Sound Effector
Updated: 8 Jan 2026
Modifies a cloner system using an audio input.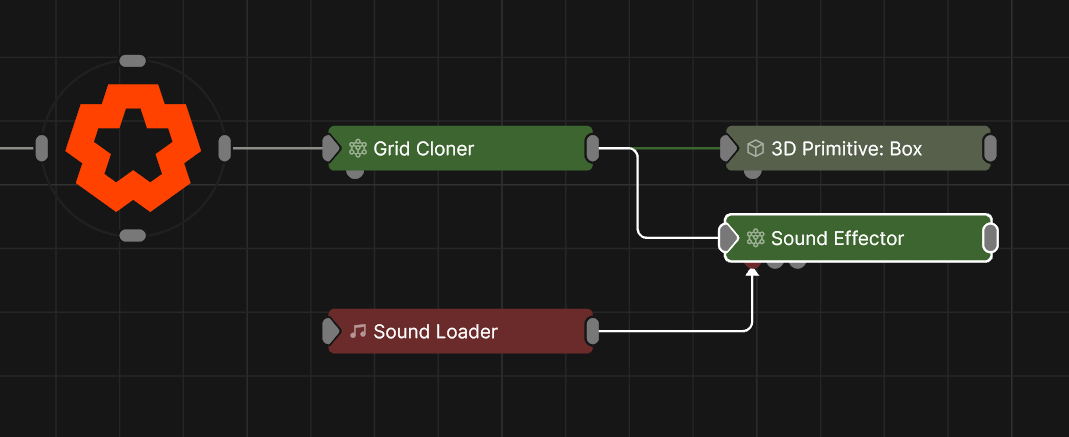
Updated: 8 Jan 2026
Modifies a cloner system using an audio input.
This node applies a transform to clones based on the analysis of an audio source. The waveform is processed using a set of parameters, allowing for greater control over how the sound is applied to the clones.
Connect the output to the effector input of any cloner node to apply it to the camera system. Multiple effectors connected to the same output will stack, and order of operations chosen by position on the nodegraph.
These properties control the 3D transforms of the node. Transforms will generally be inherited by child nodes, although they can be ignored through the Inherit Transform Channels attributes.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | The objects position along the local x-axis. |
| Position Y | The objects position along the local y-axis. |
| Position Z | The objects position along the local z-axis. |
| Rotation Heading | The objects rotation around the local y-axis. |
| Rotation Pitch | The objects rotation around the local x-axis. |
| Rotation Bank | The objects rotation around the local z-axis. |
| Scale X | The objects scale along the local x-axis. |
| Scale Y | The objects scale along the local y-axis. |
| Scale Z | The objects scale along the local z-axis. |
Control the inheritance of the transforms from the parent.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position | Toggle inheritance of the Position from the parent. |
| Rotation | Toggle inheritance of the Rotation from the parent. |
| Scale | Toggle inheritance of the Scale from the parent. |
| World Position Only | Inherit the world position from the parent only, rotation and scale will be ignored. Overrides above properties. |
| Inherit Time | Toggle inheritance of time from the parent. |
These properties control the core behaviours of the node.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Blend Amount | Controls the amount the resulting transforms of each clone after the effector is applied is blended with the original transform. |
| Space |
The transform space the Effector uses to influence the clones.
|
| Sound | Sound used to drive the effector. Can be overwritten by adding a relevant node to the Sound input. |
| Channel | Which audio channel is used. |
| Frequency Band | Sets the Band EQ to one of the given presets. |
| Band EQ | Selects and weights the frequency bands to be used from the sound file. |
| Time Offset | Offset the time the clones are modified from the time the waveform is at. |
| Change Threshold | Changes the threshold for what counts toward the effect. |
| Attack | Controls the initial time between the current values to the peak. |
| Decay | Controls the time between the peak to the sustain level. |
| Min Value | Acts as a minimum threshold for extracting a range of values from the waveform. |
| Max Value | Acts as a maximum threshold for extracting a range of values from the waveform. |
| Max Clamp | A maximum value which values will be clamped if they go above. |
| Spikiness | Accentuates peaks in the waveform so they are sharper. |
| Scale | How much the output values are scaled. |
| Smoothness | How much smoothing is applied between differing values. |
| FFT Sample Scale | Scale the size of the waveform as it is applied. |
| Waveform | Visualises the waveform of of the sound. |
| Direction |
Change how the sound is applied to the Cloner system.
