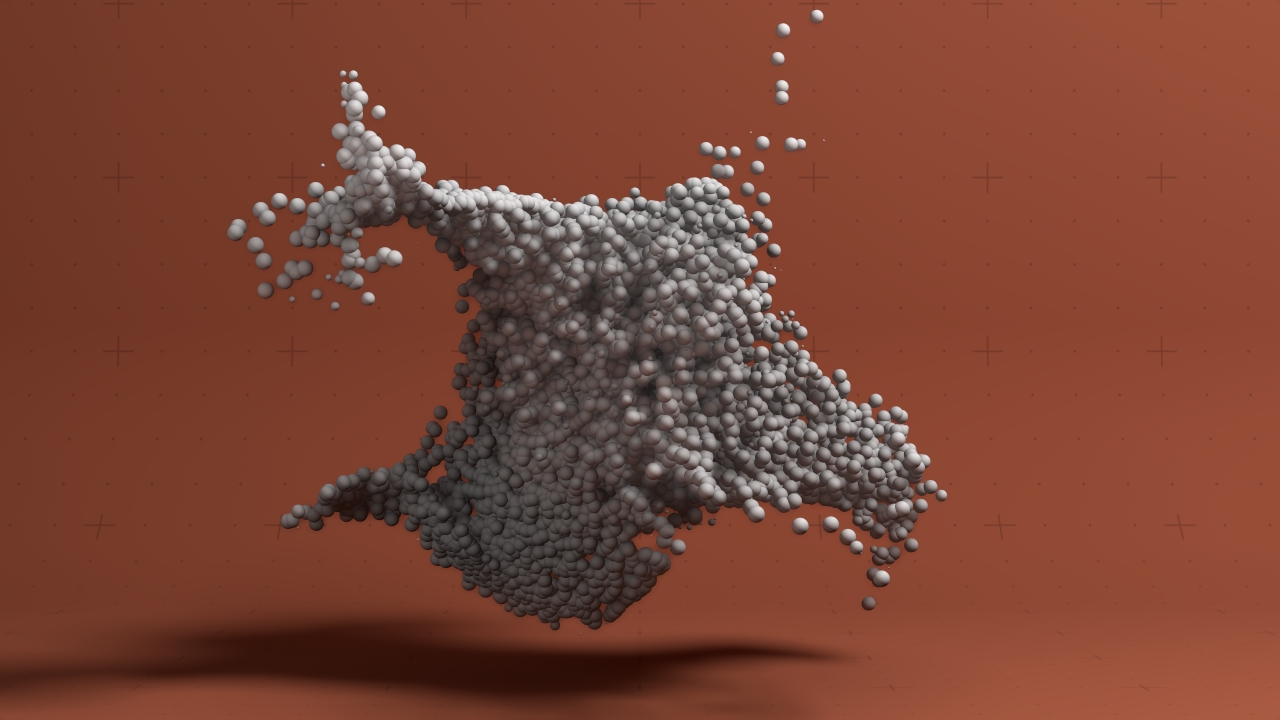 Particles To Point Geometry
Particles To Point Geometry
Renders particles as raytraced spheres.
 Point Renderer
Point Renderer
Renders a each particle as a sprite.
 Render Particles To Surfaces
Render Particles To Surfaces
Renders particles onto nearby Meshes.
 Soft Ball Renderer
Soft Ball Renderer
Renders particles as soft body spheres.
 Trail Renderer
Trail Renderer
Renders trails which follow the path of particles.
 Volume Renderer
Volume Renderer
Renders particles as a density volume.
Shading nodes change the colour or position of the particles in various ways.
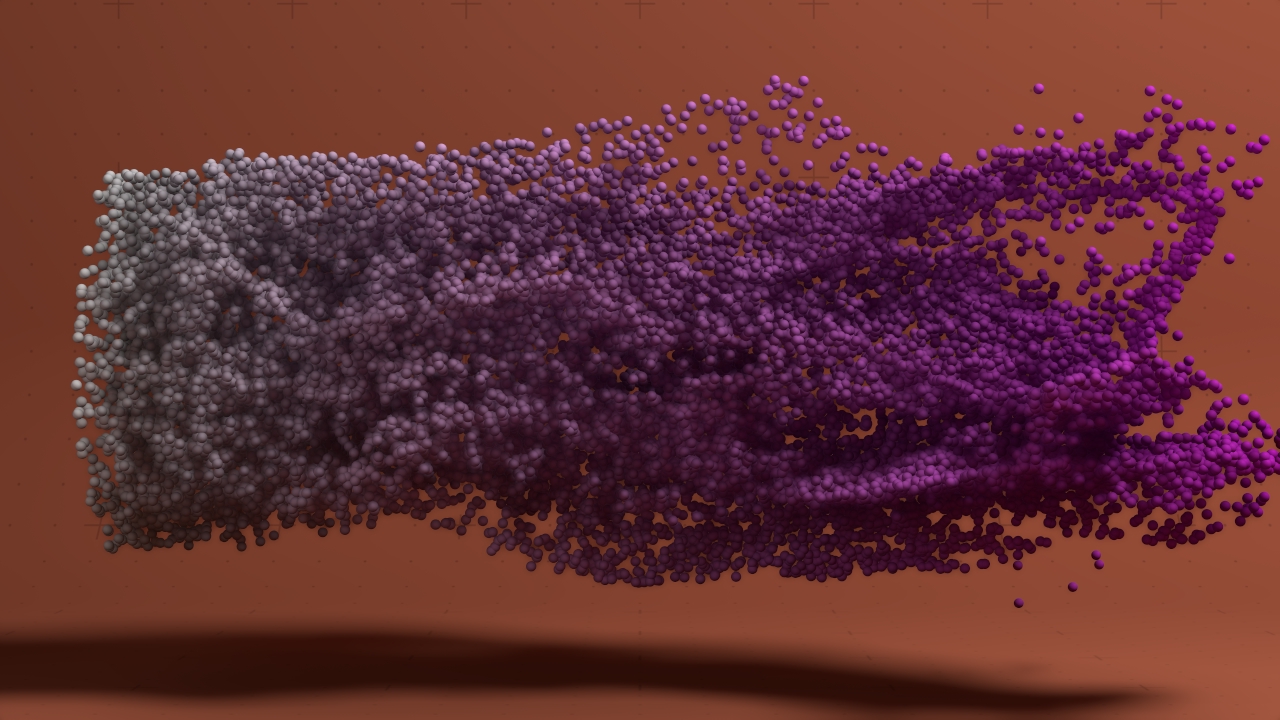 Attribute Shading
Attribute Shading
Shades particles based on their current properties.
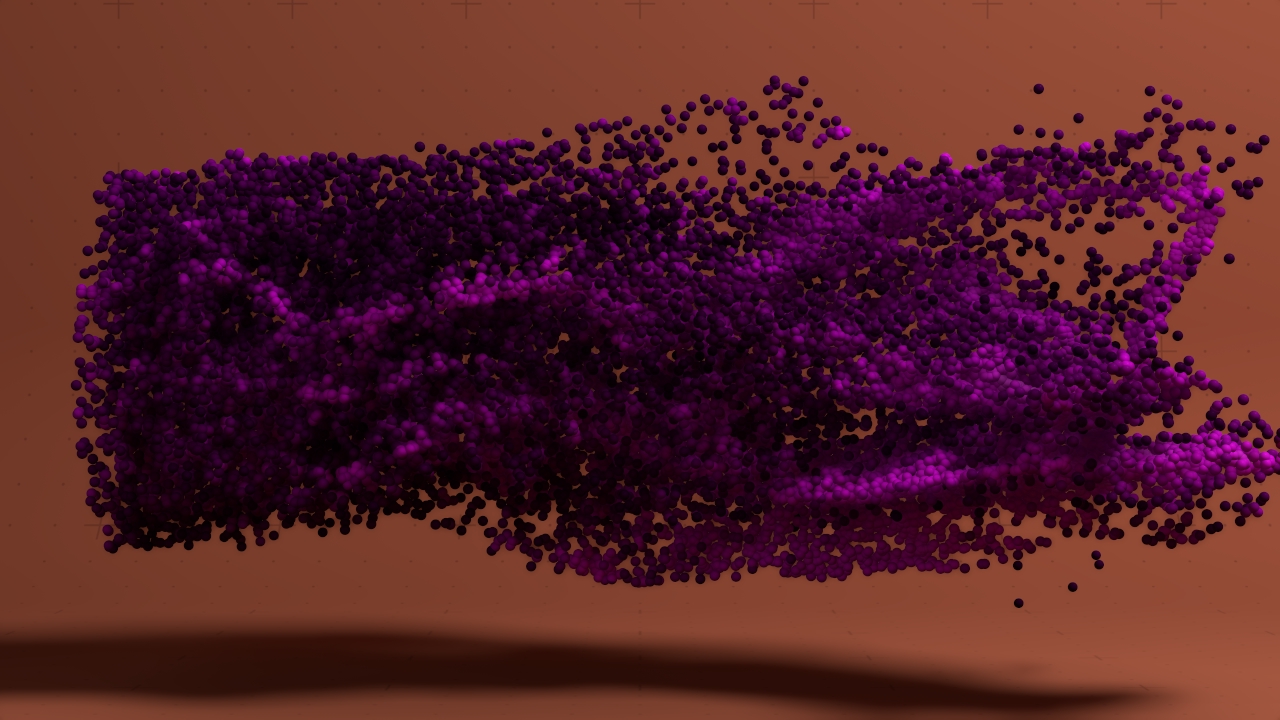 Density Shading
Density Shading
Shades particles by their density.