|
These properties control how much influence the node has on anything it affects.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Falloff Mode |
Which shape to use to calculate the falloff.
|
| Falloff Axis | Which axis the falloff should be oriented on. |
| Falloff Direction |
When using Planar mode, which directions to use to calculate the falloff.
|
| Falloff Easing Mode |
Interpolation method used to calculate the falloff within its range of influence.
|
| Falloff Size X | Size of the falloff range along the X axis. |
| Falloff Size Y | Size of the falloff range along the Y axis. |
| Falloff Size Z | Size of the falloff range along the Z axis. |
| Outer Range | Outer range of the falloff, outside of which the falloff is no longer effective. |
| Inner Range | Inner range of the falloff, inside of which the falloff is fully effective. |
| Curve Power | Controls the rate of change for the falloff between the inner and outer range. |
| Invert | Inverts the effect of the falloff. |
These properties control the selection of clones that you want the effector to influence.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Selection Mode |
Set the mode for Index-Based Weighting.
|
| Selection Operation |
Set how you want top define the selection.
|
| Index | The first clone index in the range. |
| Max Index | The last clone index in the range. |
| Index Step | The increment used in “Step” mode. |
| Index Seed | The seed used in “Random In Range” mode. |
| Index Falloff Range | Falloff amount for Index-Based Weighting. |
| Index Falloff Power | The curve power of the falloff for Index-Based Weighting. |
These properties control how an effector transforms the clones.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Position X | Offset the clones x position from the current position. |
| Position Y | Offset the clones y position from the current position. |
| Position Z | Offset the clones z position from the current position. |
| Rotation Heading | Offset the clones y rotation from the current rotation. |
| Rotation Pitch | Offset the clones z rotation from the current rotation. |
| Rotation Bank | Offset the clones x rotation from the current rotation. |
| Scale X | Offset the clones x scale from the current scale. |
| Scale Y | Offset the clones y scale from the current scale. |
| Scale Z | Offset the clones z scale from the current scale. |
| Uniform Scale | Uniformally scale the clones by the same value along all axes. |
| Object Index | Offset the clone’s index from the current clone index. Used to select which child object of the cloner is cloned where. |
| Apply To Position | Apply the position changes from the effector to the clones. |
| Apply To Rotation | Apply the rotation changes from the effector to the clones. |
| Apply To Scale | Apply the scale changes from the effector to the clones. |
| Apply To Object Index | Apply the object index changes from the effector to the clones. |
| Position Apply Mode |
The method by which the effectors position properties are applied to the clone. Affecting the previously applied position values.
|
| Rotation Apply Mode |
The method by which the effectors rotation properties are applied to the clone. Affecting the previously applied rotation values.
|
| Scale Apply Mode |
The method by which the effectors scale properties are applied to the clone. Affecting the previously applied scale values.
|
| Object Index Apply Mode |
The method by which the effectors object index properties are applied to the clone. Affecting the previously applied object index values.
|
The properties control the time at which the node is active. See Timeline for editing time segments.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Duration |
Control the duration of the node’s time segment.
|
| Node Time | The custom start and end time for the node. |
| Duration (Timecode) | The length of the node’s time segment (in time). |
| Duration (Frames) | The length of the node’s time segment (in frames). |
| Time Segment Enabled | Set whether the node’s time segment is enabled or not in the Timeline. |
| Name | Description | Typical Input |
|---|---|---|
| Sound | Use an input sound to override the sound attribute. | Sound Loader |
| Falloff Node | Use an input node to control the transformation values of the falloff. | Falloff |
| Procedural Falloff | Use a procedural system to generate falloff from. Useful for creating complex and unconventional falloffs from an Effector. | Procedural Root |
| Transform Modifiers | Apply the transforms of another node to this node. | Null |
| Target Node | Modifiy the rotations of the node to always direct the z axis towards the input. | Null |
| Local Transform Override | Apply the transforms of another node to this node, relative to its parent. | Null |