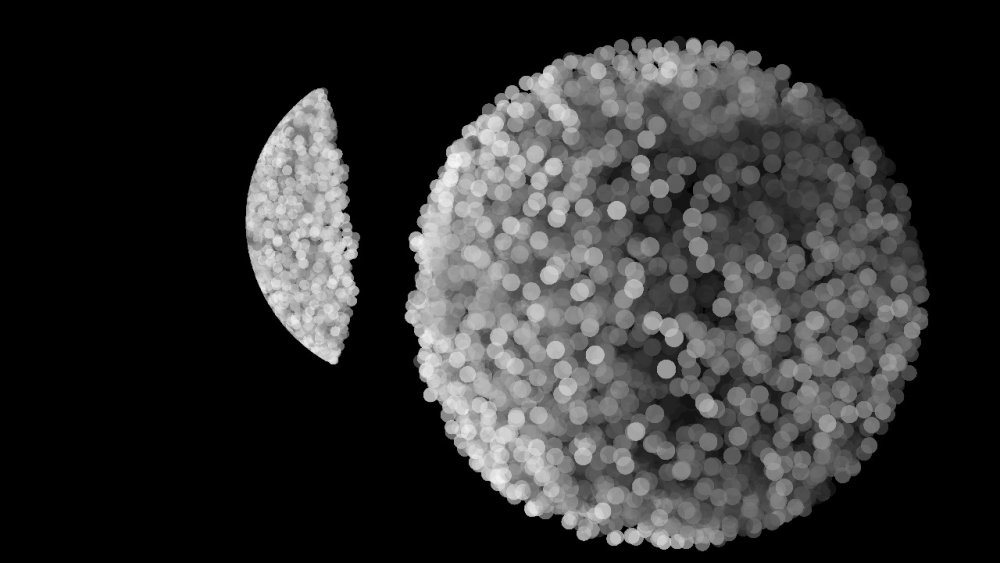 Displace To Shape
Displace To Shape
Displaces a particle to a primitive shape.
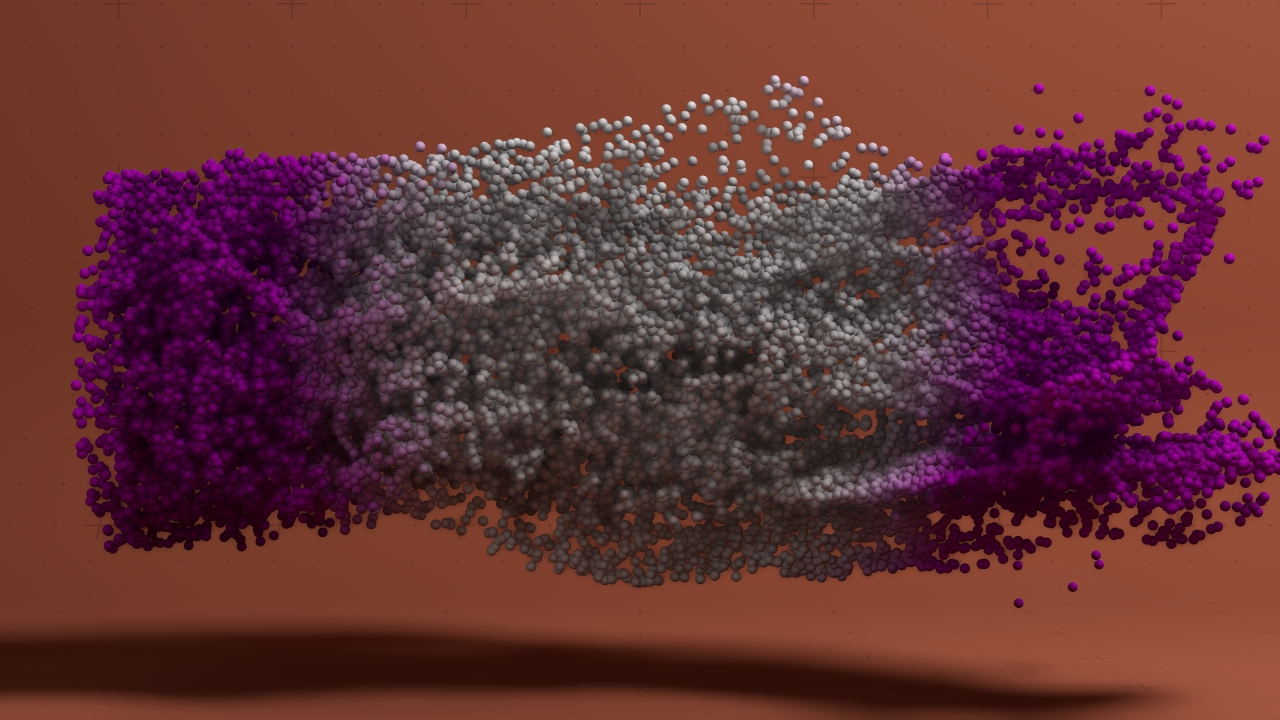 Distance Shading
Distance Shading
Shades particles based on their distance from a point.
 Image Displacement
Image Displacement
Displaces particles based on an image.
 Image Shading
Image Shading
Shades particles based on an image.
 Keyed Colour
Keyed Colour
shades particles based on a keyframe animated colour.
 Life Colour Shading
Life Colour Shading
Shades particles over their life span.
 Lighting
Lighting
Shades particles based on the area of effect from lights.
 Noise Shading
Noise Shading
Shades particles using fractal noise.
 Volume Shadow Shading
Volume Shadow Shading
Light particles using shadow volumes.
 Voxel Cone Shading
Voxel Cone Shading
Light particles using voxel cone shading.
TODO Section Description
 Attribute Weight
Attribute Weight
Generates weight values using attributes of the particle, such as its velocity.
 Mesh Attribute Weight
Mesh Attribute Weight
Generates weight values using attributes sampled from a mesh, at the closest point on the mesh to the particle.
 Noise Weight
Noise Weight
Generates weight values using noise functions.
 Primitive Weight
Primitive Weight
Generate particle weight values using 3D primitive shapes.
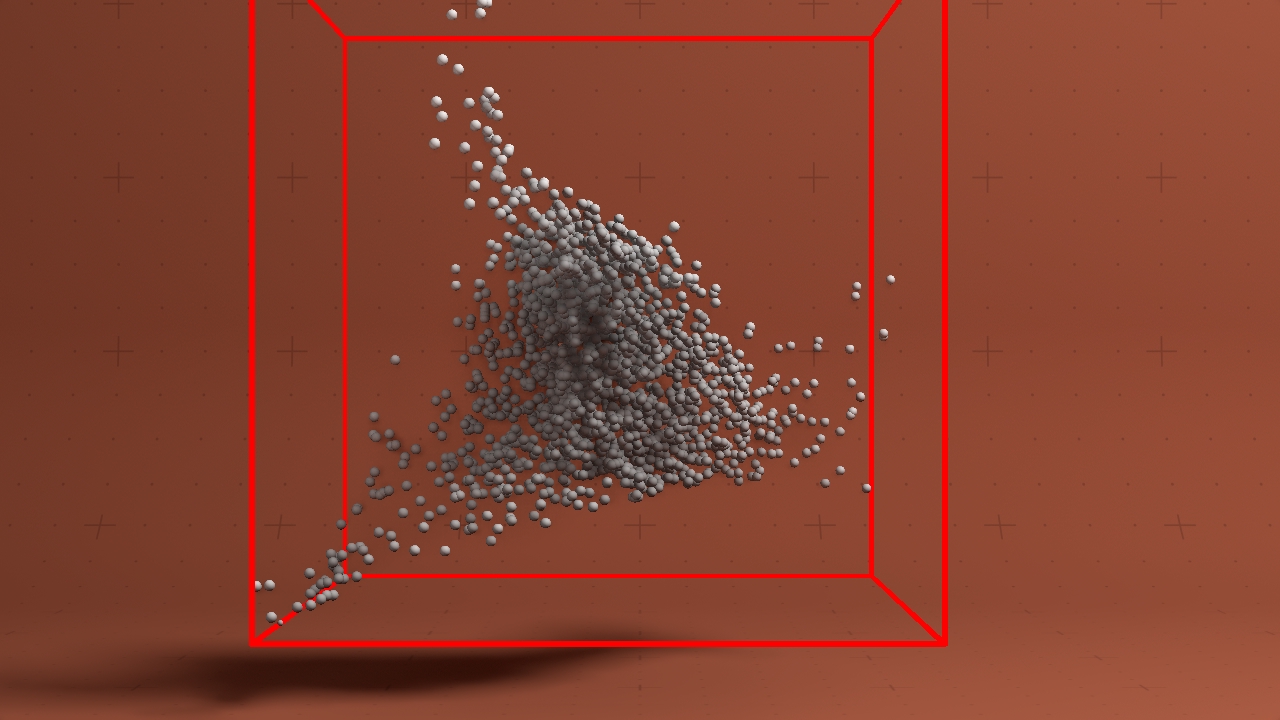 Particle Bounding Box
Particle Bounding Box
Generates a bounding box from the bounds of a particle system.
 Particle Event
Particle Event
Modify particles using a dynamic per particle event.
 Particle Root
Particle Root
The root node for a Particle system.